Sexual Reproduction
Key Notes:
Definition
- Sexual Reproduction: A biological process where two parent organisms contribute genetic material to produce offspring, resulting in genetic variation.
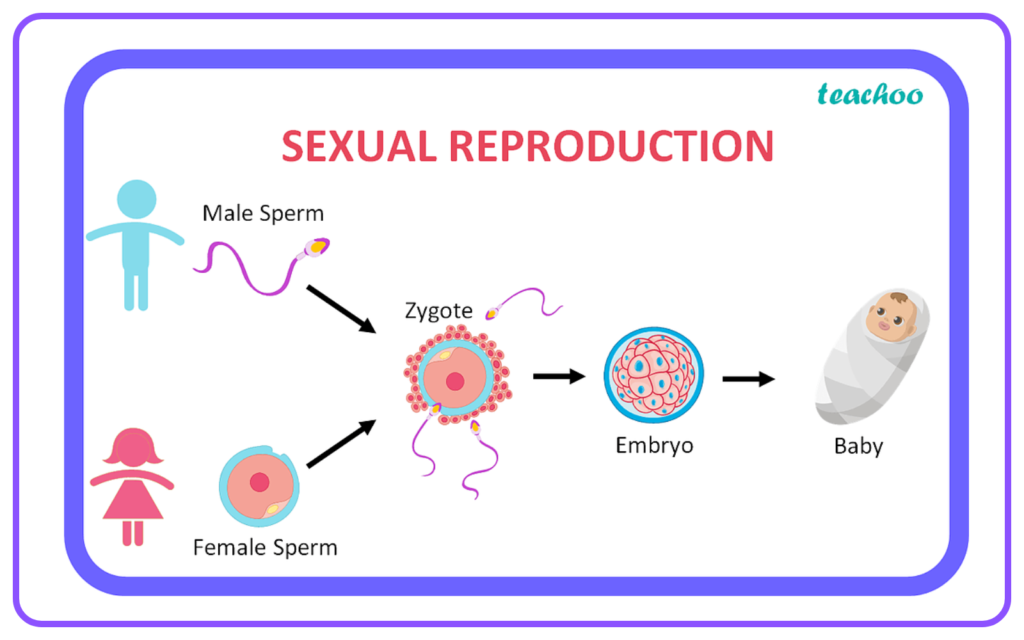
Key Features
Gametes:
- Involves the formation of specialized cells called gametes.
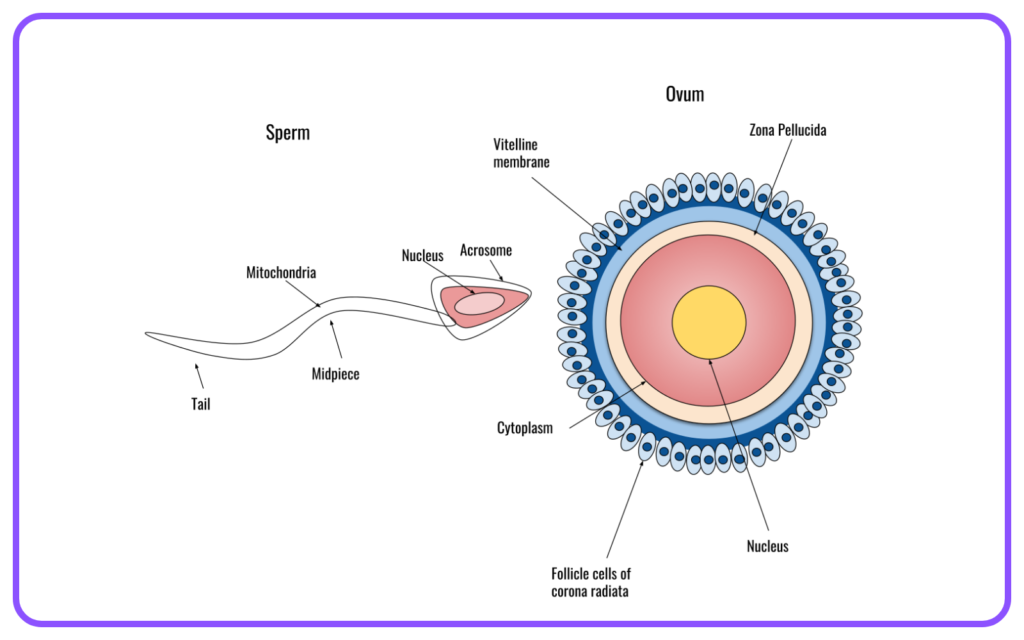
- Male Gametes: Sperm produced in the male reproductive organs.
- Female Gametes: Eggs (ova) produced in the female reproductive organs.
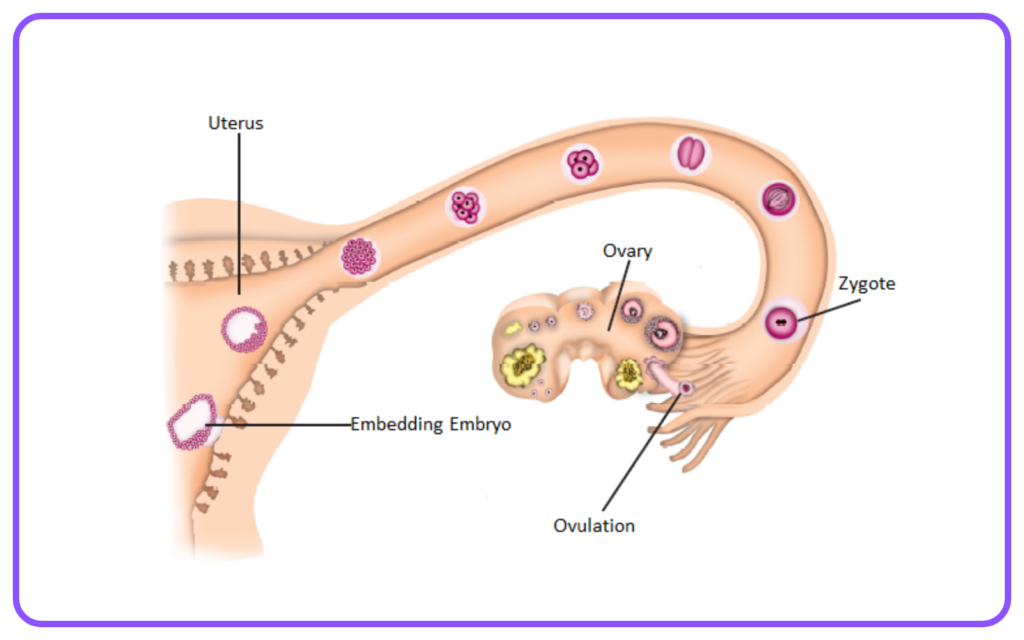
Fertilization:
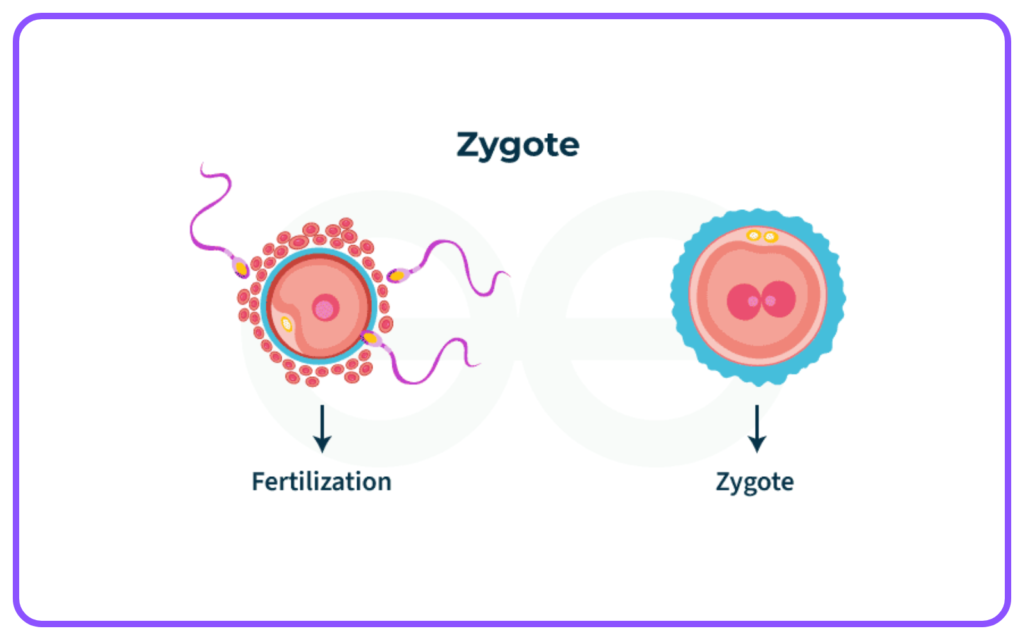
- The process where a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg) fuse to form a zygote.
- Can occur internally (within the female body) or externally (outside the bodies of the parents).
Zygote Development:
- The zygote undergoes cell division and differentiation to develop into an embryo.
- The embryo eventually develops into a mature organism.
Types of Sexual Reproduction
Internal Fertilization:
- Occurs inside the female’s body.
- Common in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
- Provides protection to the developing embryo.
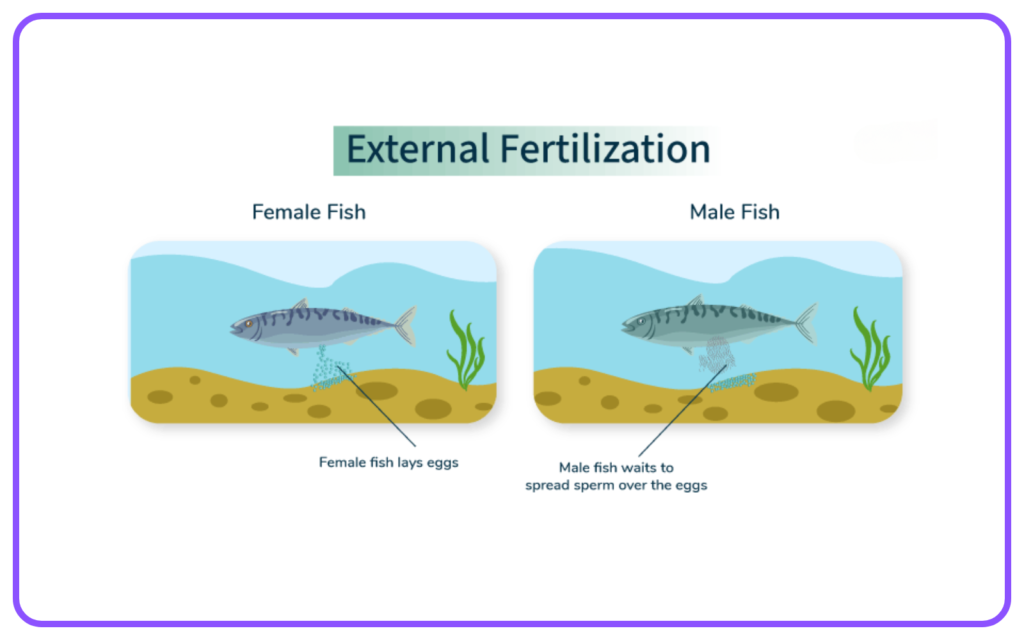
External Fertilization:
- Takes place outside the female’s body.
- Common in aquatic animals like fish and amphibians.
- Typically involves the release of eggs and sperm into the water.
Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
- Genetic Diversity: Offspring inherit a mix of traits from both parents, leading to greater genetic variation, which can enhance adaptability and survival.
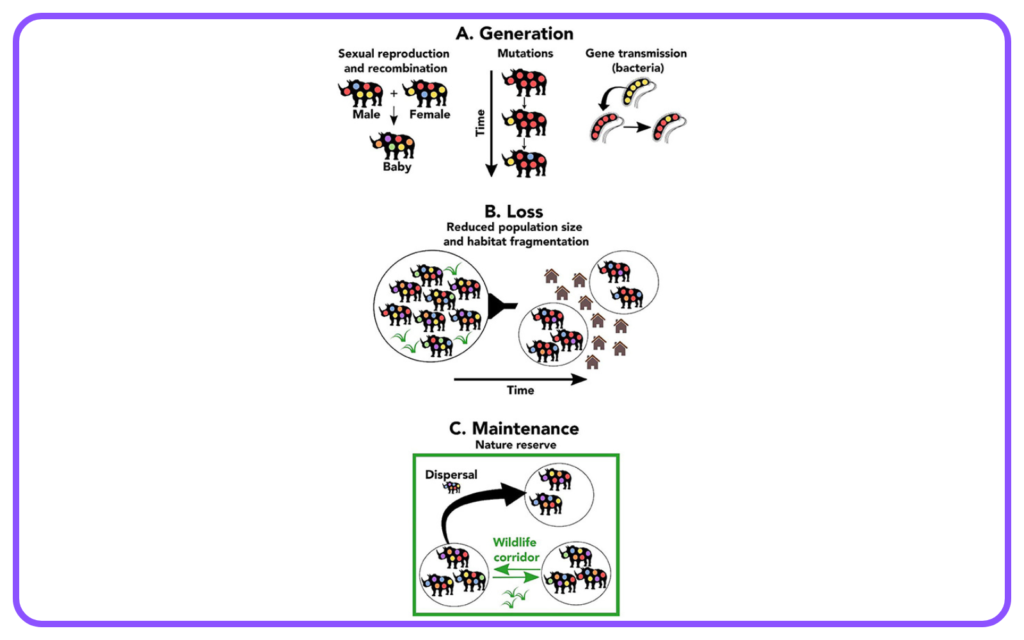
- Evolution: Sexual reproduction contributes to evolution by introducing new combinations of genes.
Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction
- Time and Energy: Requires more time and energy for finding mates and producing offspring compared to asexual reproduction.
- Risk of Disease: Increased risk of transmitting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) between parents.
Importance in Biology
- Understanding sexual reproduction is crucial for studies in genetics, evolution, and conservation biology.
- It plays a significant role in agriculture, animal breeding, and understanding human reproduction and health.
Related Terms
- Mitosis: A type of cell division resulting in two identical daughter cells.
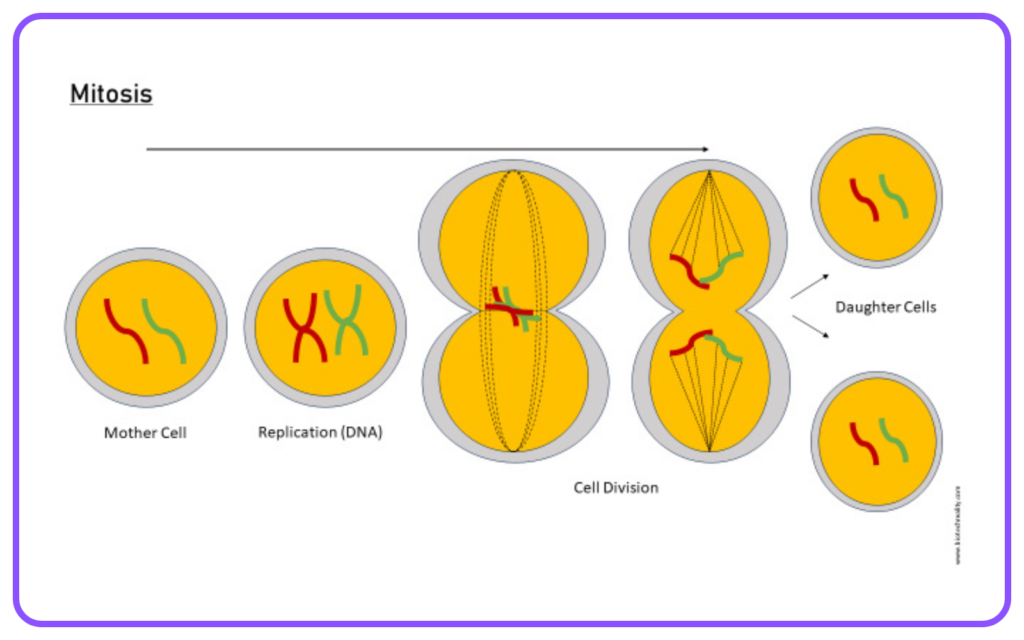
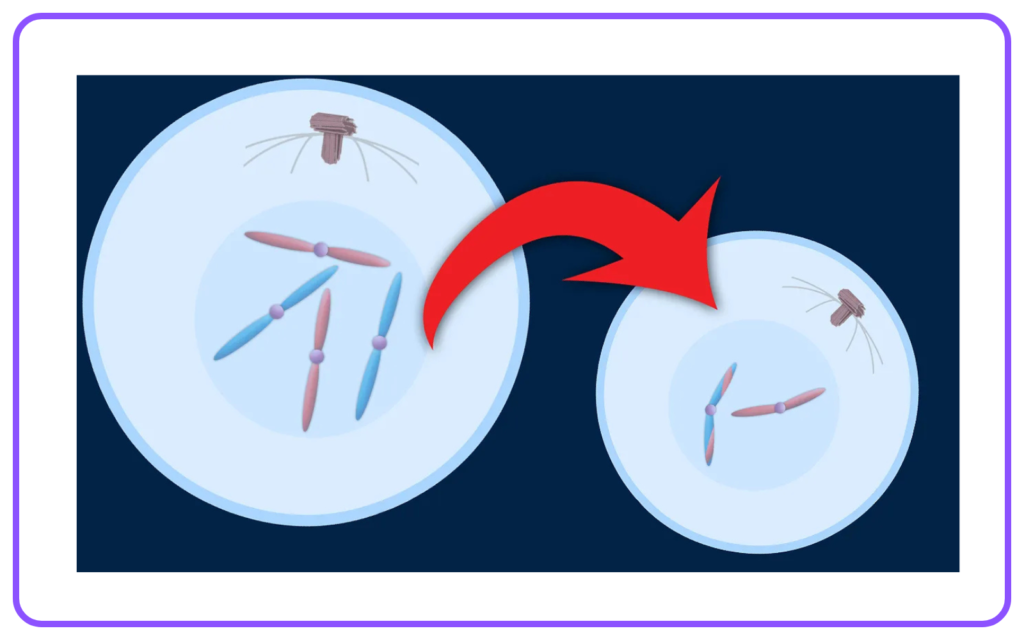
- Meiosis: A specialized form of cell division that produces gametes, resulting in four genetically diverse cells.
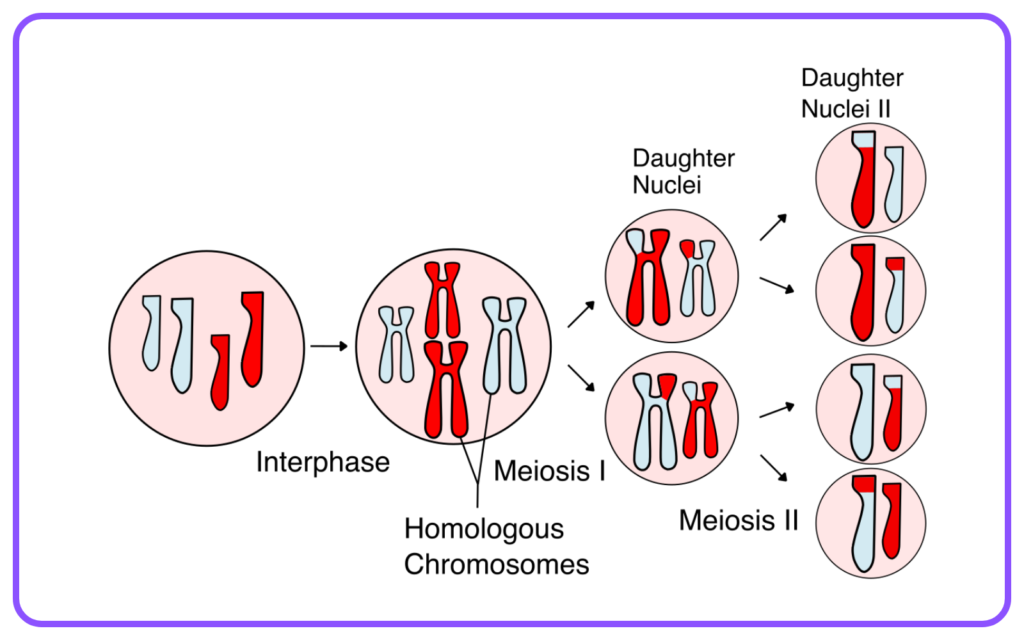
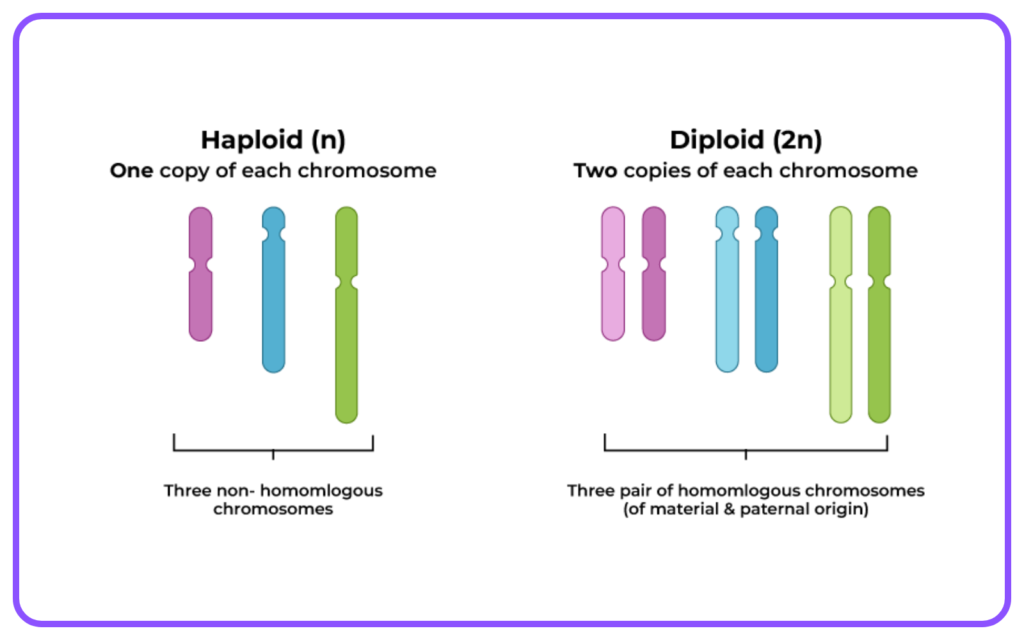
- Haploid: Cells containing one set of chromosomes (gametes).
- Diploid: Cells containing two sets of chromosomes (somatic cells).
Let’s practice!

