Making Order Out Of Chaos-Early Attempts Of Classification Of Elements
Key Notes:
Need for Classification
- The increasing discovery of elements made it essential to classify them systematically to study their properties efficiently.
- Classification helps in predicting the behavior and chemical reactions of elements.
Dobereiner’s Triads (1829)
- Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner grouped elements into triads based on similar properties.

- The atomic mass of the middle element in the triad was approximately the average of the other two (e.g., Li, Na, K).
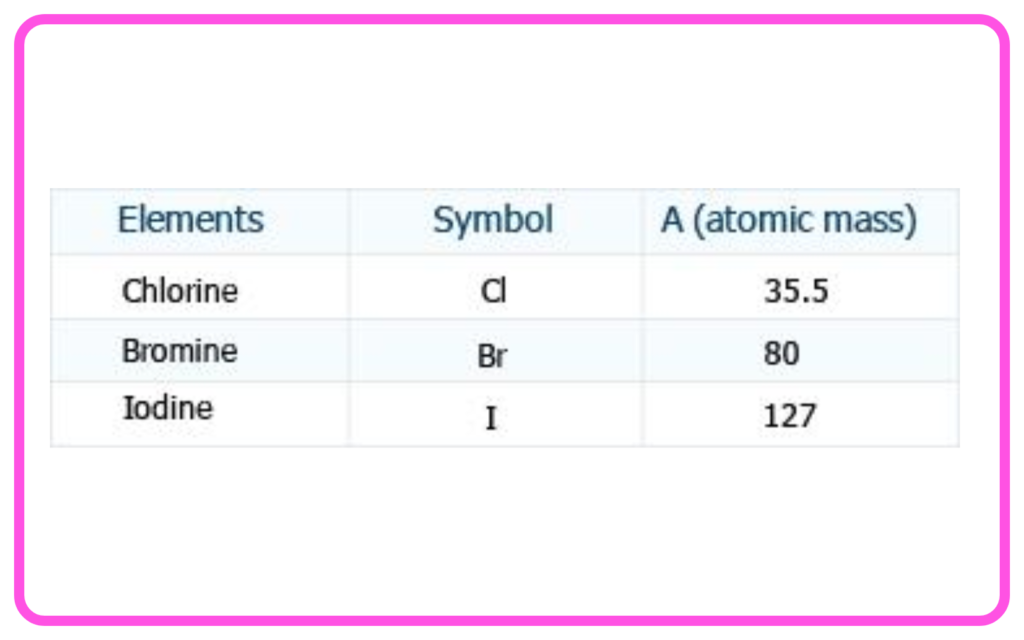
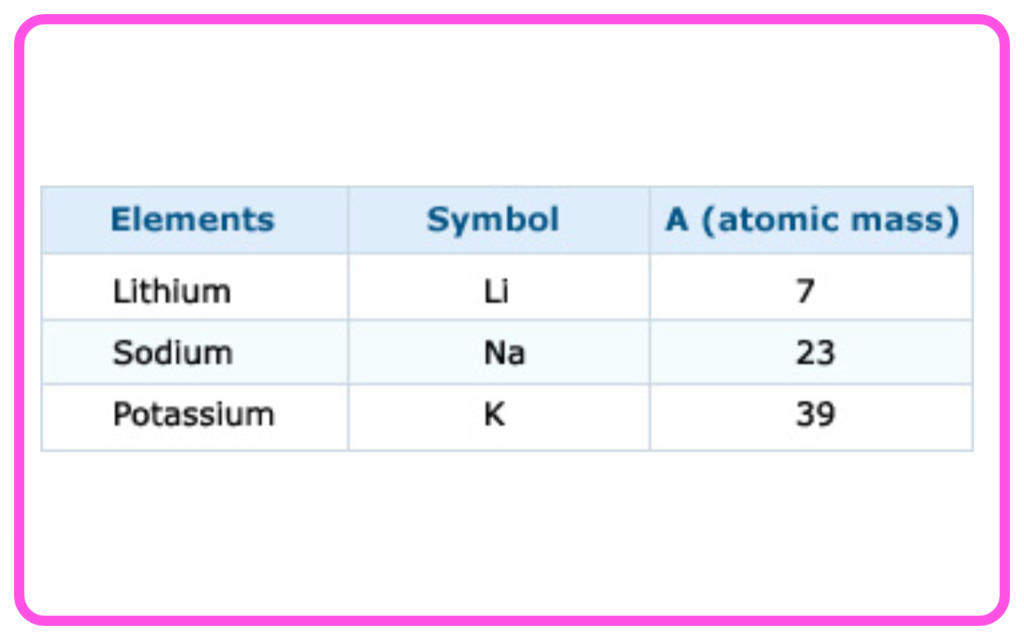
- Limitation: This method could not classify all known elements.
Newlands’ Law of Octaves (1865)
- John Newlands arranged elements in increasing order of atomic masses.

- Every eighth element had properties similar to the first, like the musical octave.
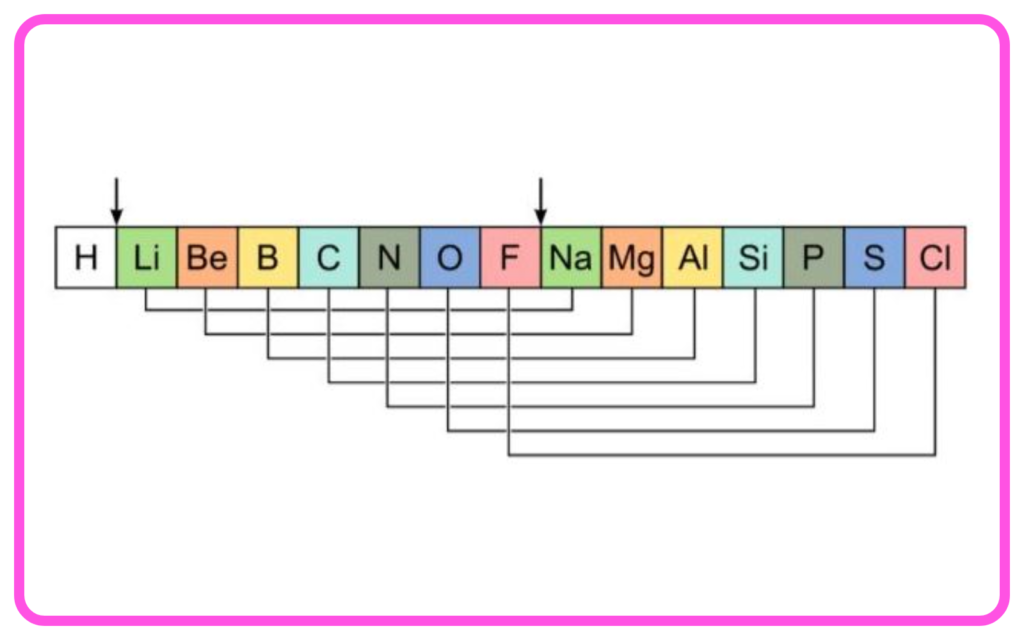
- Limitation: It worked only for elements up to calcium and did not accommodate new discoveries.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table (1869)
- Dmitri Mendeleev organized elements based on increasing atomic mass and chemical properties.

- He left gaps for undiscovered elements and predicted their properties (e.g., gallium and germanium).

- Limitation: Certain elements (e.g., iodine and tellurium) did not fit in order of increasing atomic mass but were placed based on properties.
Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- First systematic arrangement of elements.
- Predicted the existence of undiscovered elements.
- Grouped elements with similar properties together.
Limitations of Early Classification Systems
- Inconsistencies in placing elements strictly by atomic mass.
- Lack of explanation for isotopes (discovered later).
- Failure to account for the periodicity of properties based on atomic structure.
Transition to Modern Periodic Table
- Discovery of subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) and isotopes led to improvements.
- Henry Moseley proposed arranging elements by atomic number (not mass), forming the basis of the modern periodic table.
Let’s practice!

