Respiration
Key Notes:–
Definition of Respiration:
- Respiration is a biochemical process in which cells obtain energy by breaking down glucose and other molecules in the presence of oxygen. This process is essential for sustaining life.
Types of Respiration:
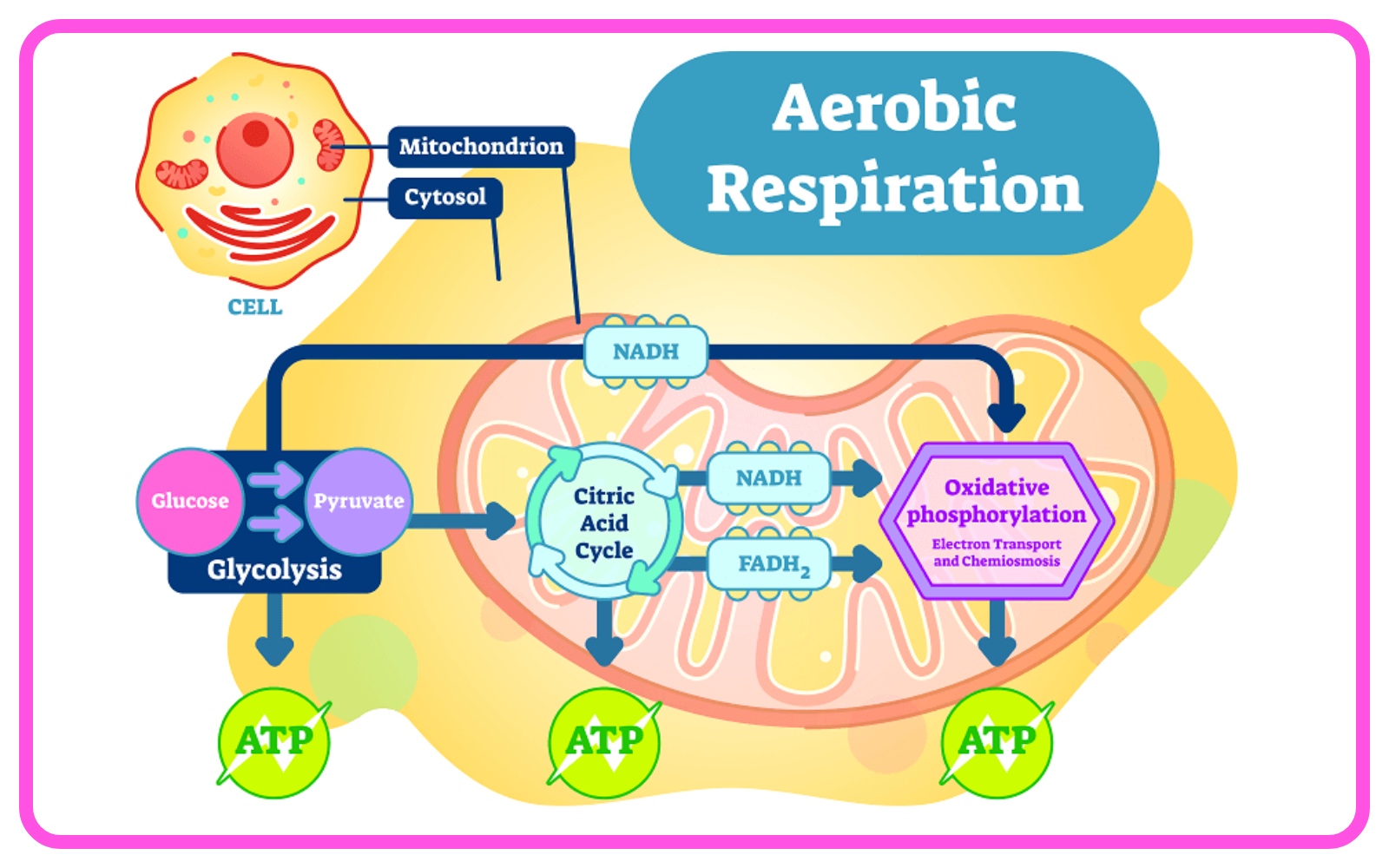
- Aerobic Respiration:
- Occurs in the presence of oxygen.
- Glucose is completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water.
- Produces a large amount of energy (approximately 36-38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule).
- Anaerobic Respiration:
- Occurs in the absence of oxygen.
- Glucose is partially broken down into lactic acid (in animals) or ethanol and carbon dioxide (in plants and yeast).
- Produces less energy (approximately 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule).
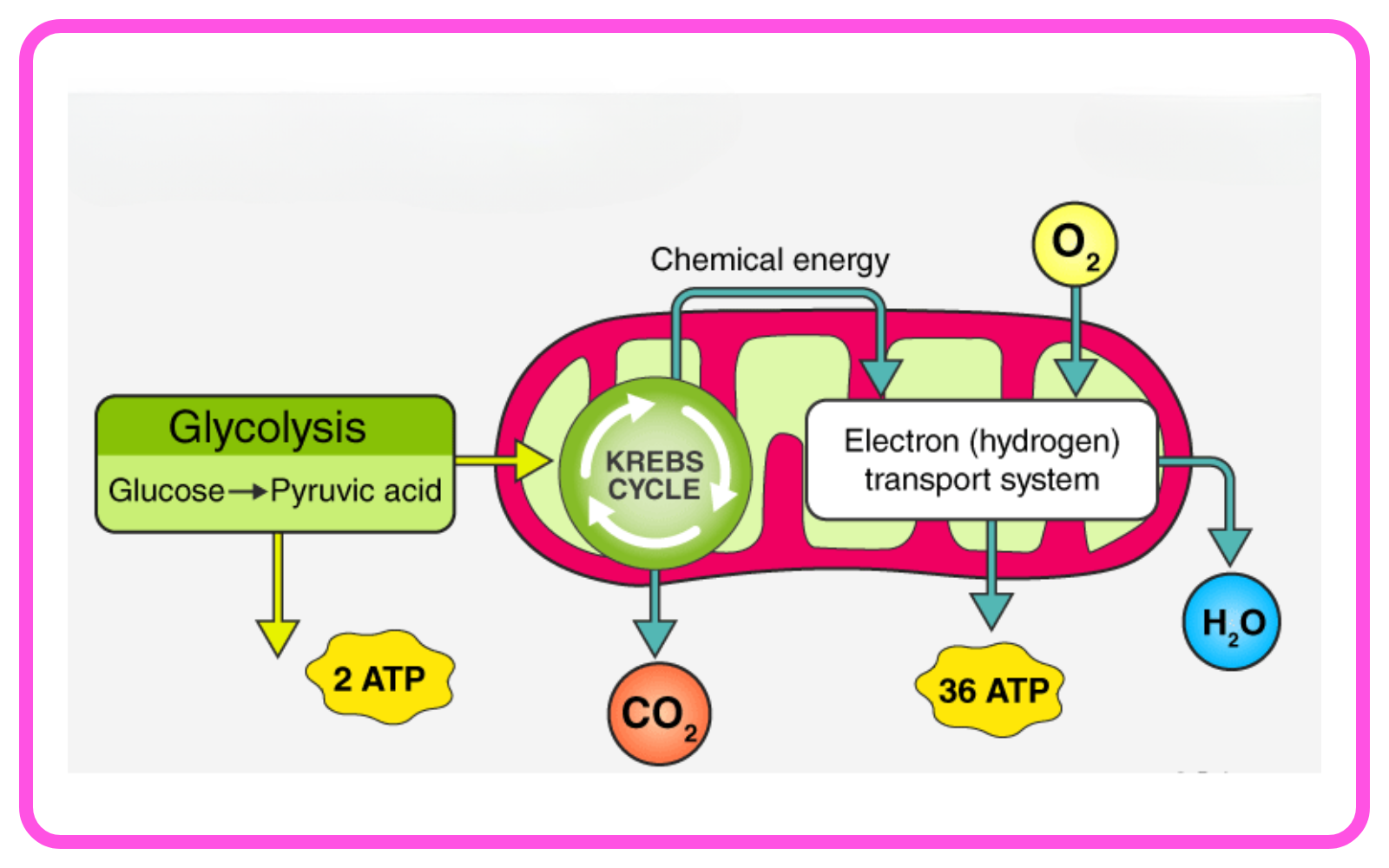
Equation of Respiration:
- Aerobic Respiration:
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
- Anaerobic Respiration (in muscles):
- C6H12O6 → 2C3H6O3 + Energy (ATP)
- Anaerobic Respiration (in yeast):
- C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + Energy (ATP)
Respiratory System:
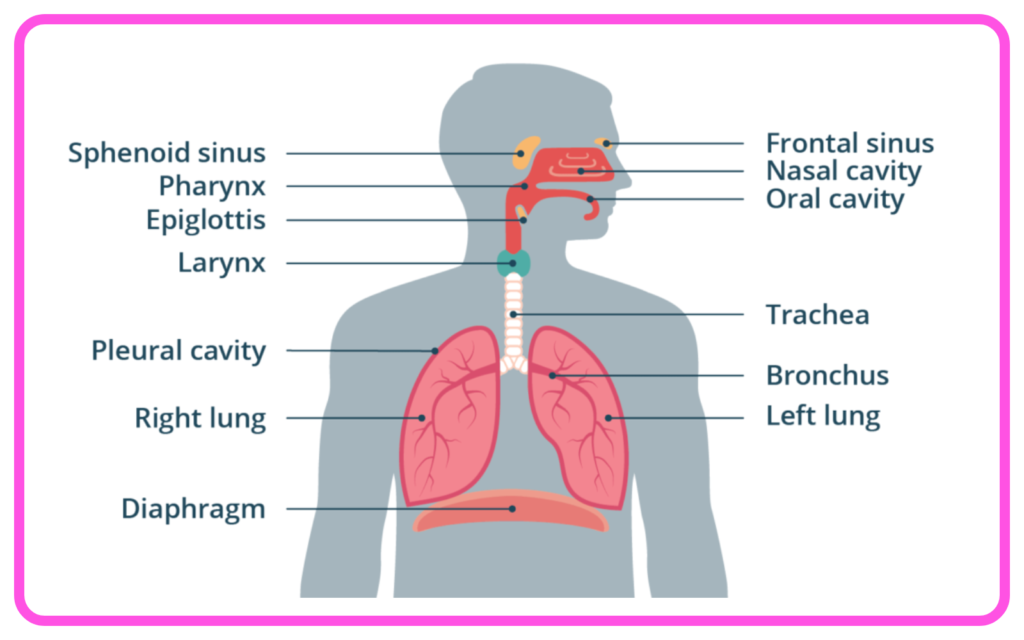
- Human Respiratory System Components:
- Nose and Nasal Cavity: Warms, moistens, and filters air.
- Pharynx: Passageway for air and food.
- Larynx (Voice Box): Contains vocal cords.
- Trachea (Windpipe): Connects larynx to bronchi; lined with cilia to trap particles.
- Bronchi and Bronchioles: Airways that lead from the trachea to the lungs.
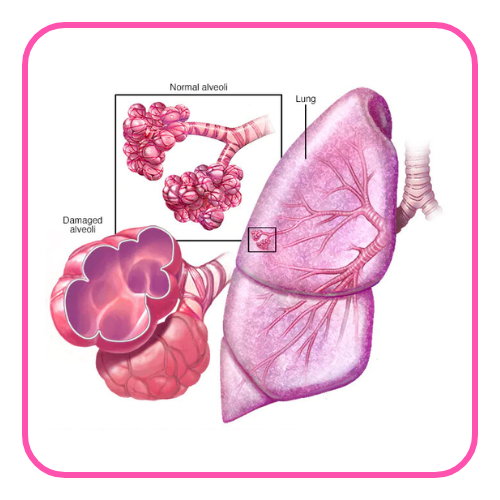
- Lungs: Main organs of respiration where gas exchange occurs.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
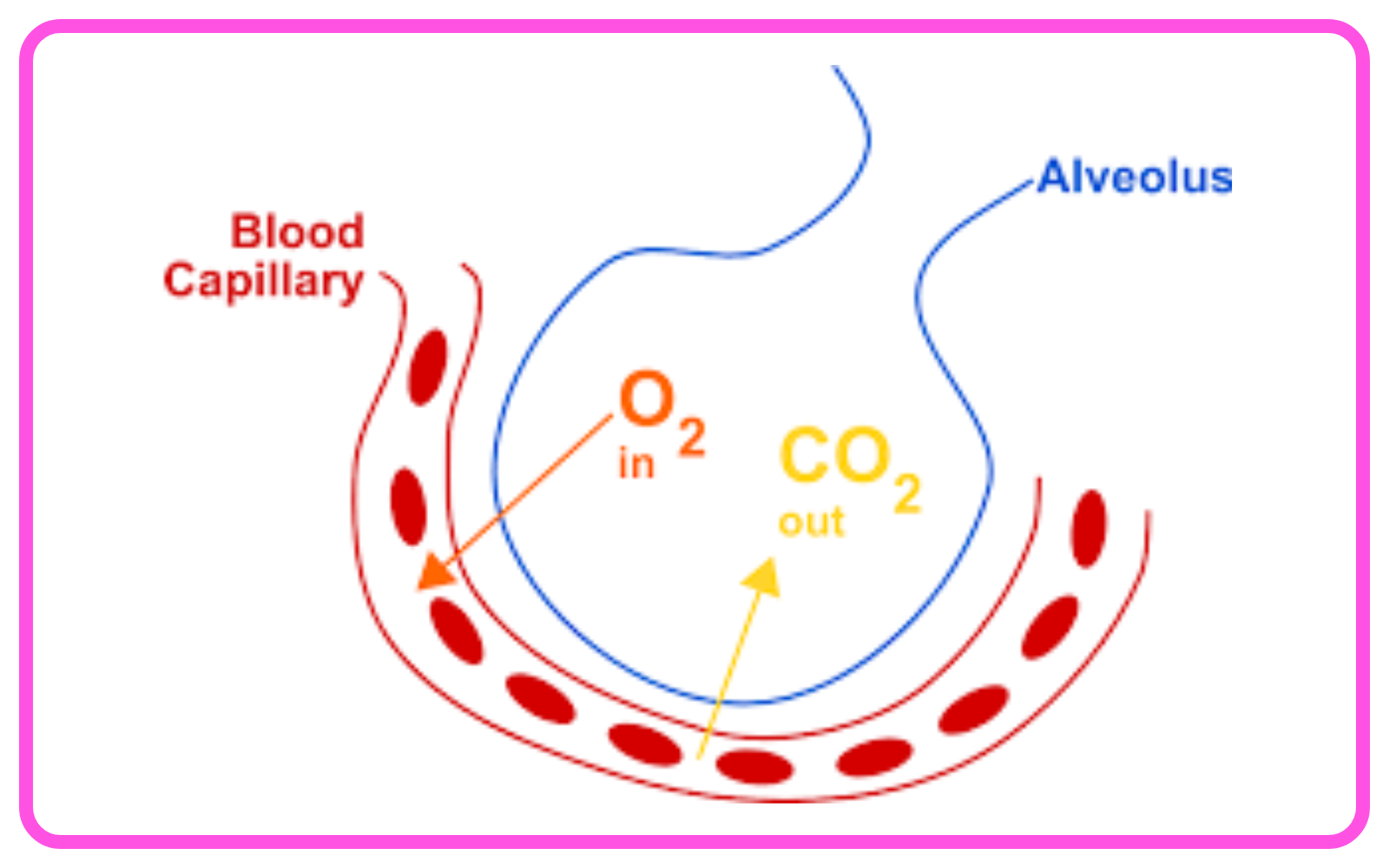
Gas Exchange:
- Occurs in the alveoli of the lungs.
- Oxygen from inhaled air diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Role of Hemoglobin:
- Hemoglobin in red blood cells binds to oxygen in the lungs and transports it to the tissues where it is released.
Energy Release and ATP:
- The energy released during respiration is stored in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), which is used by cells for various activities.
Importance of Respiration:
- Provides energy for cellular activities.
- Helps in maintaining body temperature.
- Removes carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, from the body.
Respiration vs. Photosynthesis:
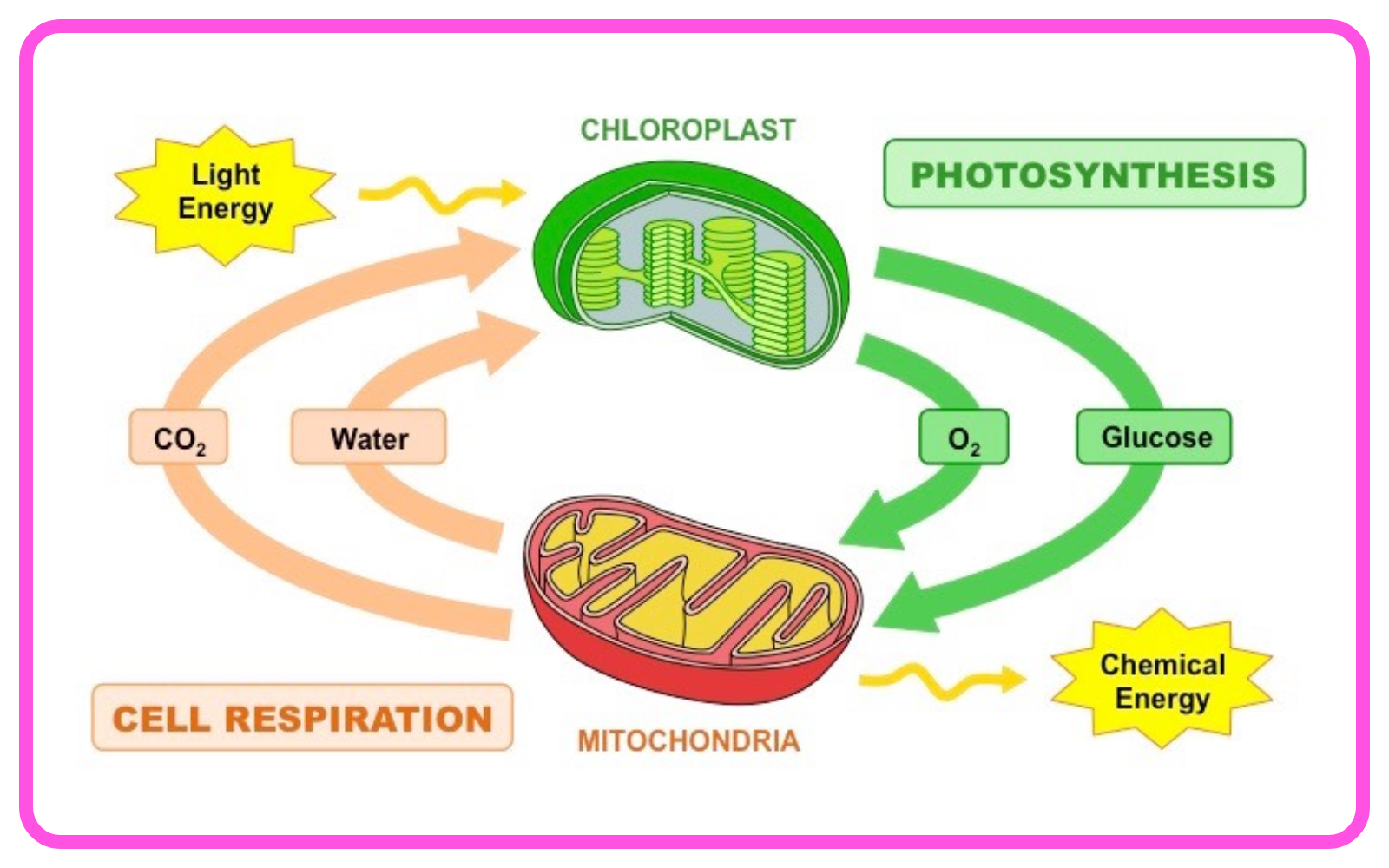
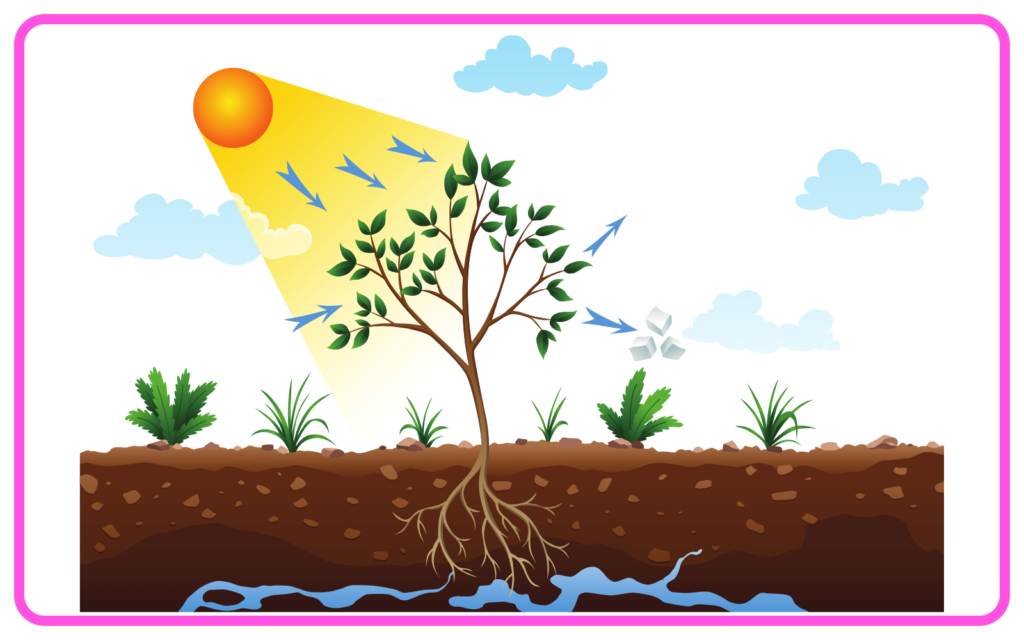
- Photosynthesis occurs in plants, using carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen.

- Respiration occurs in both plants and animals, using glucose and oxygen to produce energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
Disorders Related to Respiration:
- Asthma: A condition where the airways become narrow and inflamed, making breathing difficult.

- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to coughing and difficulty in breathing.

- Emphysema: A lung condition where the alveoli are damaged, reducing the surface area for gas exchange.
Let’s practice!

