Soaps And Detergents
Key Notes:
Definition
- Soap: A cleansing agent made from natural ingredients (fats or oils) combined with a strong base (like sodium hydroxide).

- Detergent: A synthetic cleansing agent that works similarly to soap but is made from petroleum products and other chemicals.

Chemical Composition
- Soap: Made by the saponification process, where fats/oils react with a base to produce soap and glycerol.
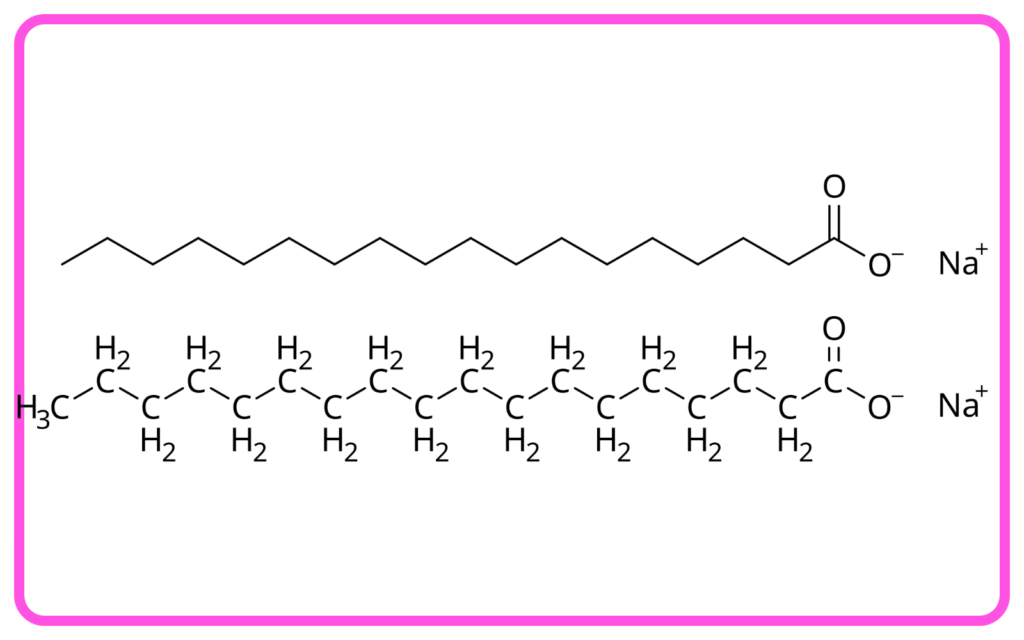
- Detergent: Composed of synthetic surfactants, which are chemicals that help dissolve dirt and grease in water.
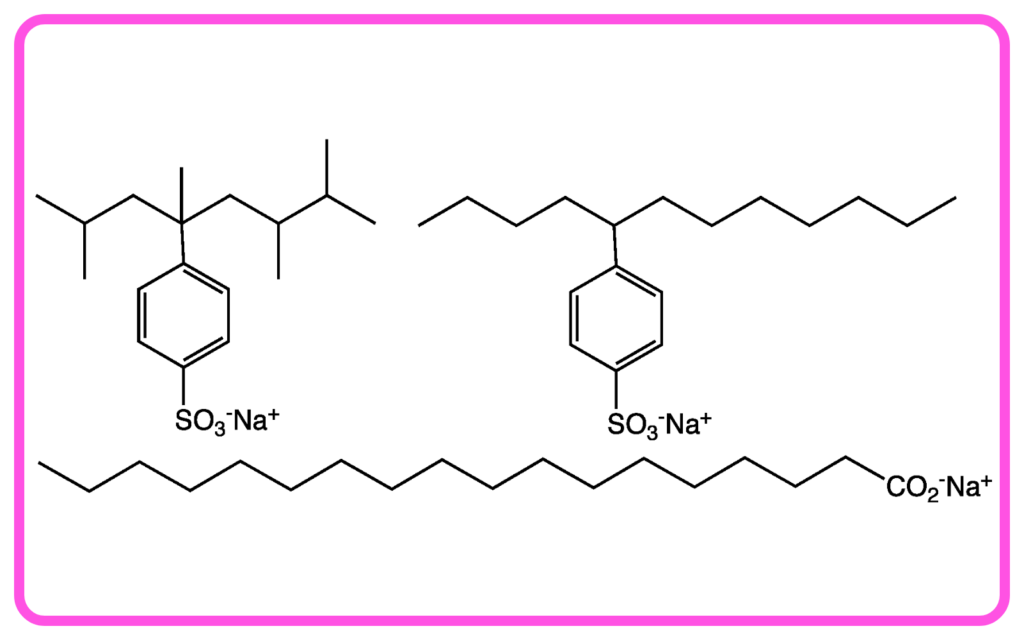
Structure
- Both soaps and detergents have a hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail that binds to oils and a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head that binds to water, allowing for the removal of dirt.
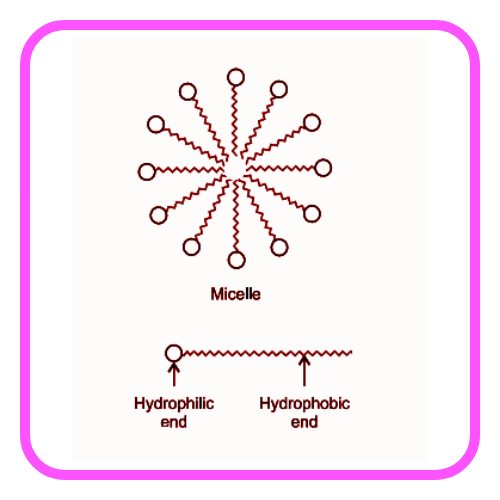
Properties of Soaps
- Biodegradable: Made from natural materials and generally less harmful to the environment.

- Not effective in hard water: Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions that form insoluble salts with soap, reducing its cleaning effectiveness.
Properties of Detergents
- Non-biodegradable (in some cases): Often made from synthetic chemicals that don’t break down easily in the environment.

- Effective in hard water: Detergents don’t form insoluble salts in hard water, making them more effective cleaners in various water conditions.
Types of Soaps
- Toilet Soap: Used for personal cleaning, with added fragrance and skin-conditioning agents.

- Laundry Soap: Used for washing clothes, with added builders to enhance cleaning.
Types of Detergents
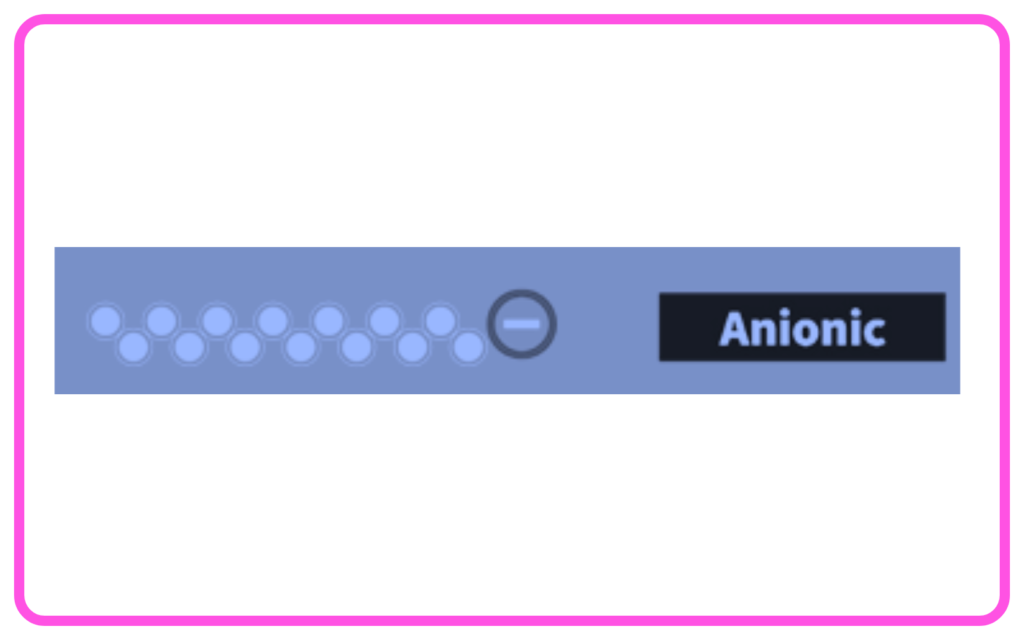
- Anionic Detergents: Have negatively charged ions; commonly used in laundry detergents.
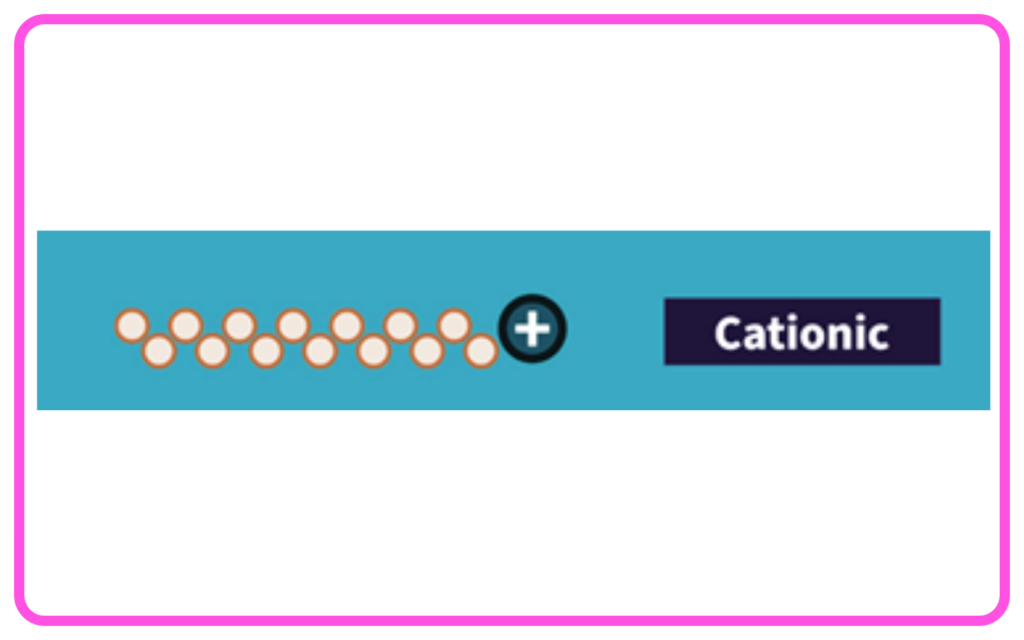
- Cationic Detergents: Have positively charged ions; often used in fabric softeners.
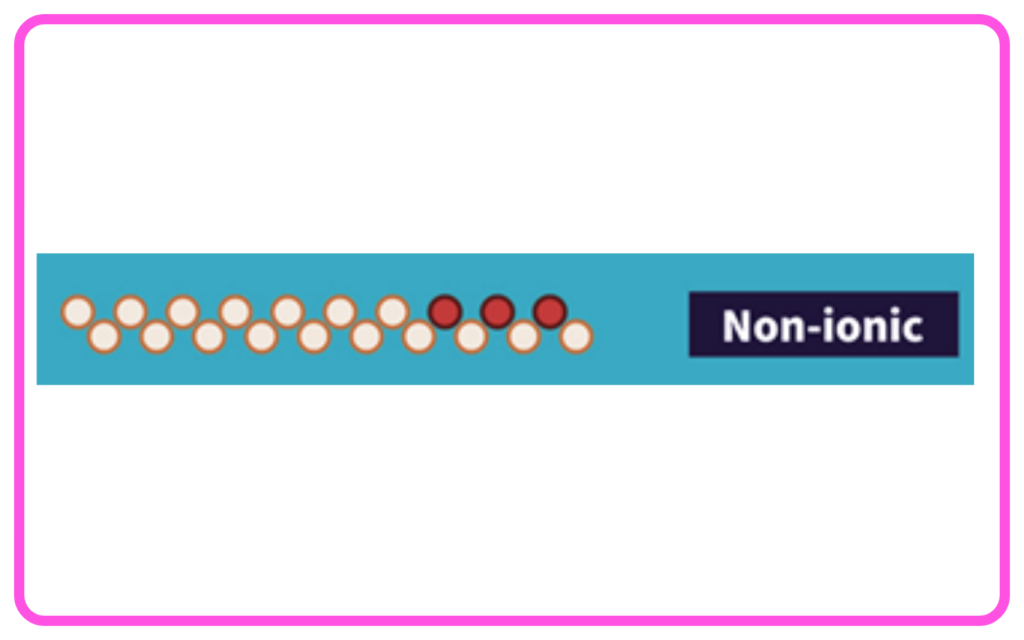
- Nonionic Detergents: Do not have any charge; used in dishwashing liquids.
Environmental Impact
- Soap: Generally eco-friendly, but can still cause water pollution if overused.
- Detergents: Some detergents contain phosphates that can lead to water pollution and eutrophication in water bodies, affecting aquatic life.
Uses of Soaps and Detergents
- Soaps are commonly used for personal hygiene, while detergents are more versatile and used in household and industrial cleaning, laundry, and dishwashing.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Soaps: Environmentally friendly but less effective in hard water.

- Detergents: Effective in all water types, but may be harmful to the environment if non-biodegradable.
Innovation in Detergents
- Modern detergents often include enzymes to break down protein-based stains and are designed to work at lower temperatures, saving energy.

Practical Applications in Daily Life
- Understanding the difference helps in choosing the right product for cleaning, knowing when to use soap vs. detergent depending on water type and cleaning need.

Let’s practice!

