How Do Metals And Non-Metals React?
Key Notes:
Nature of Metals and Non-Metals
- Metals: Generally, metals are shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. They tend to lose electrons during reactions, forming positive ions (cations).

- Non-Metals: Non-metals are usually dull, brittle (in solid form), and poor conductors of heat and electricity. They tend to gain or share electrons during reactions, forming negative ions (anions) or covalent bonds.

Reactivity
- Metal Reactions: Metals react with non-metals in a variety of ways, often depending on their position in the reactivity series. More reactive metals (like sodium and potassium) react vigorously with non-metals.

- Non-Metal Reactions: Non-metals can react with metals to form ionic compounds or with other non-metals to form covalent compounds.
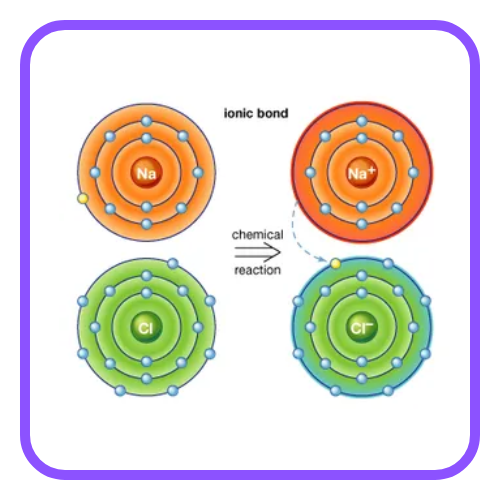
Ionic Bonding
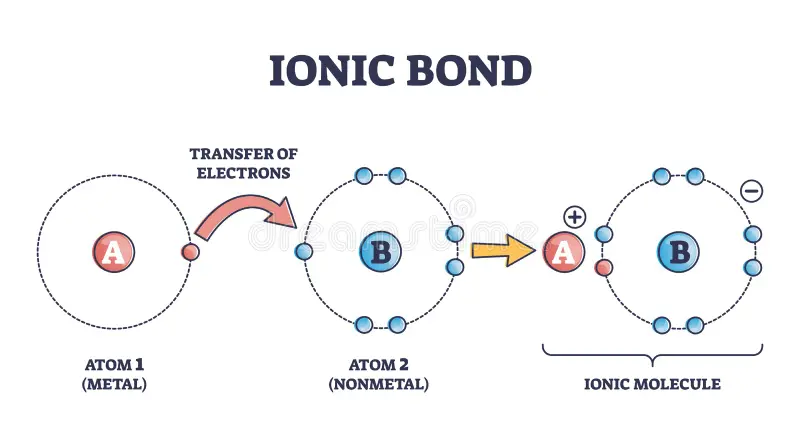
- When metals react with non-metals, they typically form ionic bonds. This occurs when a metal atom transfers one or more of its electrons to a non-metal atom.
- Example: Sodium (Na) reacts with chlorine (Cl) to form sodium chloride (NaCl), where sodium loses an electron and chlorine gains it.
Covalent Bonding
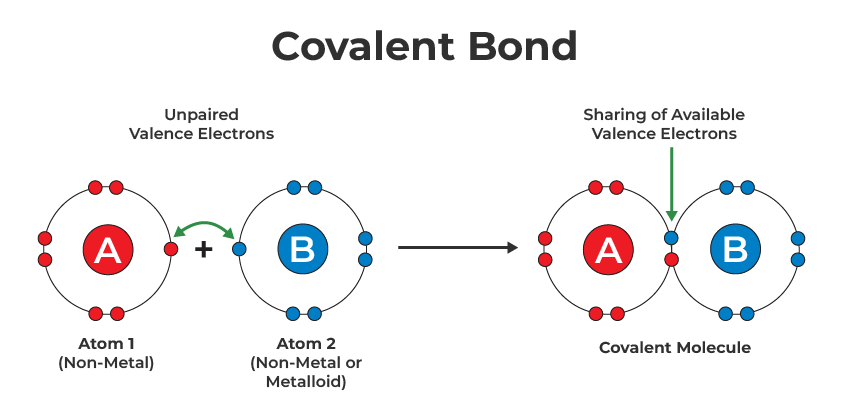
- Non-metals can also react with each other to form covalent bonds by sharing electrons.
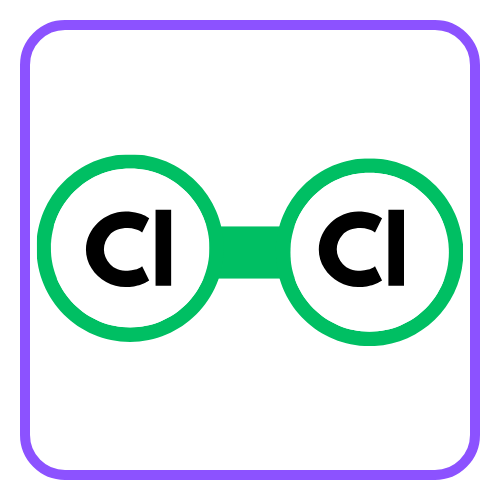
- Example: Two chlorine atoms (Cl) can bond together to form Cl₂ by sharing one pair of electrons.
Reactions with Oxygen
- Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides, often releasing heat and light (combustion).
- Non-metals also react with oxygen to form non-metal oxides. These reactions can be less vigorous than those of metals.

Acid-Base Reactions
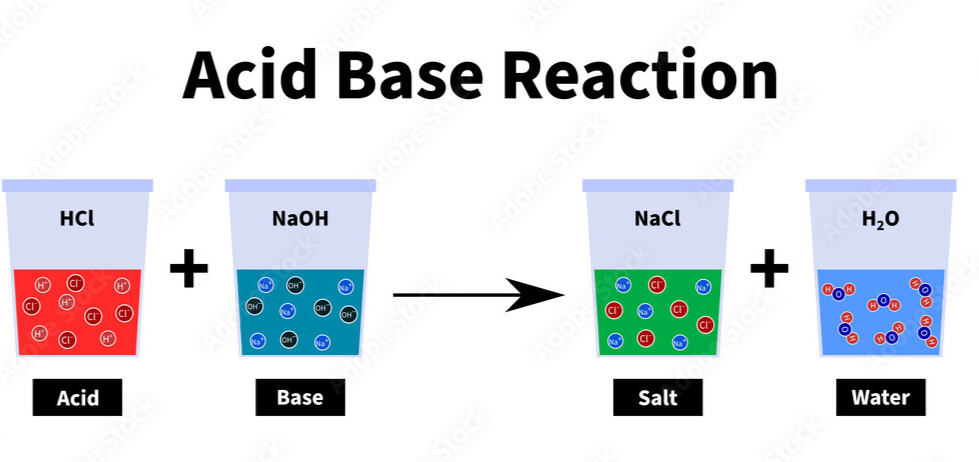
- Many metal oxides are basic and can react with acids to form salts and water.
- Non-metal oxides are typically acidic and can react with bases to also form salts and water.
Displacement Reactions
- A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its compound.
- Example: Zinc displacing copper from copper sulfate solution.

Observations During Reactions
- Many reactions between metals and non-metals are exothermic, releasing heat.
- Visible changes (such as color change, temperature change, or gas evolution) often indicate a reaction.
Applications
- Understanding how metals and non-metals react is crucial in various fields, including materials science, chemistry, and engineering.
- These reactions form the basis for the creation of many important compounds and materials used in everyday life.
Safety Precautions
- When conducting experiments involving metal and non-metal reactions, it’s important to follow safety guidelines, such as wearing goggles and gloves and conducting experiments in a well-ventilated area.

Let’s practice!

