Accumulation Of Variation During Reproduction
Key Notes:
Definition of Variation:
- Variation refers to the differences in the physical traits and characteristics among individuals of the same species.
- Variations occur due to genetic differences and environmental influences.
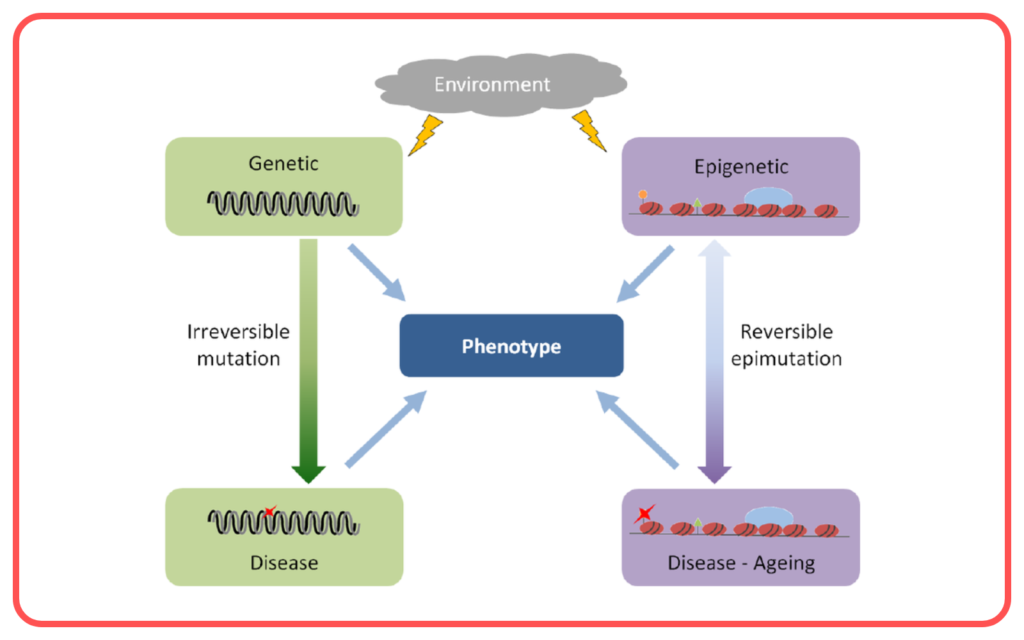
Role of Reproduction in Variation:
- Reproduction, especially sexual reproduction, is a key process that leads to variation in offspring.
- During sexual reproduction, the combination of genes from two parents leads to unique genetic makeups in their offspring.
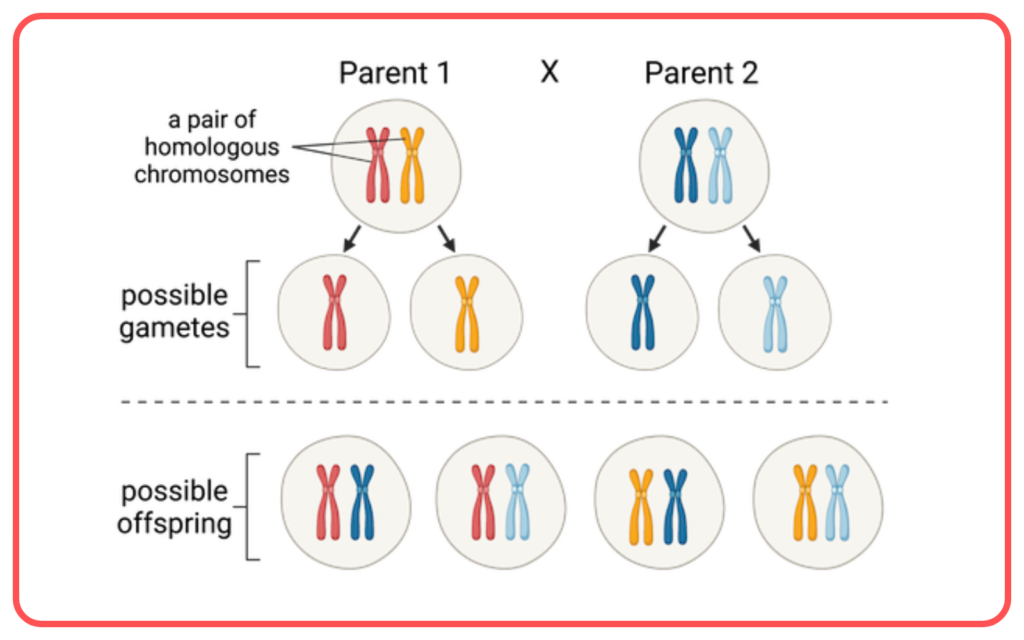
Sources of Genetic Variation:
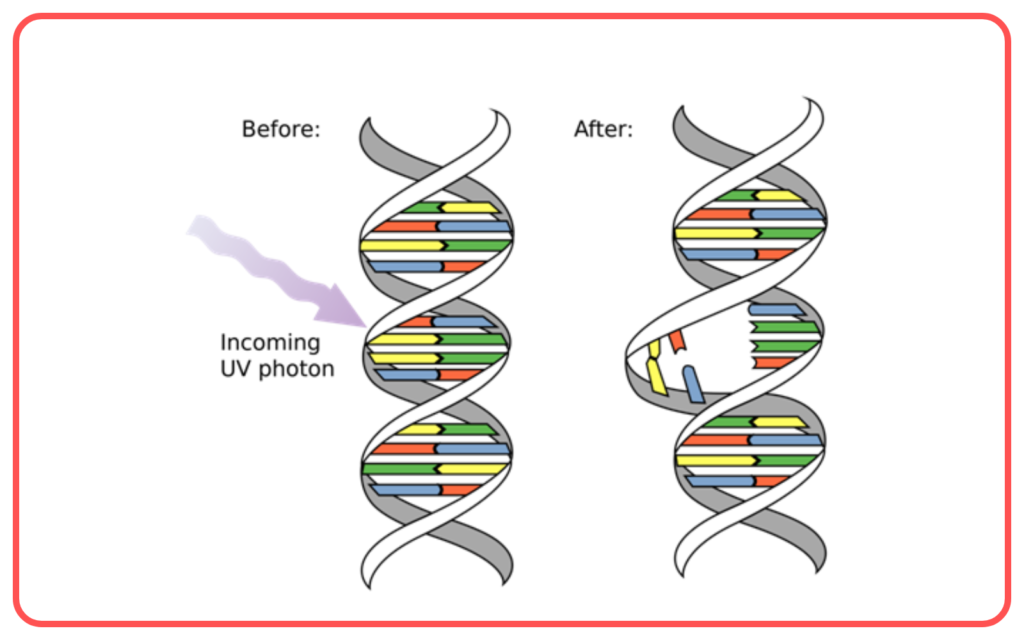
- Mutations: Changes in the DNA sequence that can occur naturally or due to external factors like radiation.
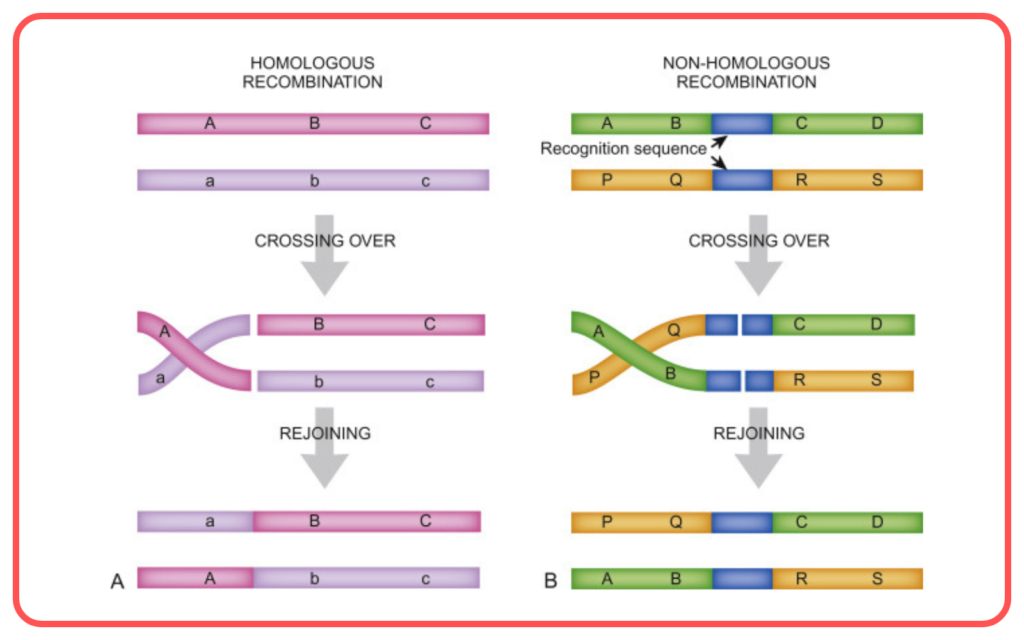
- Genetic Recombination: During meiosis, chromosomes undergo crossing over, exchanging genetic material which increases variation.
- Independent Assortment: The random distribution of chromosomes during the formation of gametes ensures diverse combinations.
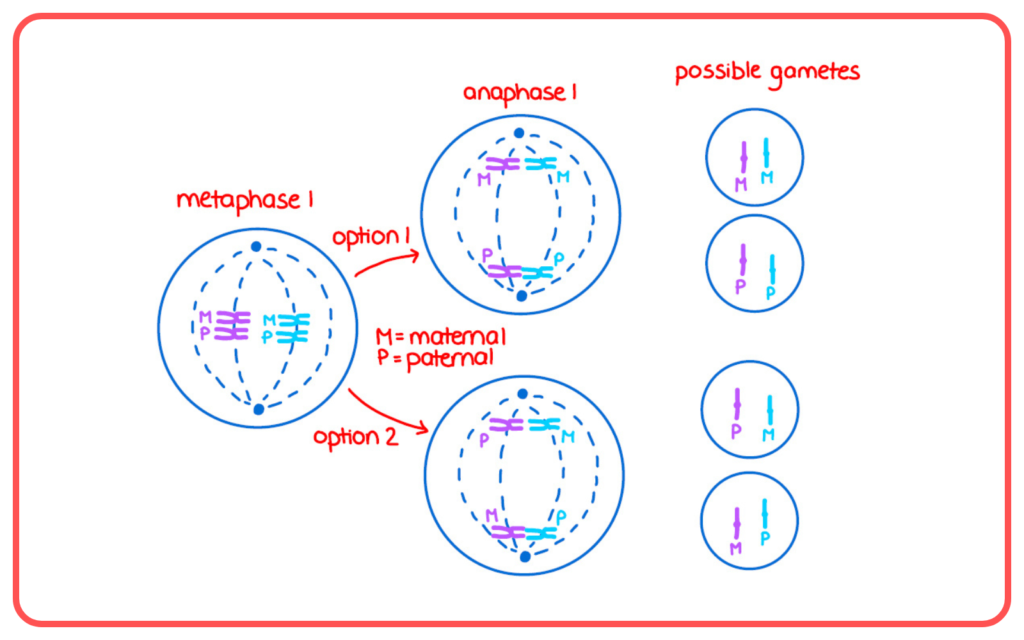
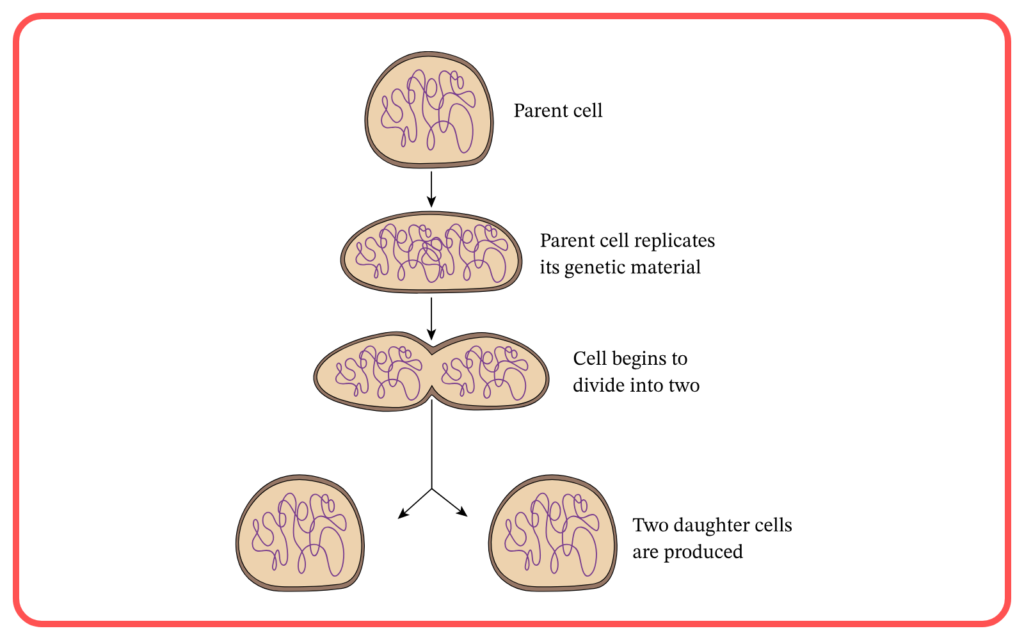
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction:
- Asexual Reproduction: Offspring are genetically identical to the parent (clones), leading to minimal variation.
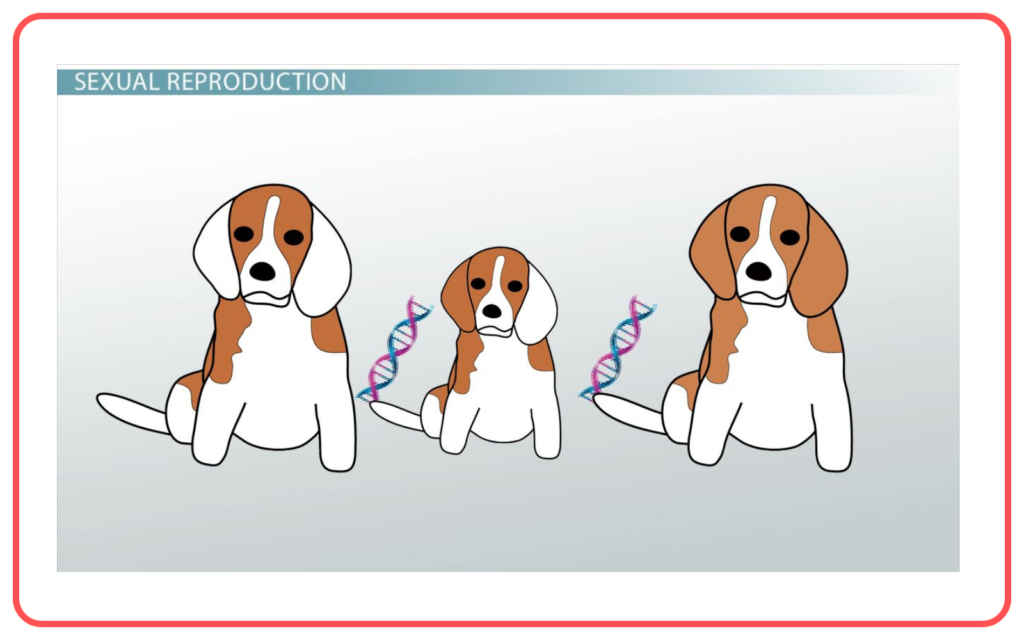
- Sexual Reproduction: Offspring have a mix of genes from both parents, resulting in greater genetic diversity.
Importance of Variation:
- Variations are essential for the survival of species in changing environments.
- Variations can make some individuals better suited to survive and reproduce under specific conditions (natural selection).
- Over time, favorable variations accumulate, leading to evolutionary adaptations.

Accumulation of Variation Over Generations:
- Small variations accumulate over many generations, leading to the gradual evolution of a species.
- The accumulation of beneficial traits increases an organism’s chances of survival and reproduction.
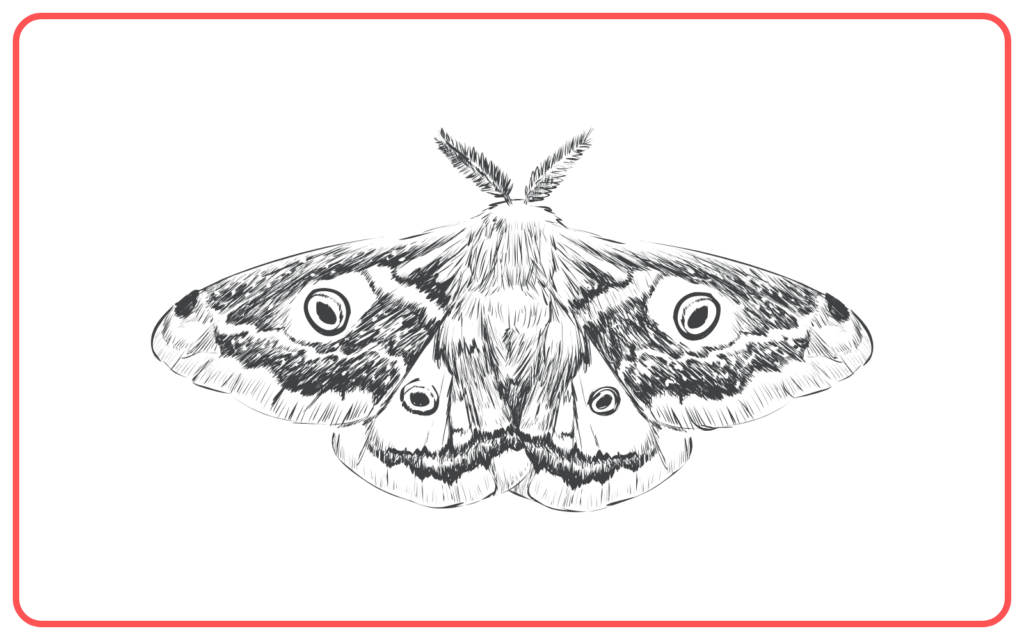
Examples:
- Peppered Moth: Variation in coloration helped moths survive during the Industrial Revolution.

- Darwin’s Finches: Beak shape variations among finches helped them adapt to different food sources on the Galápagos Islands.
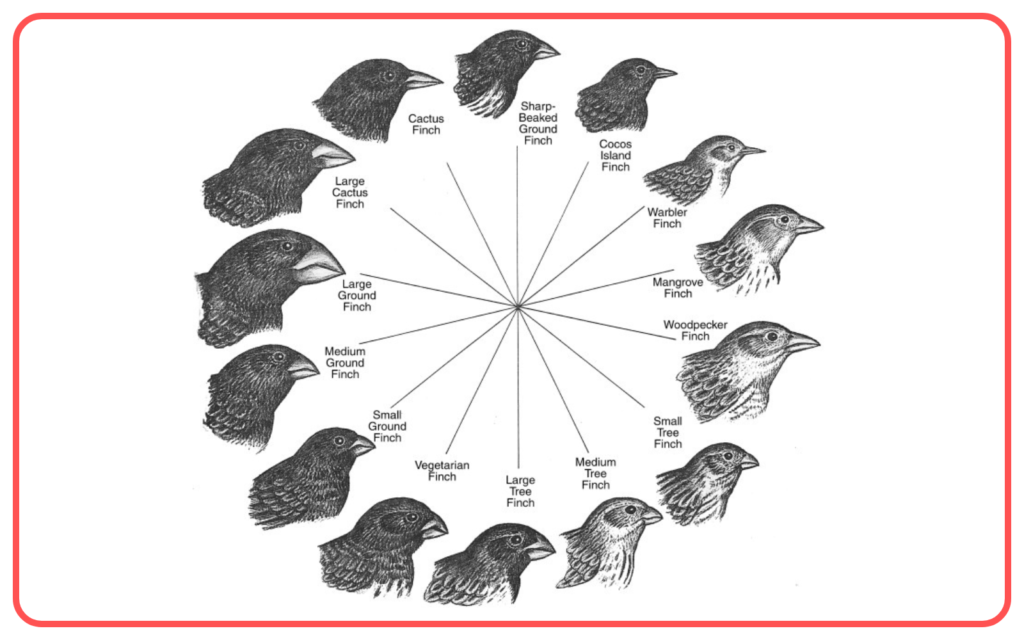
Impact on Evolution:
- Accumulated variations over long periods can lead to the emergence of new species (speciation).
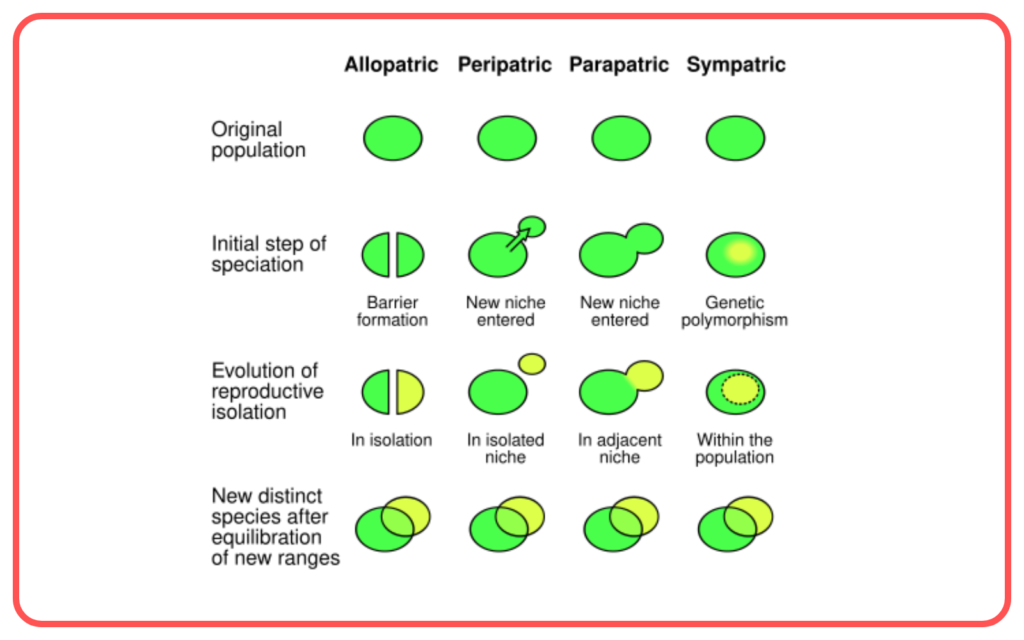
- This is the fundamental mechanism behind natural selection and the theory of evolution as proposed by Charles Darwin.
Human Implications:
- Understanding genetic variations is crucial in fields like genetics, medicine, and agriculture for developing better disease-resistant crops and understanding genetic disorders.
Let’s practice!

