Corrosion
Key Notes:
Definition of Corrosion:
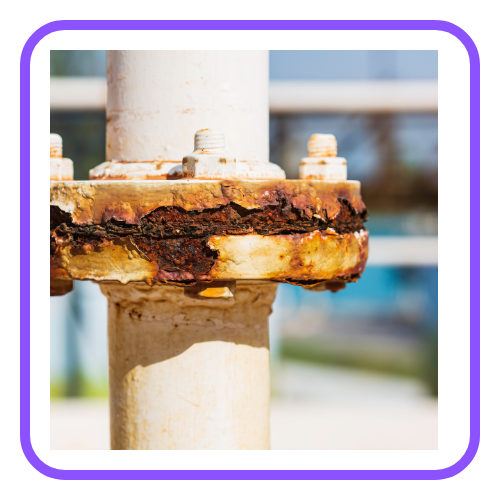

- Corrosion is the gradual destruction or deterioration of metals when they react with oxygen, water, acids, or other environmental elements.
- The most common form of corrosion is rusting, which occurs when iron reacts with oxygen and moisture to form iron oxide.
Process of Corrosion:
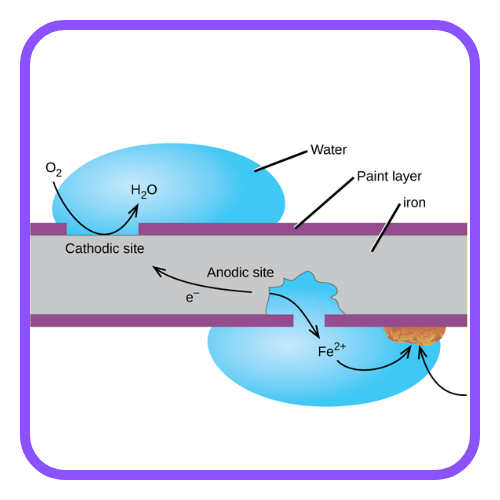
- It is an electrochemical process where metal loses electrons and becomes oxidized.
- The metal reacts with elements in the environment, such as oxygen, water, or acids, leading to the formation of compounds like oxides, hydroxides, or sulfides.
Rusting of Iron:

- Rusting is a specific form of corrosion that occurs with iron and steel.
- The chemical reaction is:
4Fe+3O2+6H2O→4Fe(OH)3
- Over time, hydrated iron (III) oxide, commonly known as rust, forms and weakens the metal.
Factors Affecting Corrosion:
- Presence of water and oxygen: Corrosion occurs more quickly in moist environments.

- Acidic or salty environments: Acid rain or saltwater can accelerate the process of corrosion.

- Temperature: Higher temperatures can speed up corrosion.

Prevention of Corrosion:
- Painting or Coating: Applying paint or a protective coating prevents oxygen and moisture from coming into contact with the metal surface.
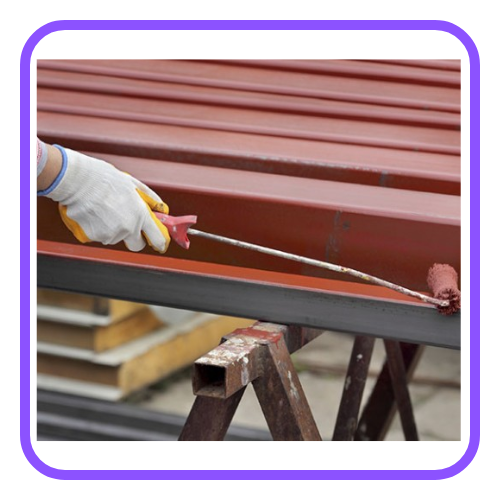

- Galvanization: Coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc to protect it from rusting.
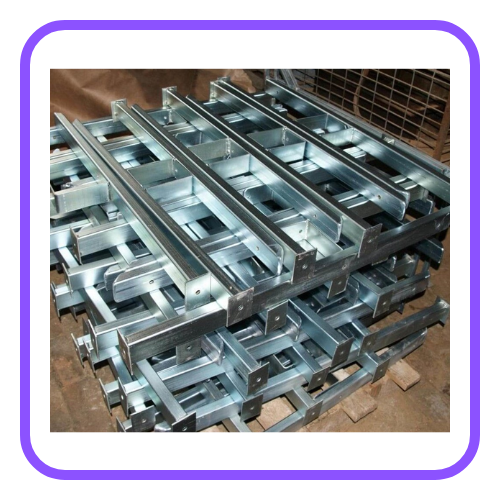

- Alloying: Mixing metals, like stainless steel (iron mixed with chromium), helps resist corrosion.

- Cathodic Protection: Using a sacrificial metal, such as zinc or magnesium, to prevent corrosion of a more valuable metal.

Types of Corrosion:
- Uniform Corrosion: Occurs evenly across the surface.

- Pitting Corrosion: Localized corrosion that leads to small holes or pits in the metal.

- Galvanic Corrosion: Occurs when two different metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte.

- Stress Corrosion Cracking: Metal cracks due to the combined effects of stress and corrosion.

Effects of Corrosion:
- Economic loss: Corrosion leads to damage of structures, vehicles, and machinery, causing significant economic losses.

- Structural failure: If left unchecked, corrosion can weaken materials and cause structural failure (e.g., bridges, pipelines).
- Safety hazards: Corrosion can cause gas or oil leaks in pipelines, leading to hazardous conditions.

Let’s practice!

