Key Notes:-
Definition of Excretion
- Excretion is the biological process of removing waste products and toxins from the body. These waste products are byproducts of cellular metabolism and other physiological activities.
Importance of Excretion
- Maintains Homeostasis: Helps maintain the body’s internal environment by regulating the composition of body fluids.
- Prevents Toxicity: Removes harmful metabolic wastes that can be toxic if they accumulate in the body.
- Regulates Water and Salt Balance: Helps control the balance of water and salts in the body, crucial for maintaining blood pressure and cellular functions.
Organs Involved in Excretion
- Kidneys: Filter blood to remove nitrogenous wastes (like urea), excess salts, and water, which are excreted as urine.
- Lungs: Excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor as waste products of respiration.
- Skin: Removes waste through sweat, which contains water, salts, and small amounts of urea.

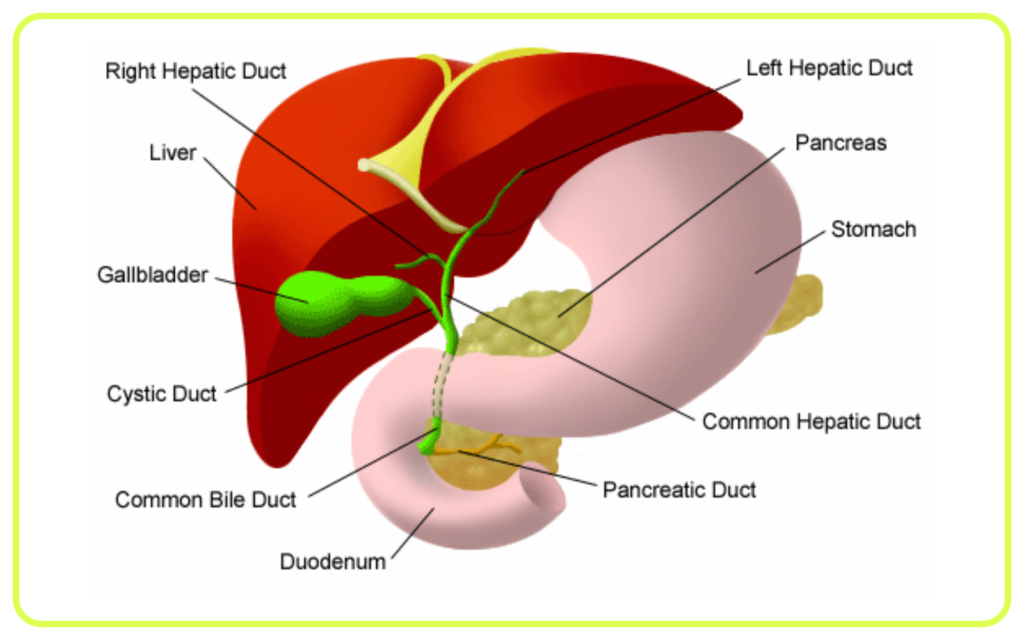
- Liver: Processes toxins and drugs, and produces bile which helps in the excretion of bilirubin, a waste product of the breakdown of red blood cells.
- Large Intestine: Expels solid waste (feces) after absorbing water and nutrients from food.
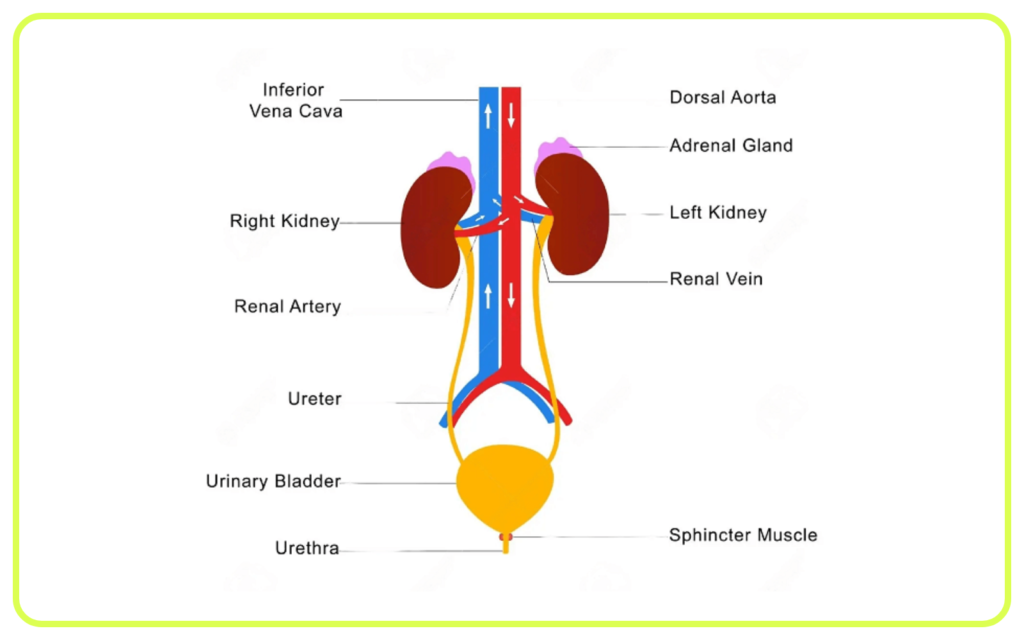
Kidneys and the Urinary System
- Nephrons: Functional units of the kidney, each nephron filters blood to form urine. Consists of a glomerulus and a tubule.
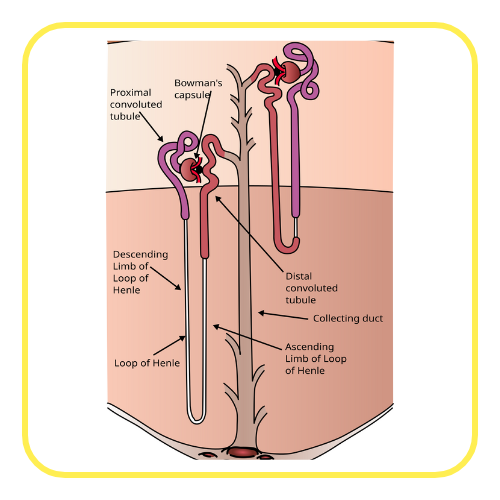
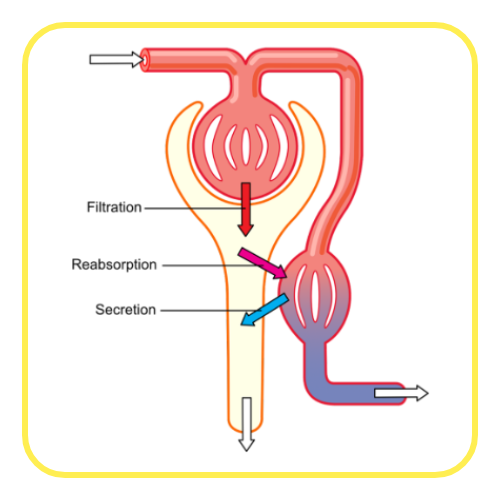
- Formation of Urine: Involves filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Blood is filtered in the glomerulus; useful substances are reabsorbed; waste products and excess substances are secreted into the tubule to form urine.
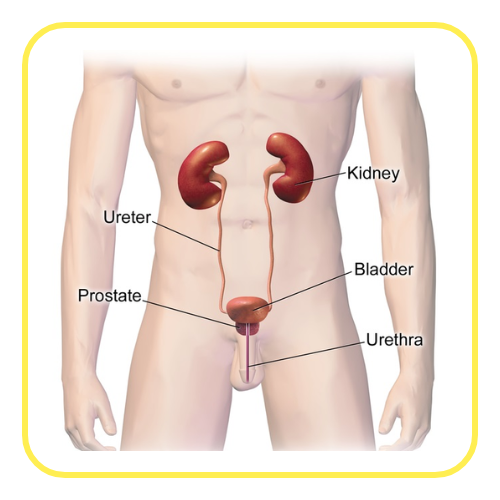
- Ureters, Bladder, and Urethra: Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder, where it is stored before being expelled through the urethra.
Excretory Products
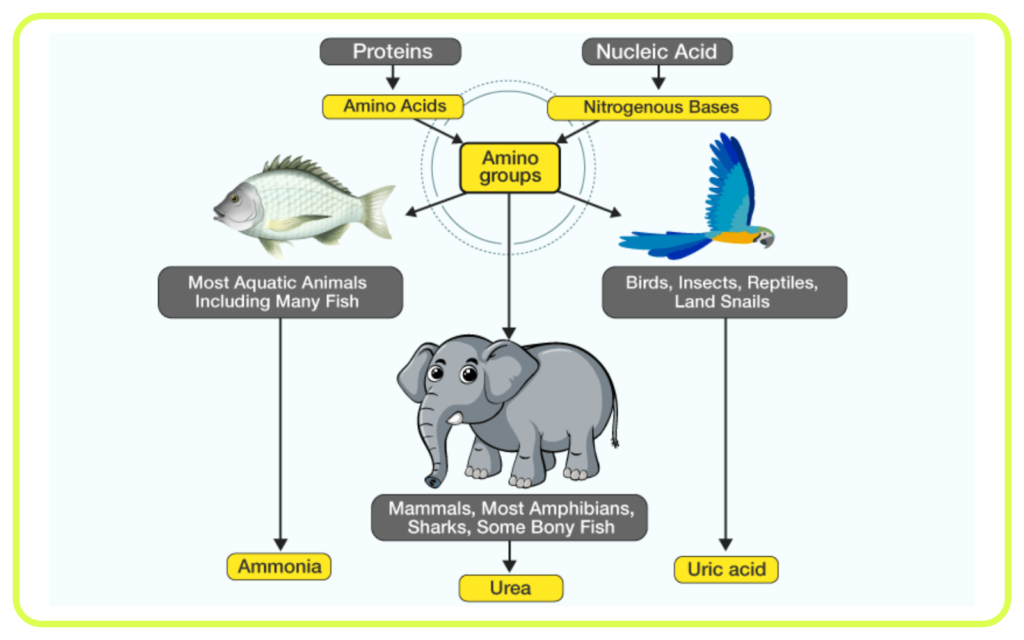
- Nitrogenous Wastes: Urea (from protein metabolism), uric acid (from purine metabolism), and ammonia.
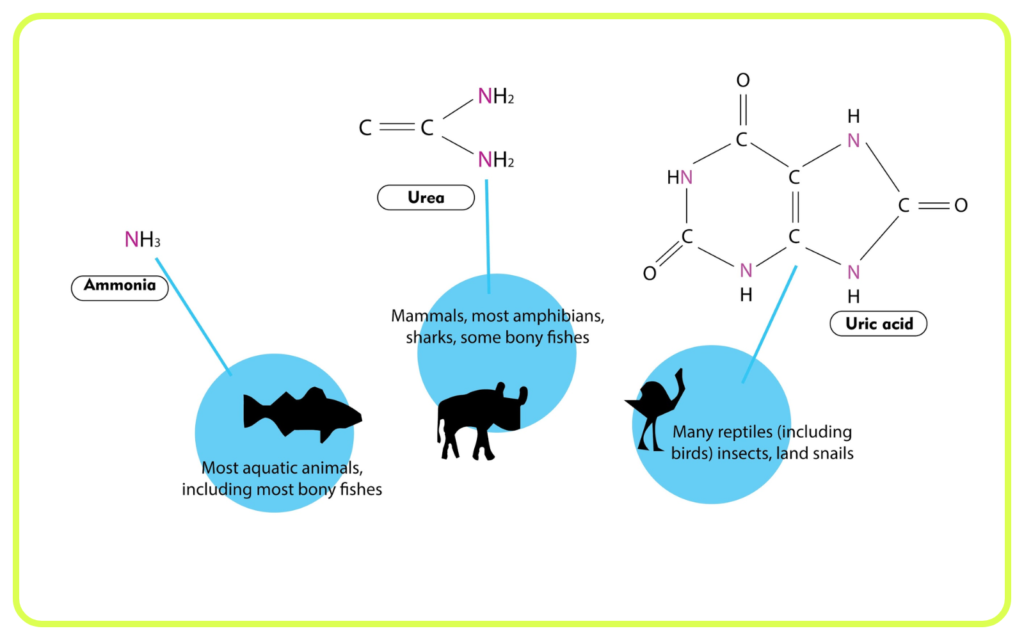
- Other Wastes: Carbon dioxide (from cellular respiration), water (from various metabolic reactions), salts, and bile pigments.
Disorders Related to Excretion
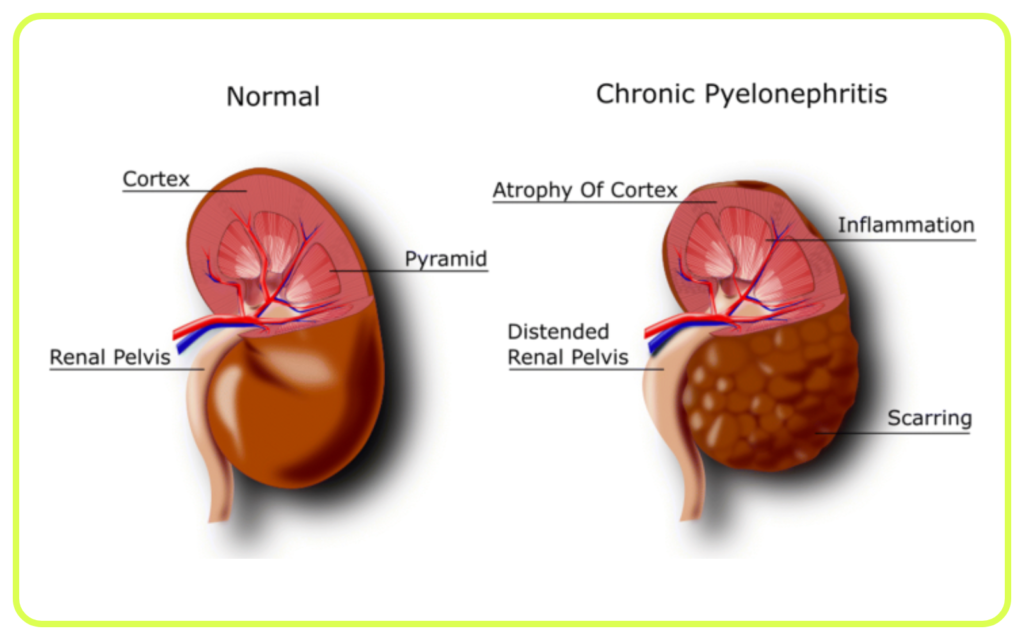
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys and can cause pain and blockage.
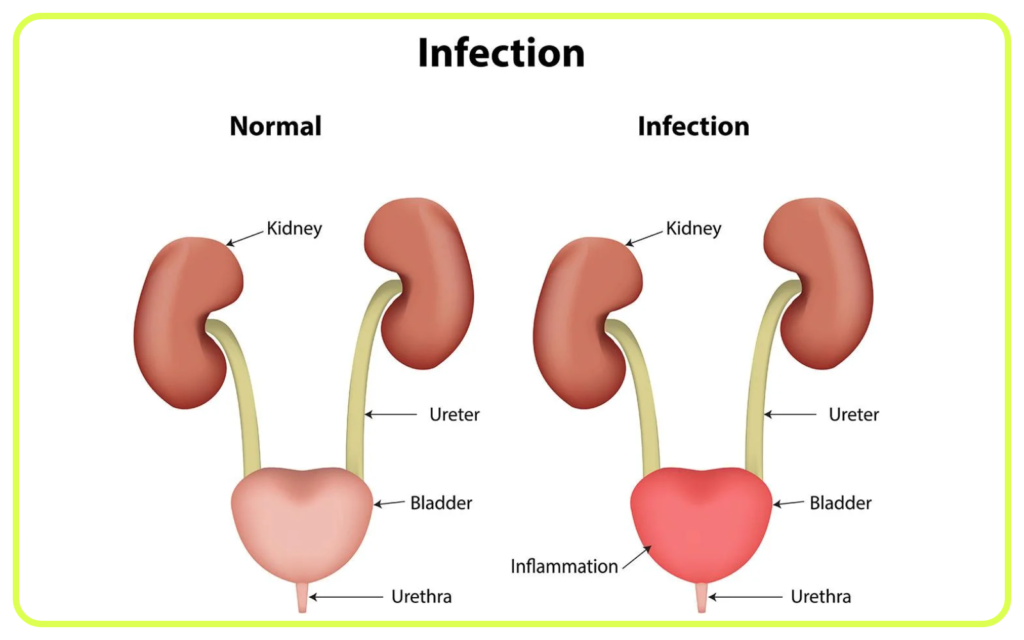
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections in any part of the urinary system, commonly the bladder and urethra.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Gradual loss of kidney function over time, which can lead to kidney failure if not managed properly.
Maintaining Healthy Excretory System
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water to help kidneys flush out toxins.

- Diet: A balanced diet with limited salt and protein intake to prevent overburdening the kidneys.

- Regular Check-ups: Monitoring blood pressure and blood sugar levels, which can affect kidney function.

Comparative Excretion
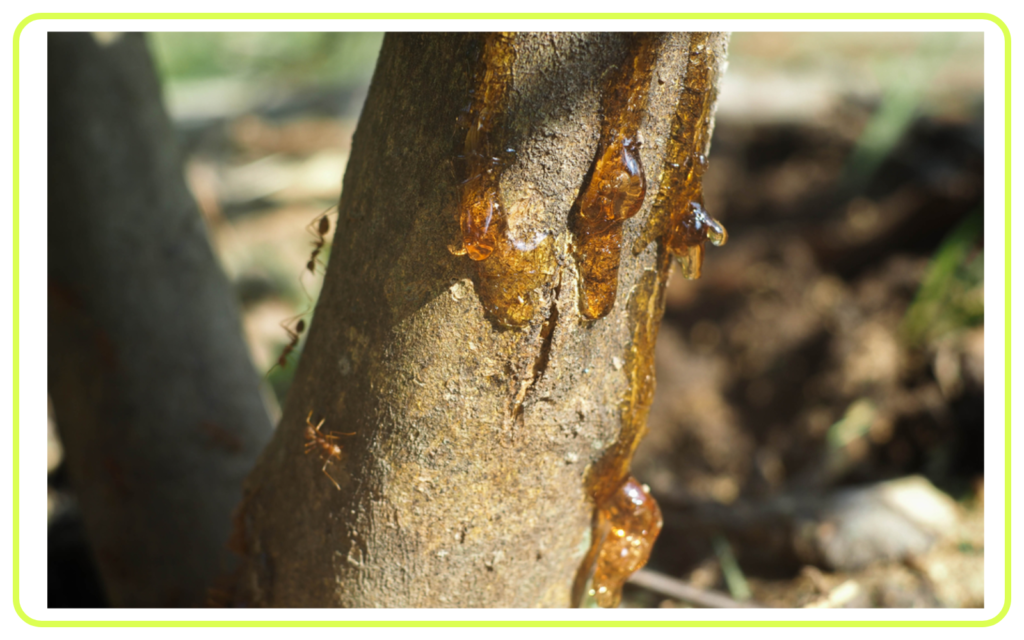
- Plants: Excrete oxygen (as a byproduct of photosynthesis) and carbon dioxide (from respiration). Some plants excrete waste products through leaves, bark, or roots.

- Other Animals: Different animals have different excretory systems; for example, insects use Malpighian tubules, and fish excrete ammonia directly into the water.
Let’s practice!

