Modes Of Reproduction Used By Organisms
Key Notes:
Definition of Reproduction
- Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced from their parents.
- It ensures the continuation of a species.
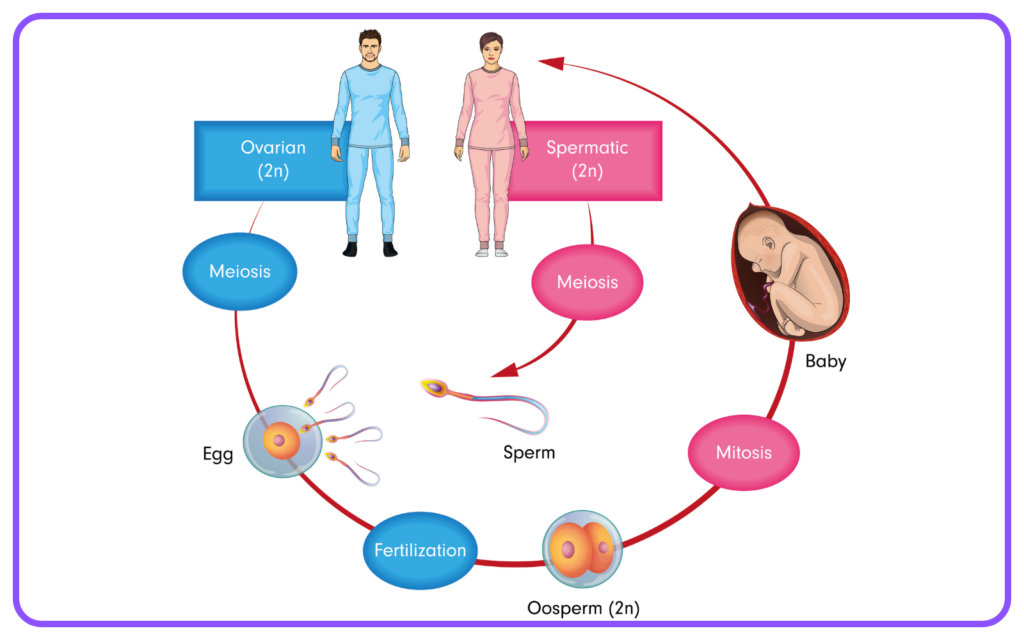
Types of Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
- Involves a single parent organism.
- Offspring are genetically identical to the parent (clones).
- Common methods include:
- Binary Fission: Common in unicellular organisms like bacteria; the organism divides into two equal parts.
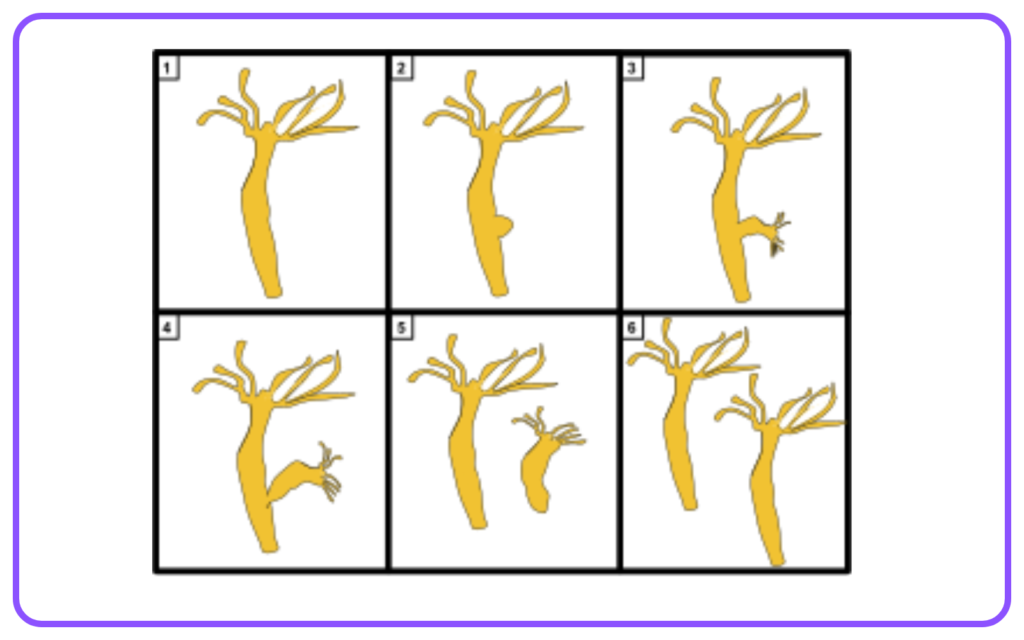
- Budding: New individuals form from an outgrowth (bud) of the parent organism, seen in yeast and hydra.
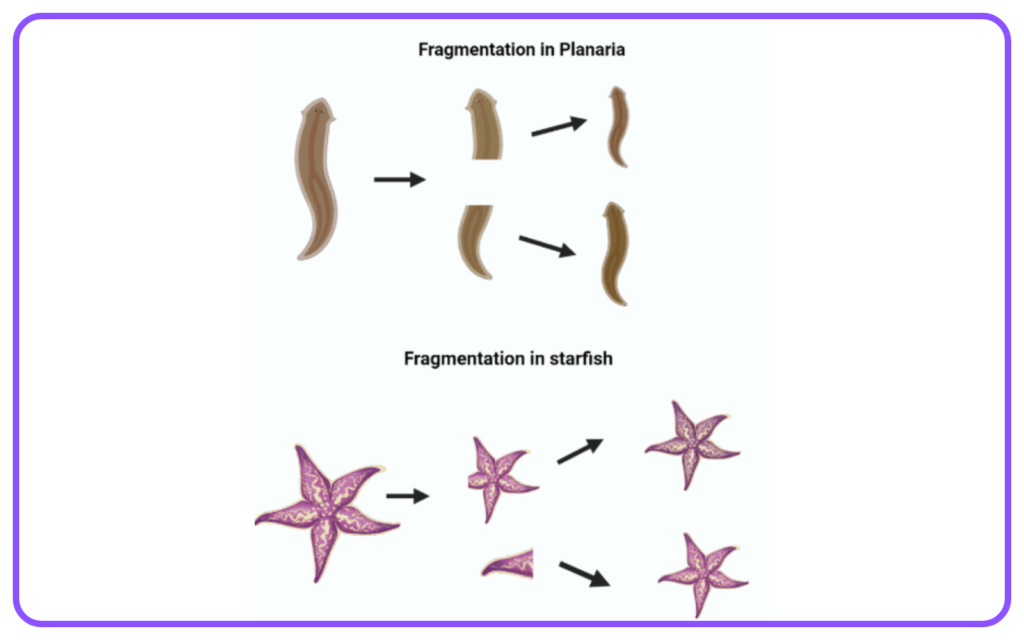
- Fragmentation: Organisms break into fragments, each capable of growing into a new individual (e.g., starfish).
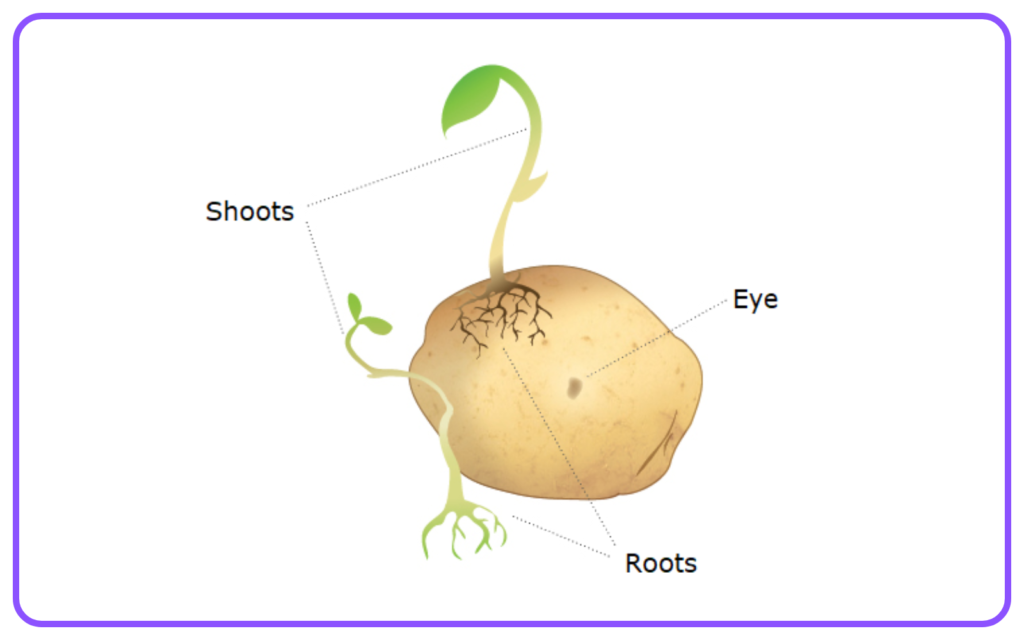
- Vegetative Reproduction: In plants, new individuals grow from parts of the parent plant, such as runners, tubers, or bulbs.
Sexual Reproduction
- Involves two parents contributing genetic material.
- Offspring have genetic variation, leading to increased adaptability.
- Key processes include:
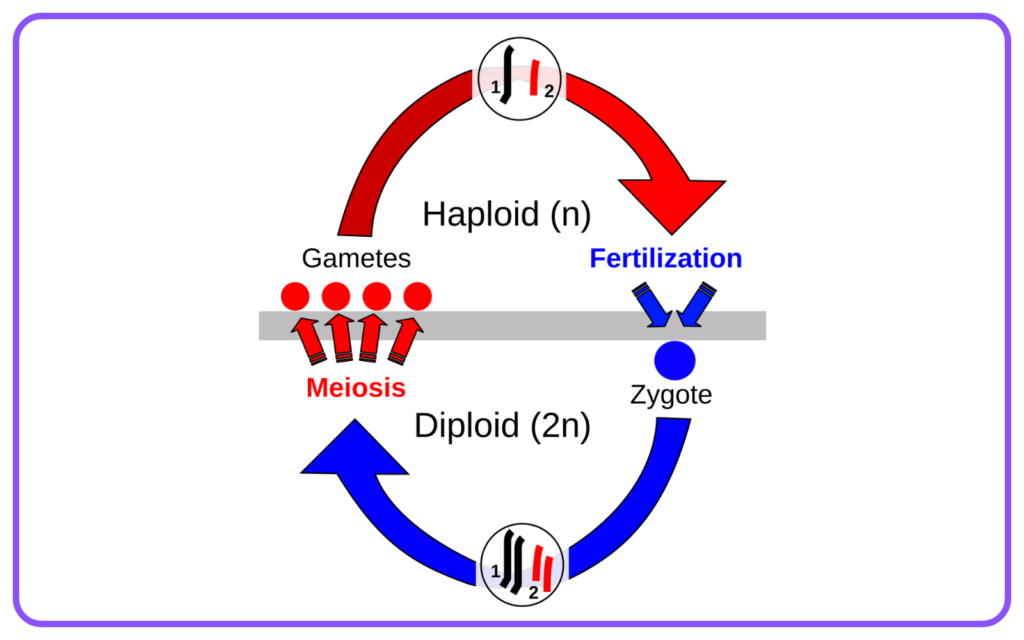
- Gamete Formation: Male and female gametes (sperm and egg) are produced through meiosis.
- Fertilization: The fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- Development: The zygote develops into a new organism, which may occur internally (as in mammals) or externally (as in fish and amphibians).
Advantages and Disadvantages
Asexual Reproduction
Advantages:
- Faster reproduction rates.
- No need for a mate; beneficial in stable environments.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of genetic diversity, making populations vulnerable to disease and environmental changes.
Sexual Reproduction
Advantages:
- Increases genetic diversity, enhancing adaptability and survival.
Disadvantages:
- Slower reproduction rates and requires energy for finding a mate.
Examples of Organisms
- Asexual Reproduction: Bacteria (binary fission), hydra (budding), potatoes (vegetative).

- Sexual Reproduction: Humans, most animals (via internal fertilization), and many plants (via pollination).
Environmental Influence
- Some organisms can switch between asexual and sexual reproduction based on environmental conditions (e.g., some plants and certain species of fungi).
- This flexibility allows them to optimize their reproductive strategy for survival.
Conclusion
- Understanding the modes of reproduction is crucial for studying biodiversity and the survival strategies of different organisms.
- Each mode has evolved to suit specific ecological niches and environmental conditions.
Let’s practice!

