Some Important Carbon Compounds Ethanol And Ethanoic Acid
Key Notes:
Introduction to Carbon Compounds
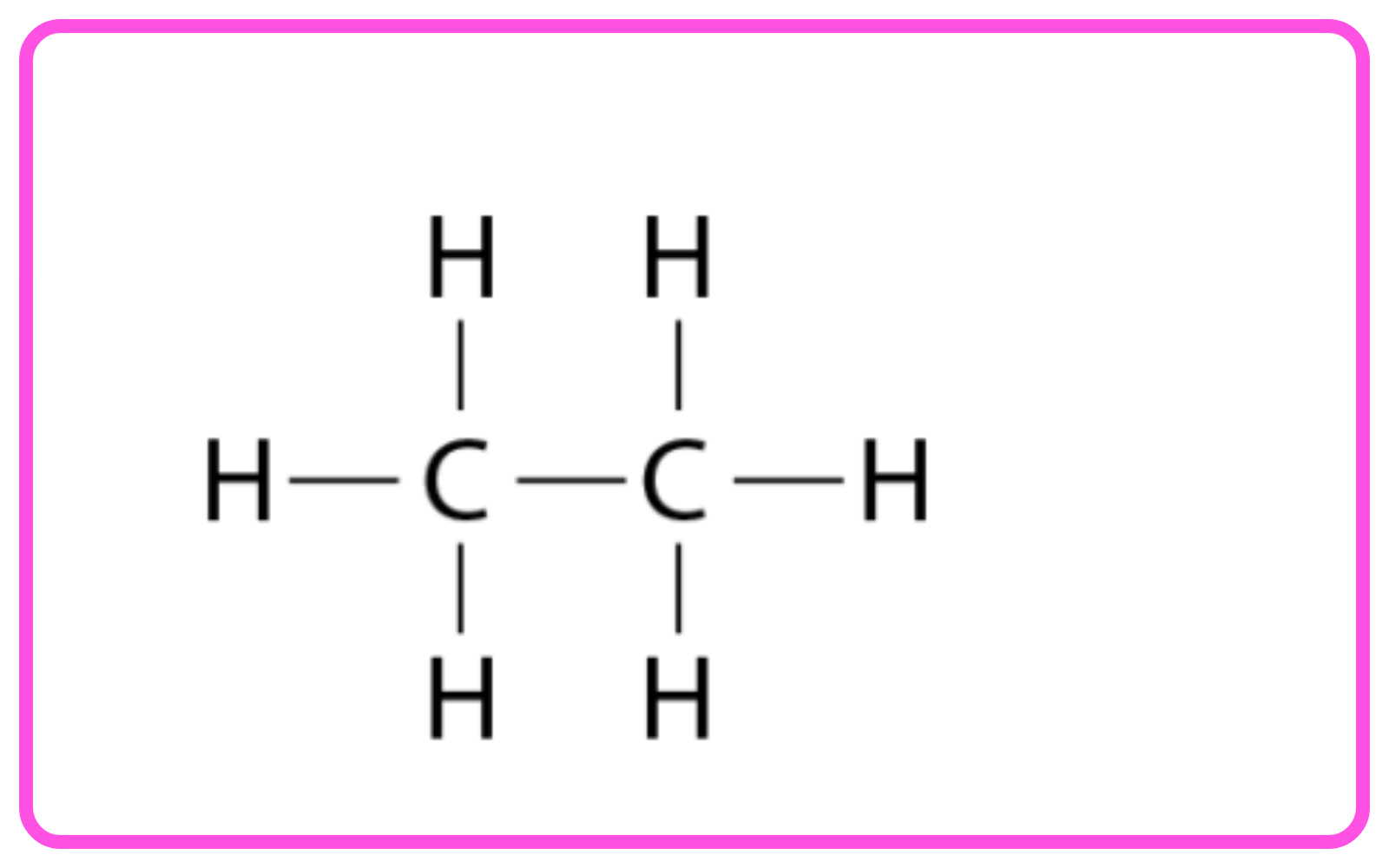
- Carbon compounds are molecules that contain carbon atoms bonded to other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
- Organic compounds are primarily carbon-based and include alcohols, acids, hydrocarbons, etc.
Ethanol (Ethyl Alcohol) – C2H5OH
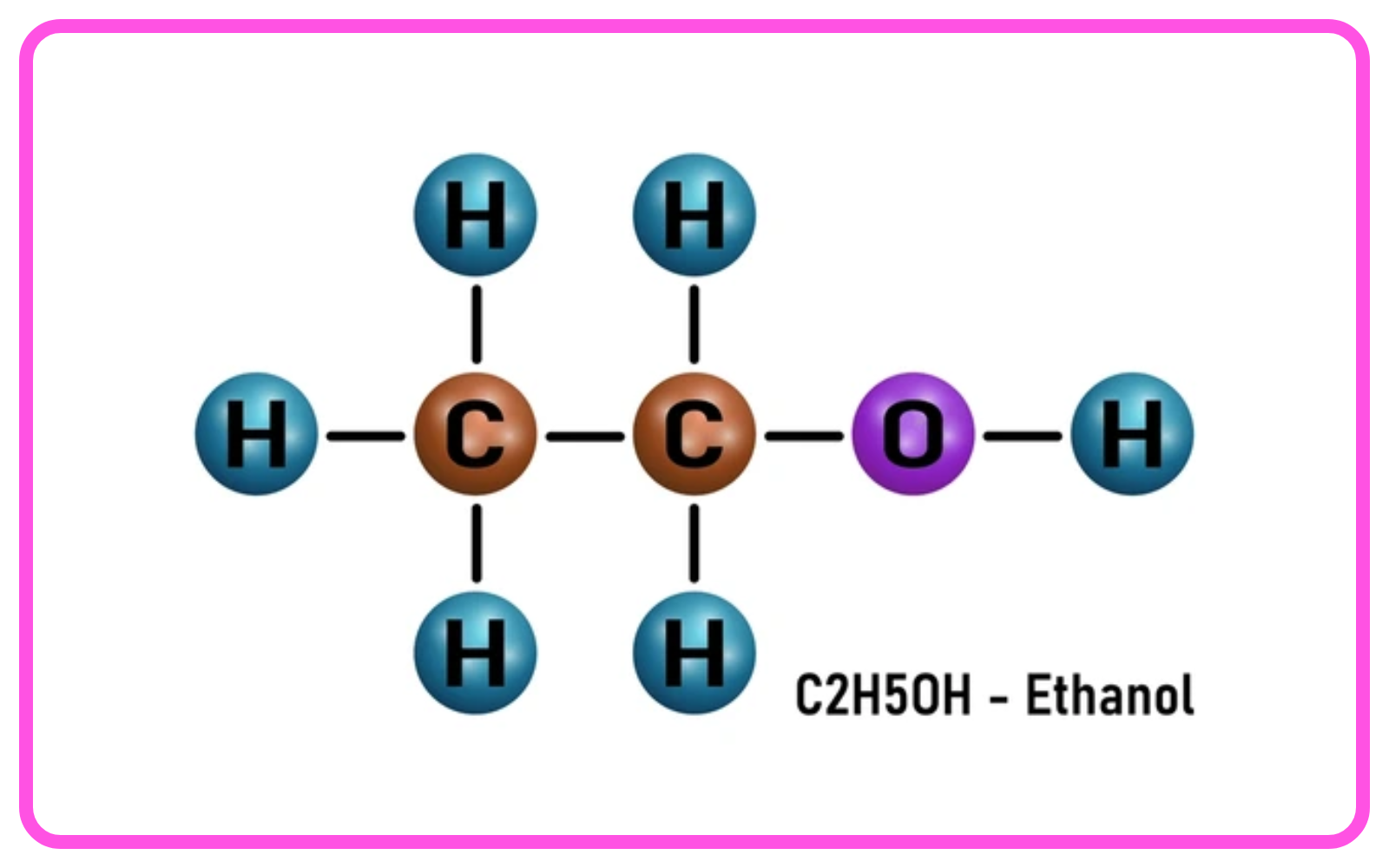
- Structure: Ethanol has the molecular formula C2H5OH, with an -OH (hydroxyl) functional group attached to an ethyl group.

- Physical Properties:
- A colorless, volatile liquid with a characteristic odor.
- Soluble in water and has a boiling point of about 78.5∘C.
- Chemical Properties:
- Combustion: Ethanol burns in air to produce carbon dioxide and water.
C2H5OH+3O2→2CO2+3H2O
- Reaction with Sodium: Produces sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas.
2C2H5OH+2Na→2C2H5ONa+H2
- Oxidation: Oxidizes to ethanoic acid (acetic acid) using oxidizing agents like potassium dichromate.
- Uses:
- Used as a solvent, in alcoholic beverages, as a fuel (bioethanol), and in medicines.
Ethanoic Acid (Acetic Acid) – CH3COOH
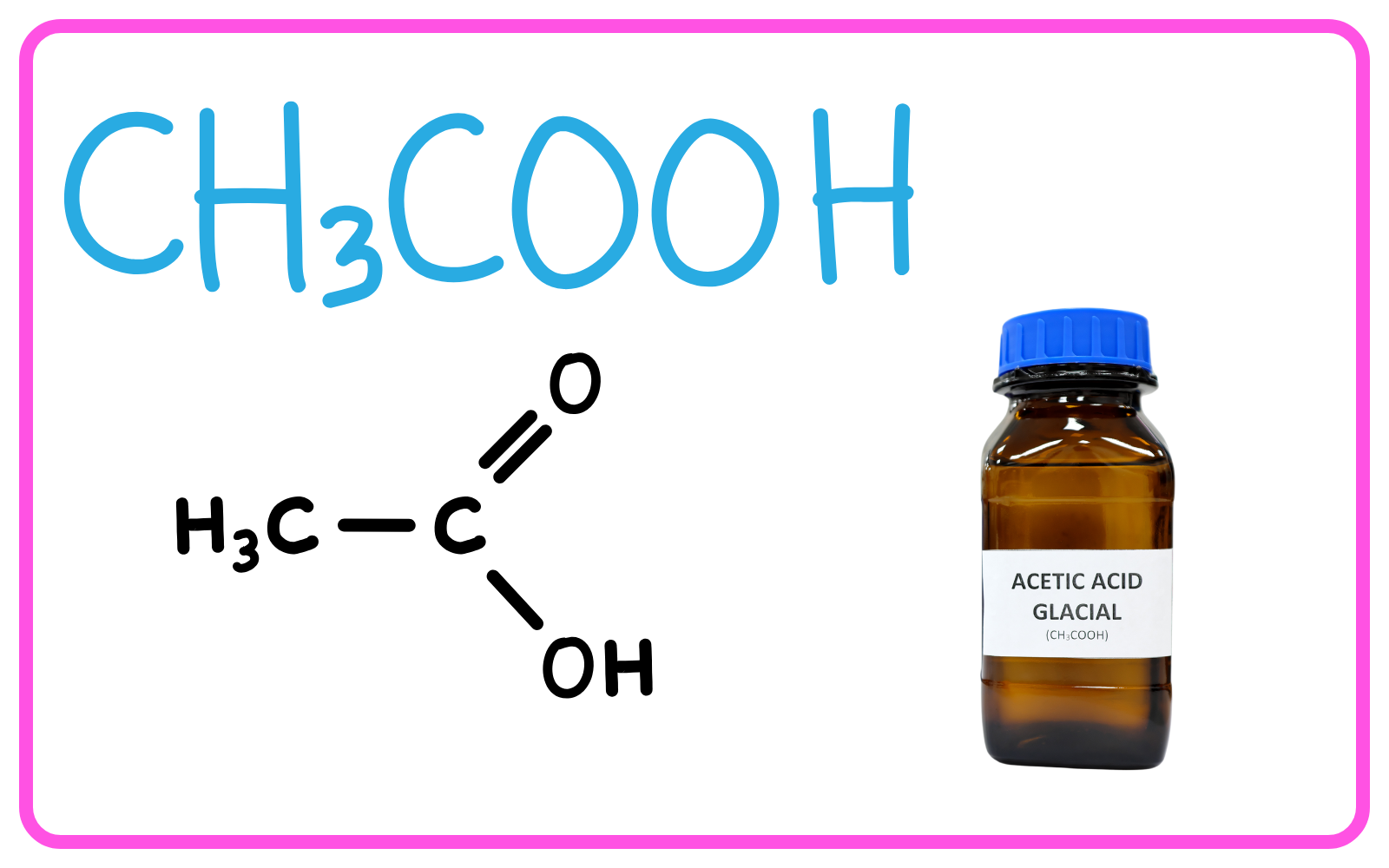
- Structure: Ethanoic acid has the molecular formula CH3COOH, with a carboxyl (-COOH) functional group.
- Physical Properties:
- A colorless liquid with a strong, pungent smell (like vinegar).
- Miscible with water and has a boiling point of about 118∘C.

- Chemical Properties:
- Acidic Nature: Ethanoic acid is a weak acid and partially dissociates in water to release hydrogen ions.
CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO− + H+
- Reaction with Bases: Forms salts and water (neutralization reaction).
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
- Esterification: Reacts with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst to form esters.
CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
- Uses:
- Used in the production of vinegar, synthetic fibers, and as a preservative in food.
Distinguishing Between Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid
- Litmus Test: Ethanoic acid turns blue litmus paper red, while ethanol does not affect litmus paper.

- Sodium Bicarbonate Test: Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to release carbon dioxide gas, while ethanol does not.
Common Uses and Applications
- Ethanol: Biofuel, antiseptic, solvent in perfumes and cosmetics.

- Ethanoic Acid: Used in vinegar (5-8% solution), food preservation, and in the manufacture of synthetic materials.

Health and Safety Considerations
- Ethanol is flammable and should be handled with care.
- Ethanoic acid is corrosive; concentrated solutions can cause skin burns and damage to eyes.

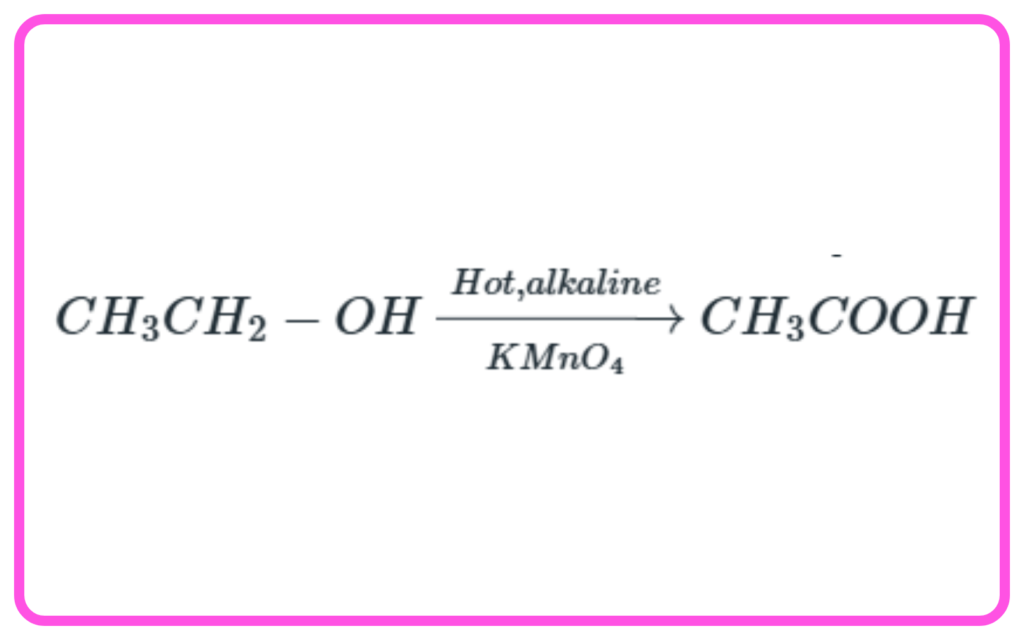
Laboratory Preparation of Ethanoic Acid
- Ethanol can be oxidized to ethanoic acid using strong oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate (KMnO4).
Let’s practice!

