Hormones In Animals
Key Notes:
Introduction to Hormones
- Definition: Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system that regulate various physiological processes in the body.
- Function: They travel through the bloodstream to target organs and tissues, influencing growth, metabolism, reproduction, and mood.
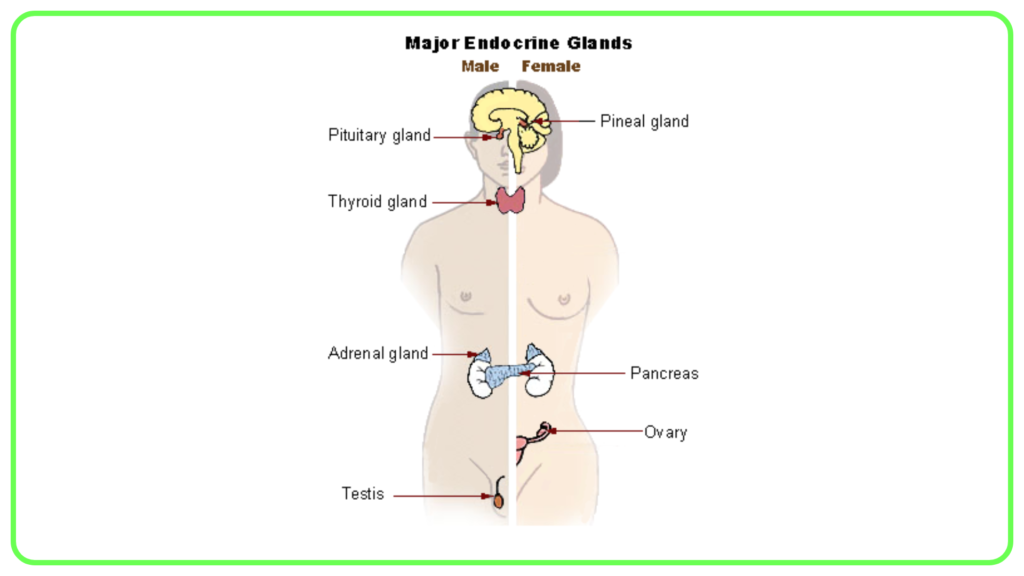
Major Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones
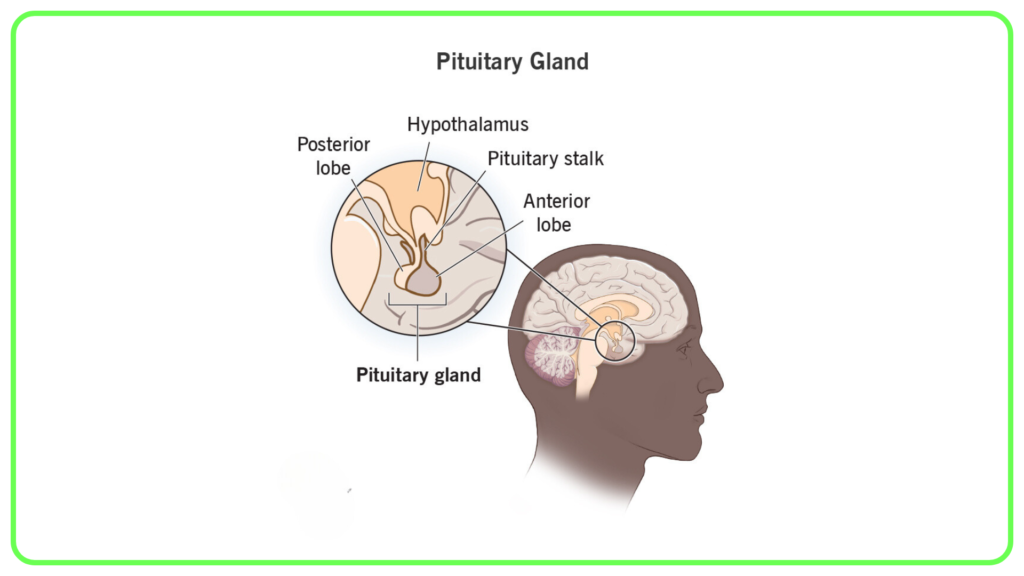
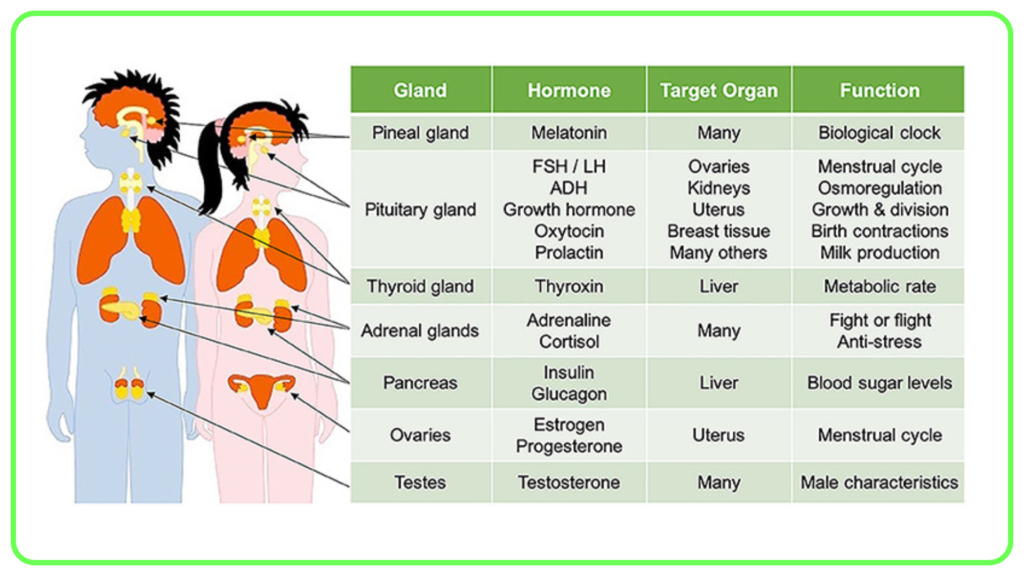
Pituitary Gland:
- Often referred to as the “master gland” because it regulates other endocrine glands.
- Produces hormones such as:
- Growth Hormone (GH): Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
- Prolactin: Promotes milk production in lactating females.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): Stimulates the adrenal glands.
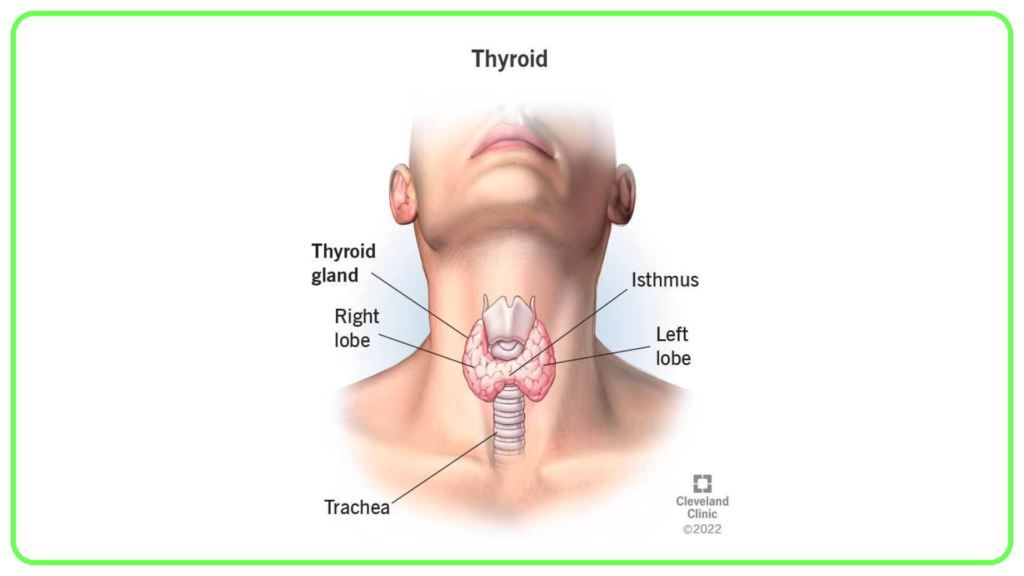
Thyroid Gland:
- Produces hormones like:
- Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3): Regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth.
- Calcitonin: Helps lower blood calcium levels.
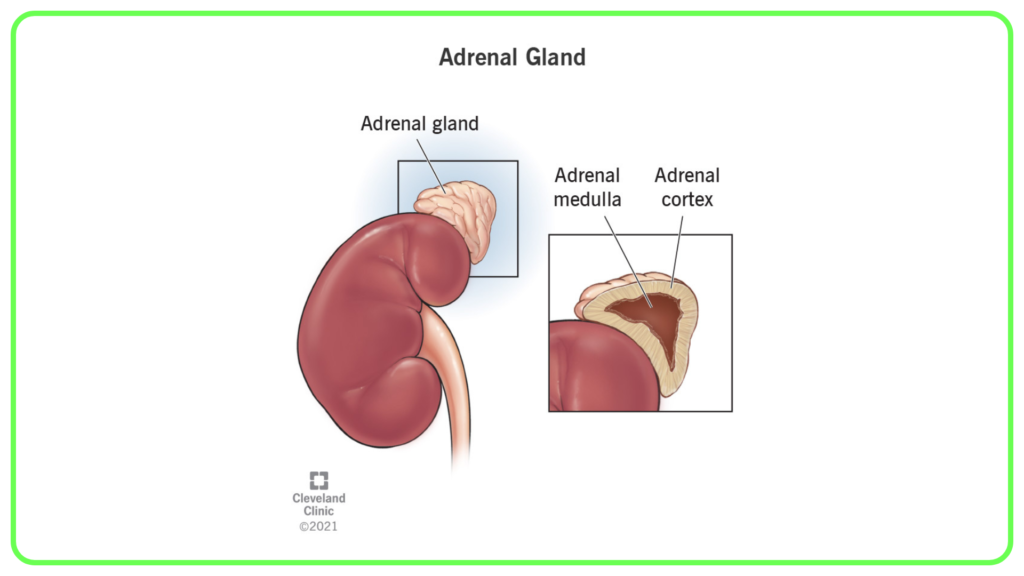
Adrenal Glands:
- Located on top of the kidneys, produce:
- Cortisol: Helps manage stress and metabolism.
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine): Increases heart rate and energy levels during stress (“fight or flight” response).
- Aldosterone: Regulates sodium and potassium levels.
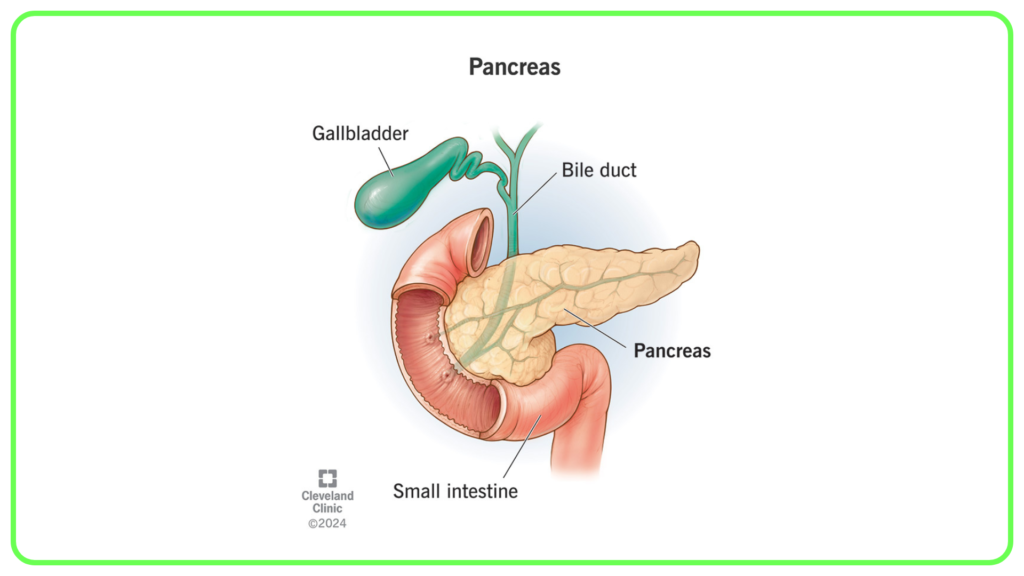
Pancreas:
- Produces insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin: Lowers blood sugar by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells.
- Glucagon: Raises blood sugar by promoting the release of glucose from the liver.
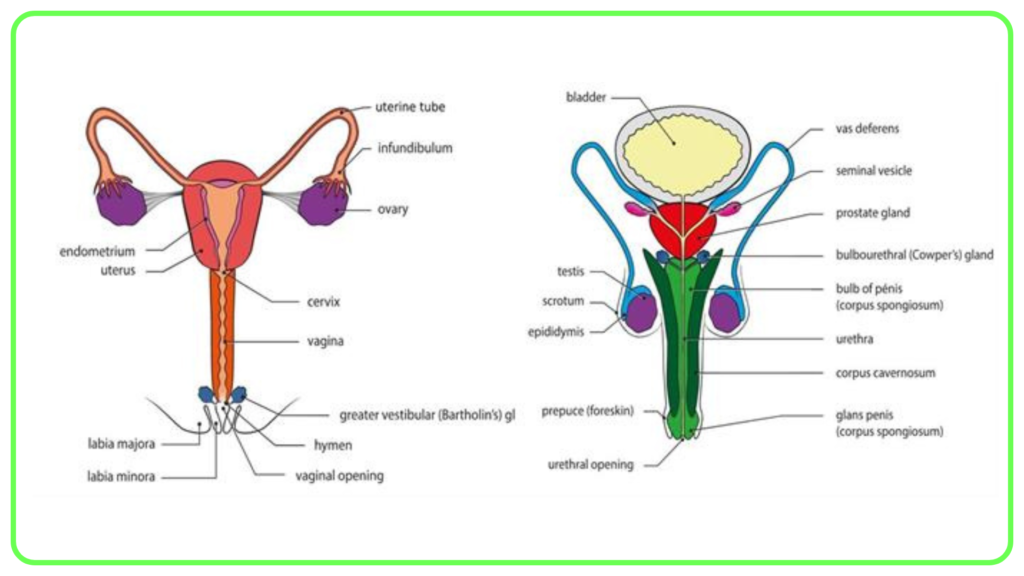
Gonads (Ovaries and Testes):
- Produce sex hormones:
- Estrogens: Regulate female reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics.
- Testosterone: Regulates male reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics.
Functions of Hormones
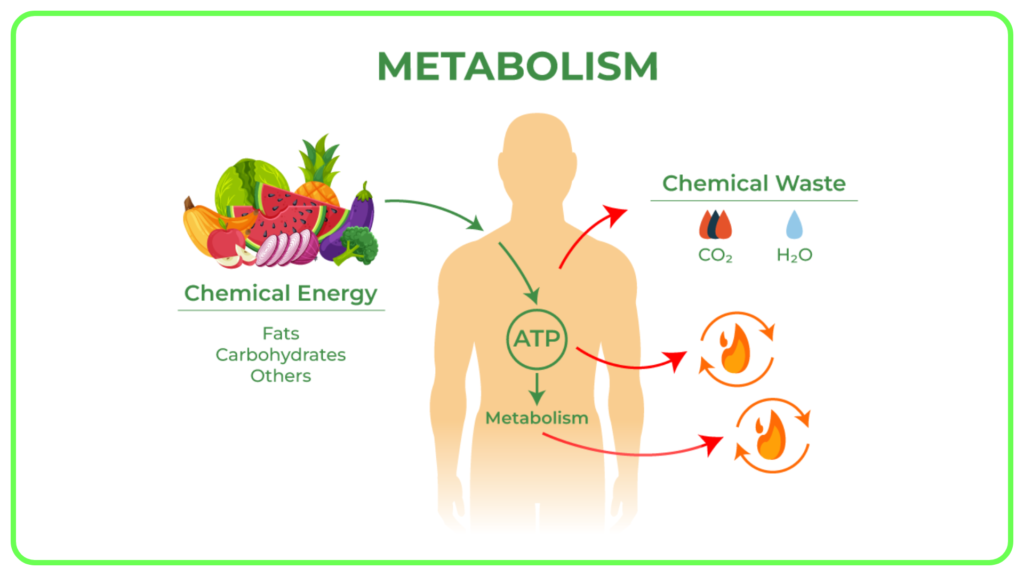
- Metabolism: Hormones regulate the conversion of food into energy and manage how the body uses nutrients.
- Growth and Development: Hormones influence physical growth, sexual maturation, and development of body structures.
- Homeostasis: Hormones help maintain stable internal conditions (e.g., temperature, pH, hydration).
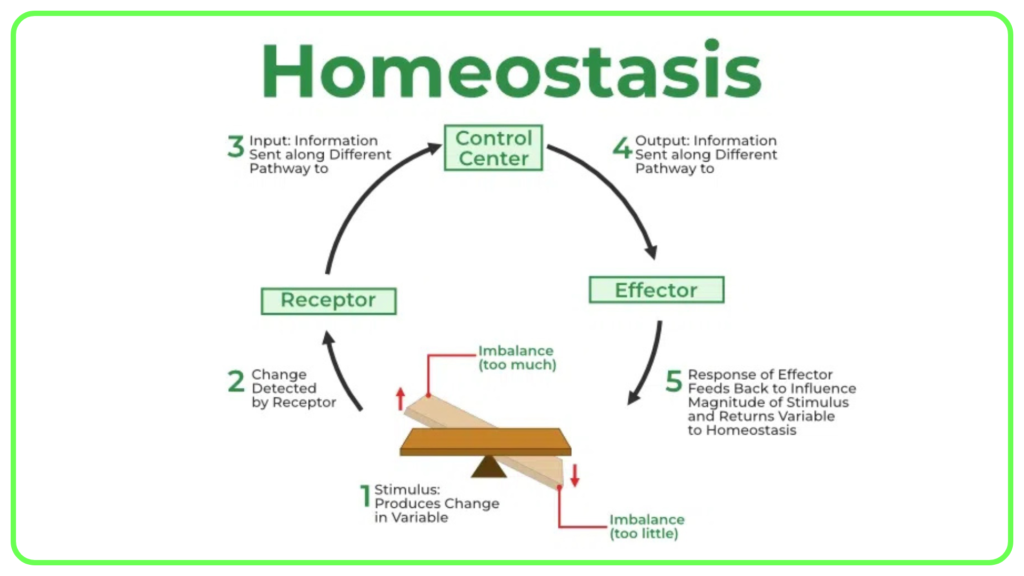
- Reproduction: Hormones control the menstrual cycle in females and sperm production in males.
Hormonal Imbalances
- Causes: Can result from disease, genetic factors, stress, or environmental factors.
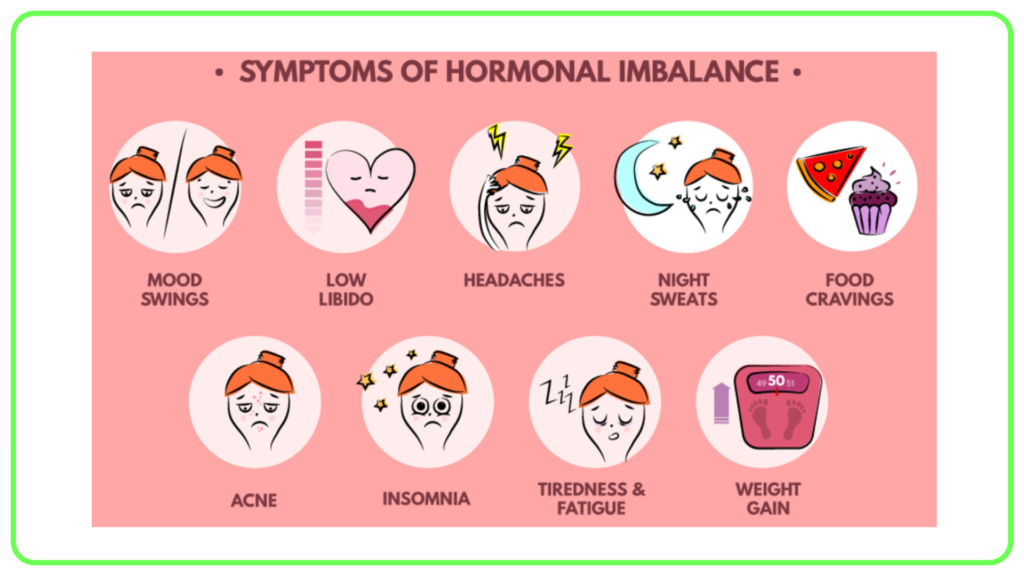
- Effects: Can lead to various health issues such as diabetes (insulin imbalance), hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormones), or hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormones).
Conclusion
- Hormones are essential for regulating numerous body functions. Understanding their roles helps us grasp how our bodies respond to different stimuli and maintain balance.
Let’s practice!

