Animal -Nervous System
Key Notes:
Definition of the Nervous System
- The nervous system is a complex network of cells and tissues that coordinates the actions and sensory information of an organism.
- It consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Main Divisions
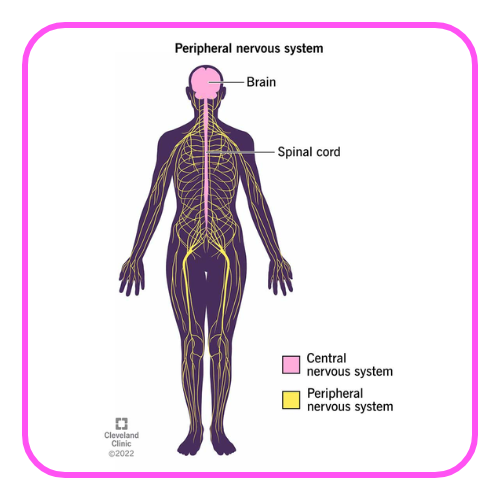
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprises the brain and spinal cord; responsible for processing information and controlling responses.
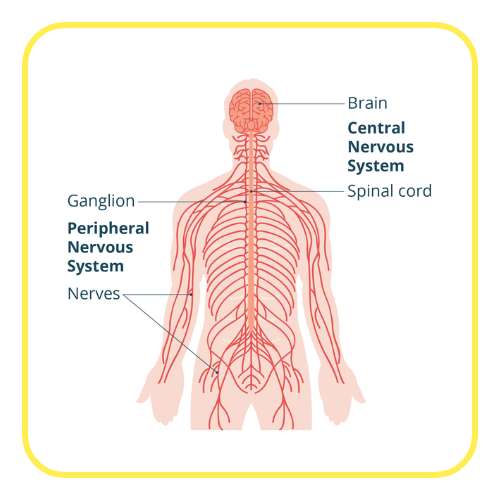
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Includes all the nerves outside the CNS; connects the CNS to limbs and organs.
Functions of the Nervous System
- Sensory Function: Receives stimuli from internal and external environments through sensory receptors.

- Integration: Processes and interprets sensory information to determine the appropriate response.
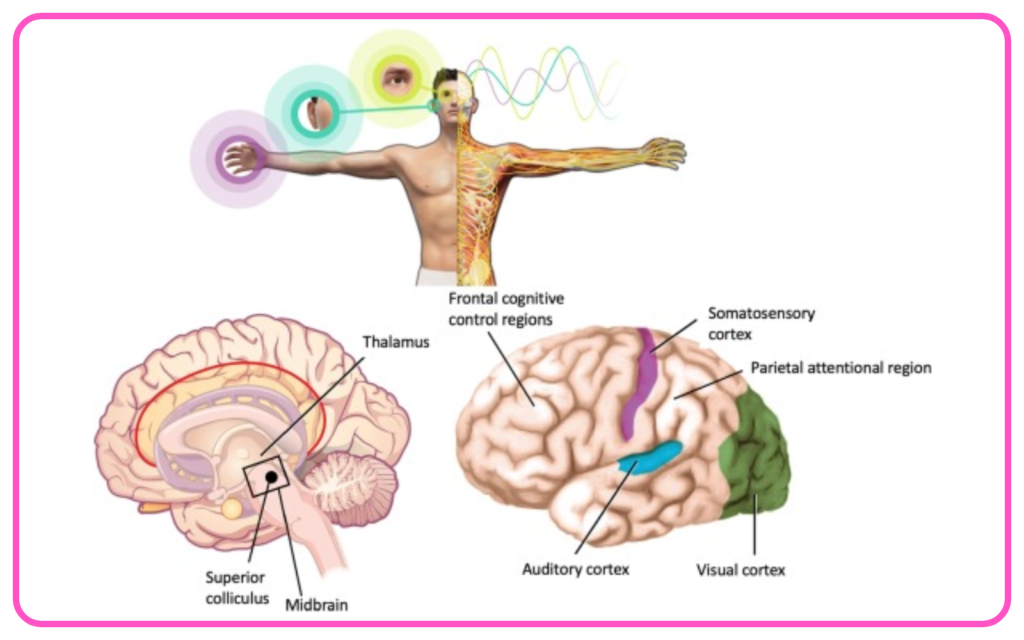
- Motor Function: Sends signals to muscles and glands to initiate actions.
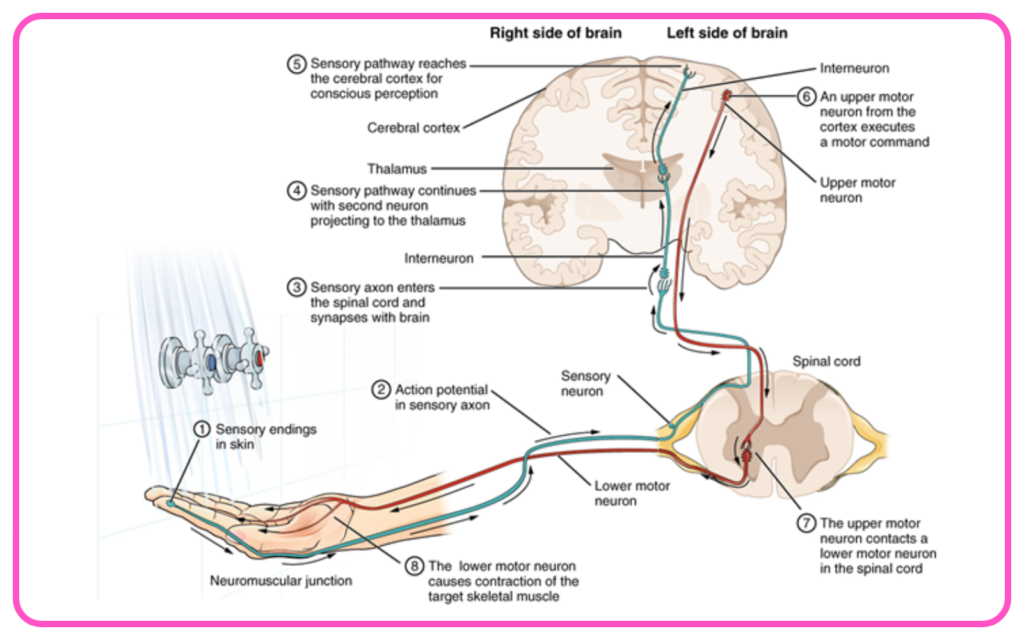
Types of Neurons
- Sensory Neurons: Transmit sensory information from receptors to the CNS.
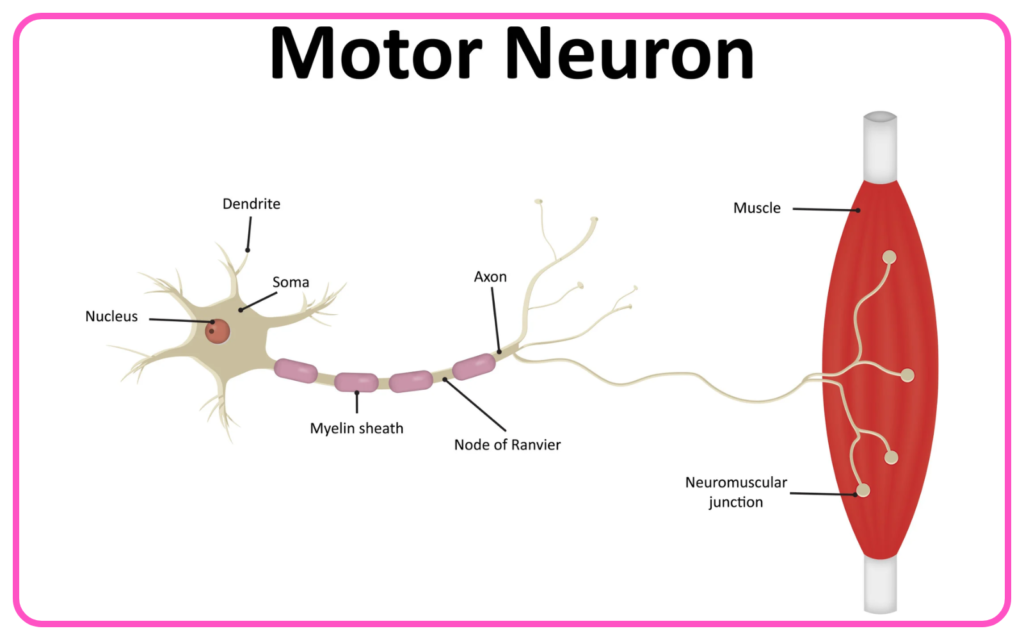
- Motor Neurons: Carry signals from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands).
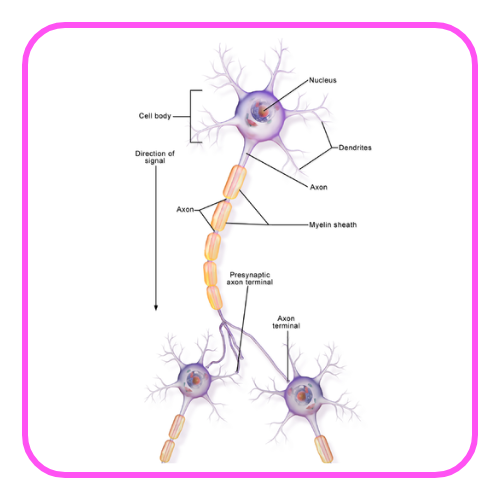
- Interneurons: Connect sensory and motor neurons within the CNS, facilitating communication.
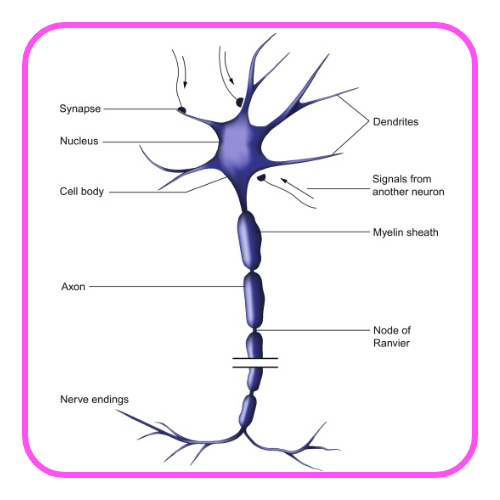
Structure of Neurons
- Cell Body: Contains the nucleus and organelles.
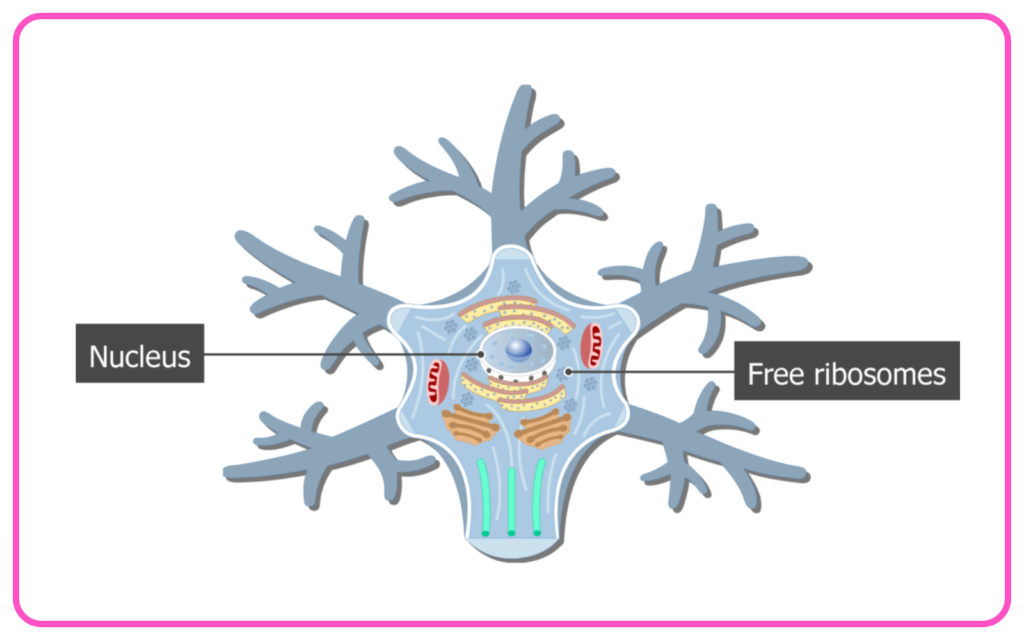
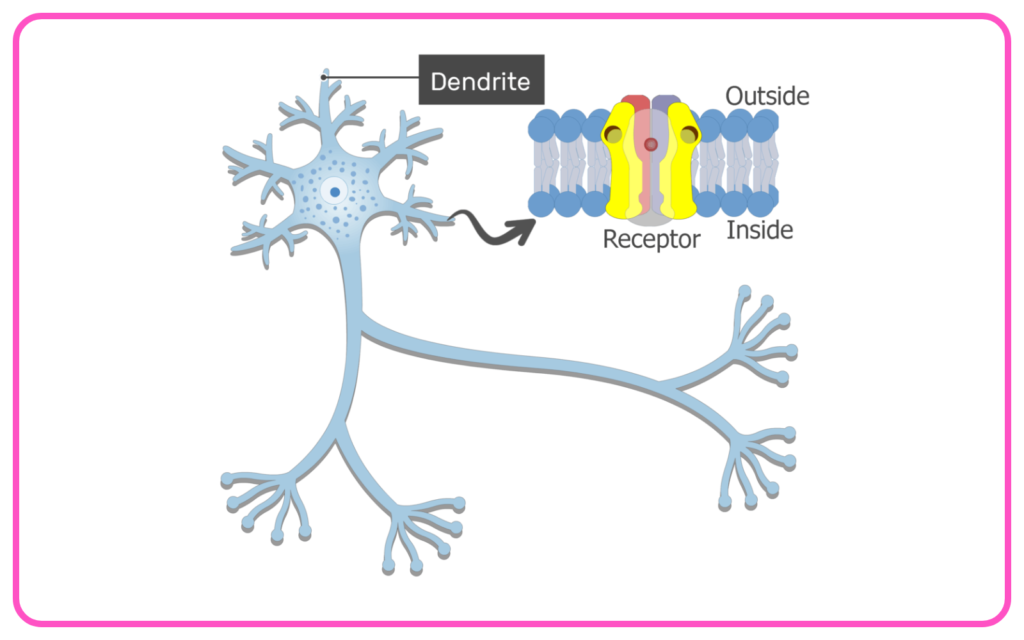
- Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons.
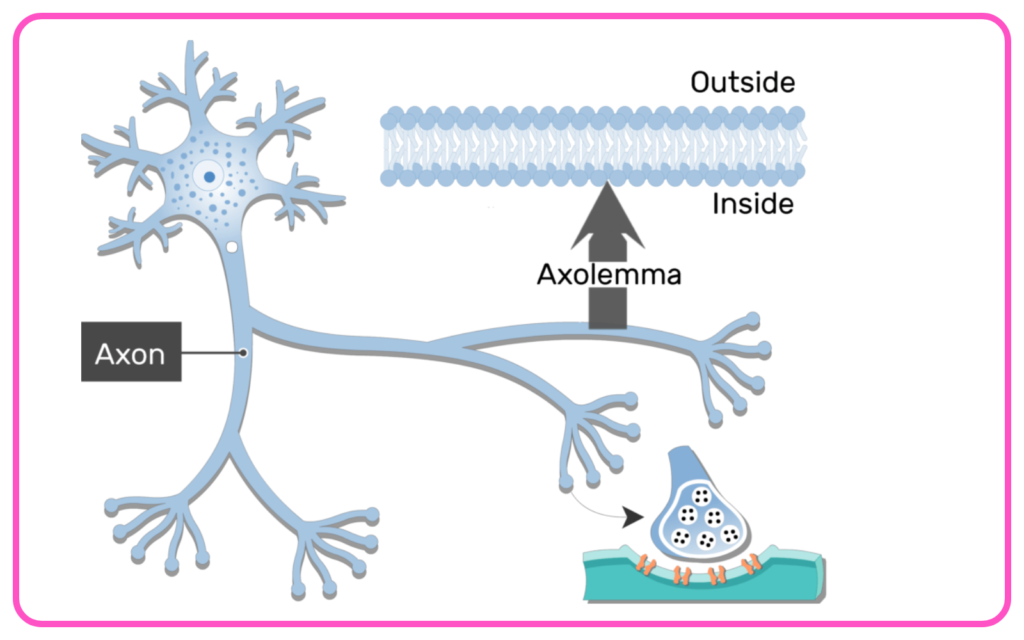
- Axon: Conducts impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
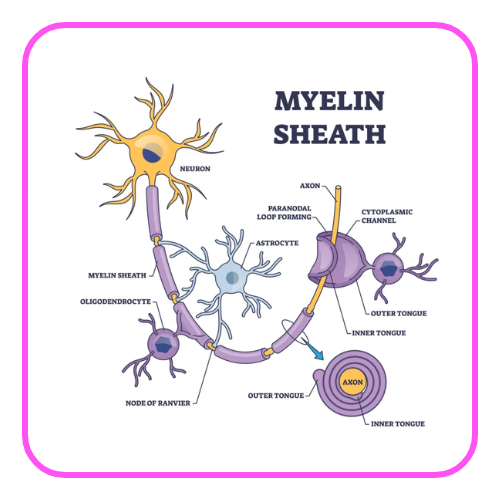
- Myelin Sheath: Insulates the axon to speed up signal transmission.
Synapses
- Junctions where neurons communicate with each other or with target cells (muscles, glands).
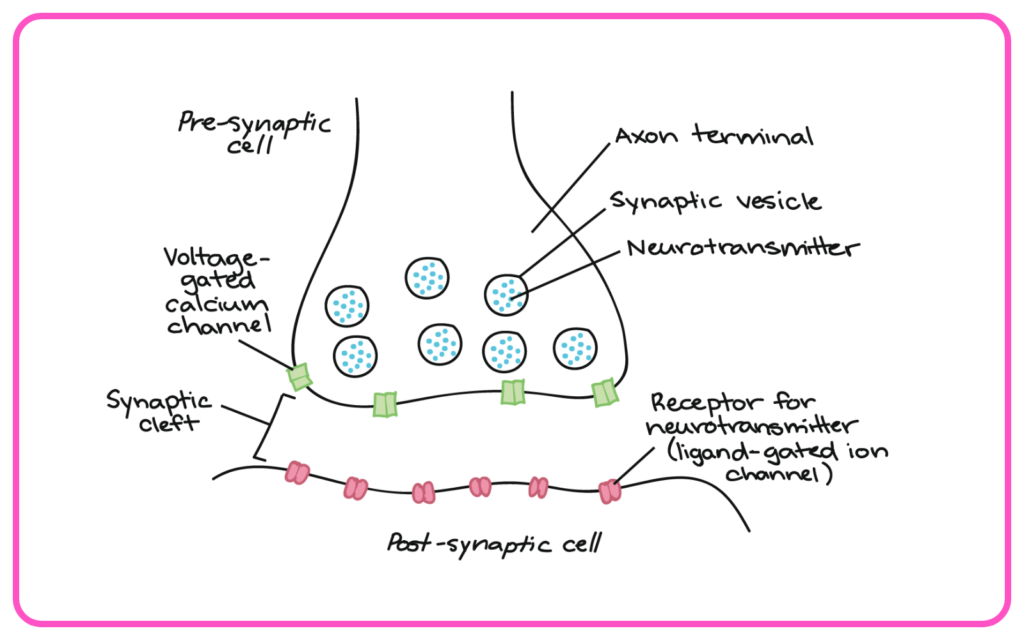
- Neurotransmitters are released from one neuron and bind to receptors on another, facilitating signal transmission.
Nervous System Disorders
- Common disorders include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.

- These conditions can affect cognitive functions, movement, and overall nervous system health.
Importance of the Nervous System
- Controls voluntary and involuntary actions.
- Enables communication between different parts of the body.
- Facilitates response to changes in the environment.
Interaction with Other Systems
- Works closely with the endocrine system to regulate bodily functions.
- Coordinates with the muscular system for movement and reaction.
Adaptation and Evolution
- Nervous systems have evolved in complexity across different animal species, reflecting adaptations to their environments and lifestyles.
Let’s practice!

