Heredity
Key Notes:
Definition of Heredity:
- Heredity is the process by which traits or characteristics are passed down from parents to their offspring through genes.
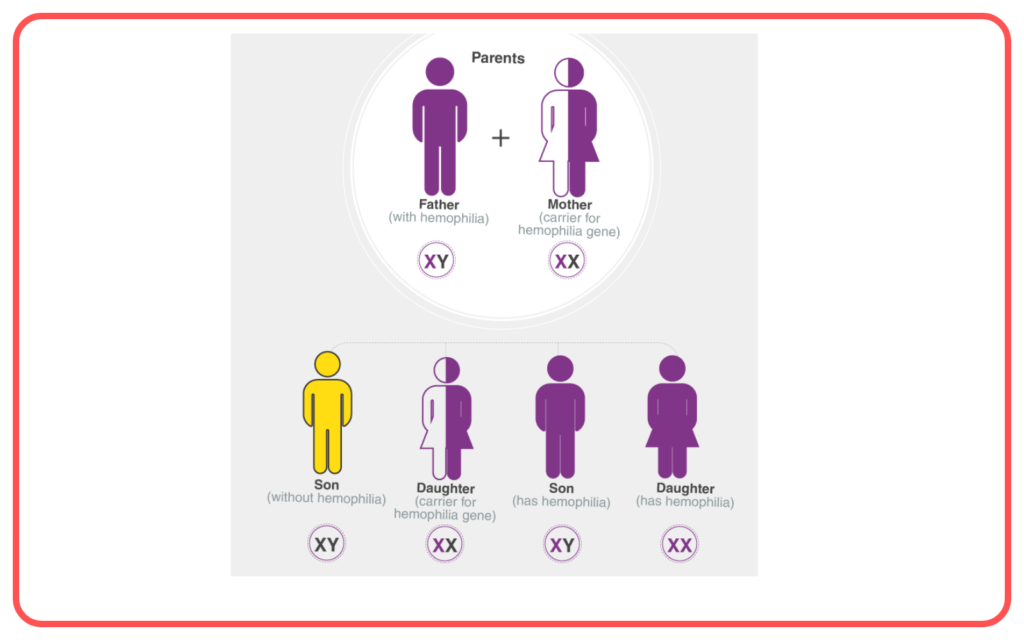
- It is the reason why children often resemble their parents and have certain physical or behavioral traits.
Genes and Chromosomes:
- Genes are the basic units of heredity, made up of DNA. They carry instructions for the development of traits.
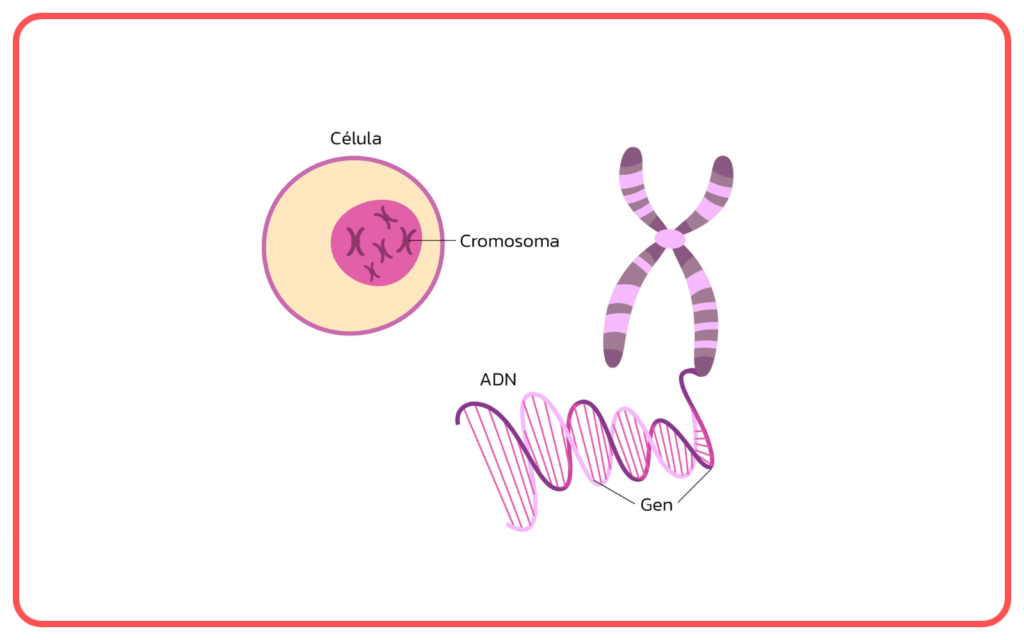
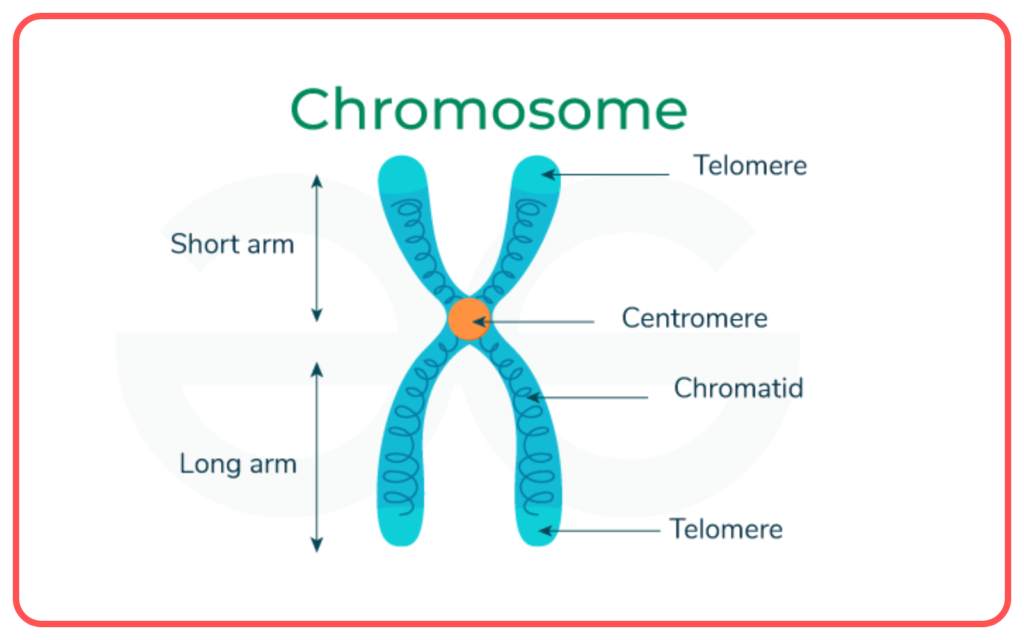
- Chromosomes are structures that contain genes. Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs), with one set inherited from each parent.
Mendelian Inheritance:
- Gregor Mendel, known as the “Father of Genetics,” discovered the basic principles of heredity through experiments with pea plants.
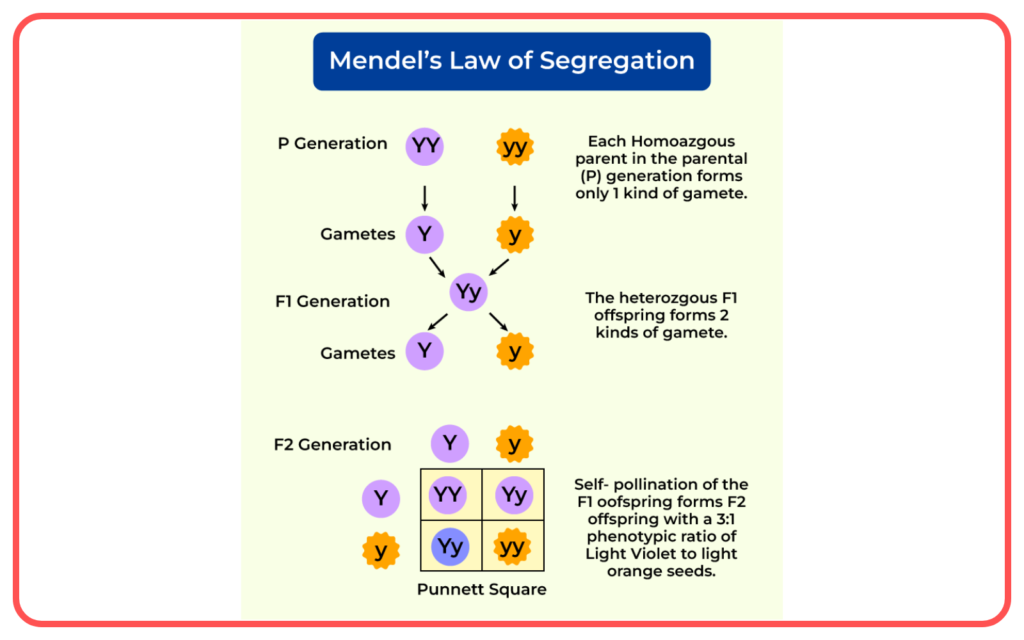
- Mendel’s Laws:
- Law of Segregation: Each organism carries two alleles for a trait, which separate during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg).
- Law of Independent Assortment: Genes for different traits are passed independently of one another.

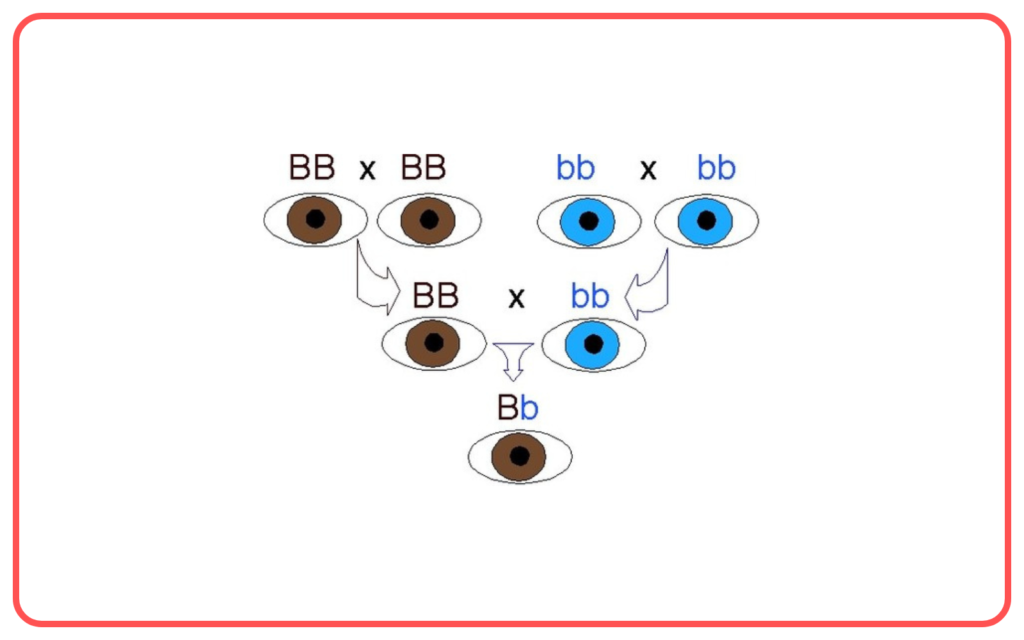
Alleles and Dominance:
- Alleles are different versions of a gene. They can be dominant (expressed even if only one copy is present) or recessive (expressed only if two copies are present).
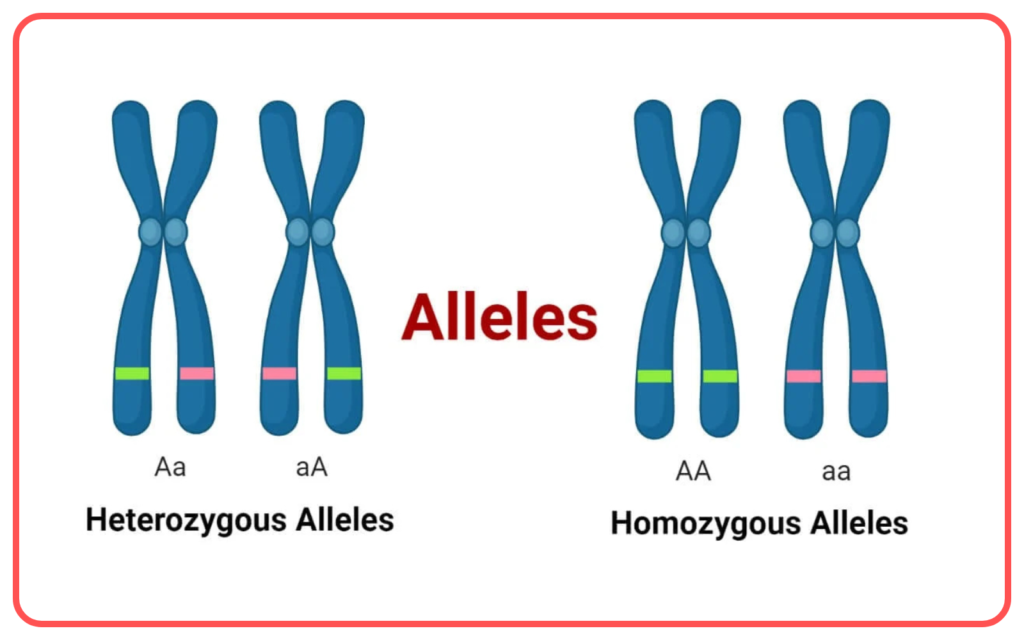
- An individual can be homozygous (having two identical alleles) or heterozygous (having two different alleles) for a trait.
Genotype and Phenotype:
- Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism (e.g., TT, Tt, or tt).
- Phenotype refers to the observable traits or characteristics (e.g., tall or short height).
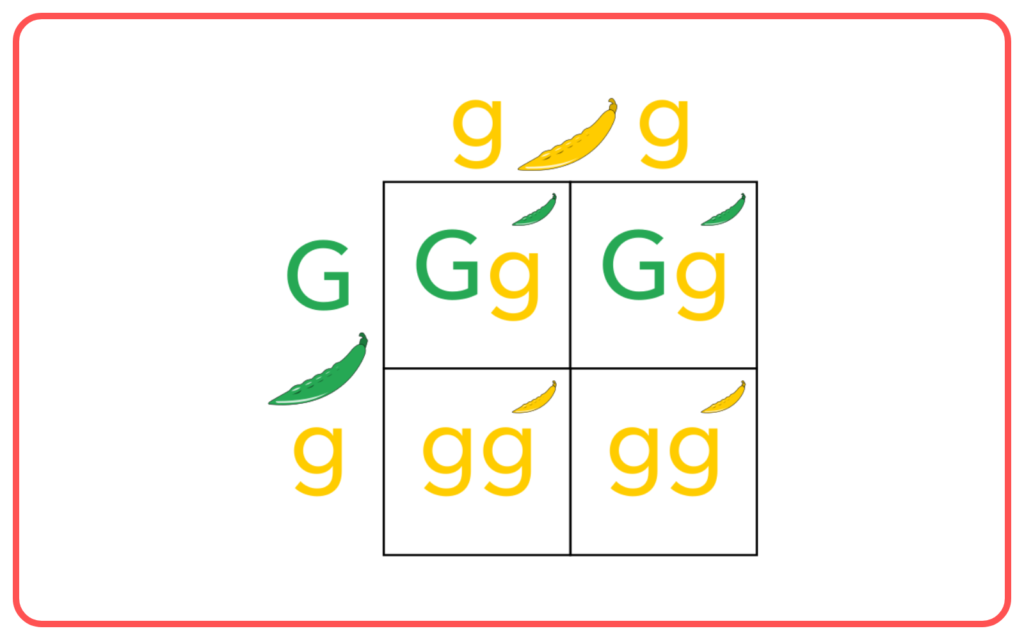
Punnett Square:
- A tool used to predict the probability of offspring inheriting certain traits.
- It shows how alleles from each parent can combine during fertilization.
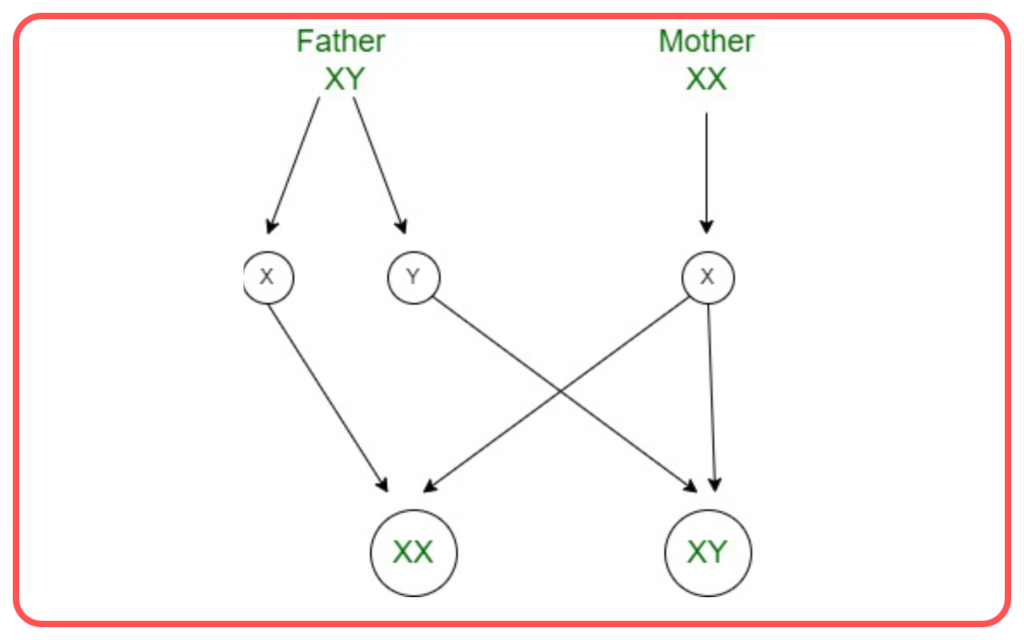
Sex Determination:
- The sex of an offspring is determined by the combination of sex chromosomes.
- Females have XX chromosomes, while males have XY chromosomes. The father’s sperm determines the sex of the child.
Variations in Traits:
- Continuous Variation: Traits like height and skin color show a range due to the influence of multiple genes (polygenic inheritance).
- Discontinuous Variation: Traits that fall into distinct categories, such as blood type.
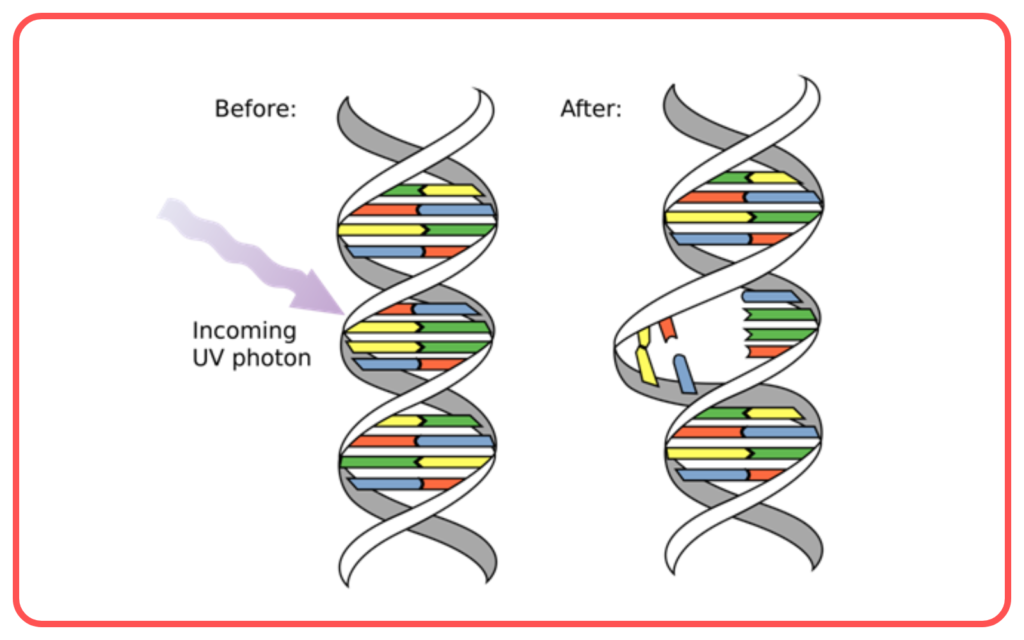
Mutations:
- Mutations are sudden changes in the DNA sequence that can affect genes and lead to new traits.
- Some mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect.
Importance of Heredity in Evolution:
- Heredity provides the genetic variation necessary for evolution.
- Natural selection acts on variations, leading to the survival of organisms best adapted to their environment.
Let’s practice!

