Experimental probability
Key Notes:
Definition: Experimental probability refers to the probability of an event occurring based on experimental or observed data rather than theoretical calculations. It is determined by performing an experiment multiple times and recording the results.
Formula for Experimental Probability:
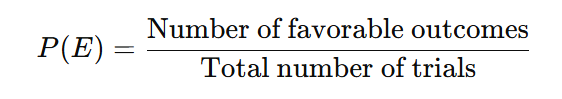
- P(E) is the probability of event E occurring.
- The numerator is the count of favorable outcomes (how often the event of interest happens).
- The denominator is the total number of trials or experiments conducted.
Steps to Calculate Experimental Probability:
- Conduct the experiment multiple times.
- Count the number of times the event occurs (favorable outcomes).
- Count the total number of trials.
- Use the formula to calculate the probability.
Example: If you roll a die 100 times and get a 4 on 18 occasions, the experimental probability of rolling a 4 is.
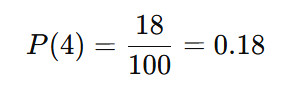
This means the experimental probability of rolling a 4 is 0.18 or 18%.
Learn with an example
📚 At Burger Haven, 6 of the last 9 customers wanted cheese on their burgers. What is the experimental probability that the next customer will want cheese on his or her burger?
📚 Simplify your answer and write it as a fraction or whole number.
📚 P(cheese) =_____
- Write the experimental probability as a fraction in simplest form.
- P(cheese) = cheese/total
- =6/9
- =2/3
- So, P(cheese) =2/3
📚 A grocery store recently sold 12 tins of soup, 6 of which contain split pea soup. What is the experimental probability that the next tin sold will be split pea soup?
📚 Simplify your answer and write it as a fraction or whole number.
📚 P(split pea) =______
- Write the experimental probability as a fraction in simplest form.
- P(split pea) = split pea/total
- =6/12
- =1/2
- So, P(split pea) =1/2
📚 At a T-shirt stand on the boardwalk, 2 of the last 10 shirts sold were yellow. What is the experimental probability that the next shirt sold will be yellow?
📚 Simplify your answer and write it as a fraction or whole number.
📚 P(yellow) = _______
- Write the experimental probability as a fraction in simplest form.
- P(yellow) =yellow/total
- =2/10
- =1/5
- So, P(yellow) =1/5
Let’s practice!🖊️

