Chemical Properties Of Metals
Key Notes:
Reaction with Oxygen
- Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides.
- General reaction: Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide

- Metal oxides are usually basic in nature (e.g., sodium oxide, magnesium oxide), but some metal oxides like zinc oxide and aluminum oxide are amphoteric, meaning they can react with both acids and bases.
Example:
- Magnesium: 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
- Iron: 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 (forms rust)

Reaction with Water
- Some metals react with water to form a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- Metals like sodium and potassium react vigorously with cold water.


- Less reactive metals like iron react slowly with water and only at higher temperatures.
Example:
- Sodium: 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
- Magnesium: Mg + 2H2O → Mg(OH)2 + H2 (with hot water)

Reaction with Acids
- Most metals react with dilute acids to form a salt and release hydrogen gas.
- Reactivity series determines the speed and vigor of the reaction.
Example:
- Zinc: Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
- Magnesium: Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Reaction with Bases
- Some metals react with strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH), forming complex salts and hydrogen gas.

- This is usually observed with amphoteric metals like aluminum and zinc.
Example:
- Aluminum: 2Al + 2NaOH + 6H2O → 2Na[Al(OH)4] + 3H2
Displacement Reactions
- A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its compound in a solution.
- This is a basis of the reactivity series of metals.
Example:
- Zinc displaces copper from copper sulfate solution:
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Corrosion
- Corrosion is a chemical process where metals react with substances in the environment (like oxygen, moisture, acids) to form oxides or other compounds.
- Rusting is the corrosion of iron, forming iron oxide (Fe2O3).
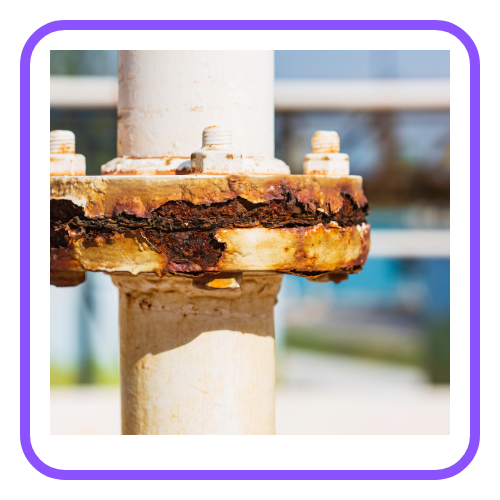

- Corrosion can be prevented by galvanization, painting, or alloying.

Reaction with Non-Metals
- Metals react with non-metals like chlorine, sulfur, and nitrogen to form ionic compounds.

Example:
- Sodium and Chlorine: 2Na + Cl2 → 2 NaCl
- Magnesium and Nitrogen: 3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
Let’s practice!

