Physical Properties
Key Notes:
Definition:
Physical properties are characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing its chemical identity.
Types of Physical Properties:
- Intensive properties: These do not depend on the amount of substance, e.g., density, boiling point, color, hardness, and melting point.
- Extensive properties: These depend on the quantity of matter, e.g., mass, volume, and length.
Examples of Physical Properties:
- Color: The visual perception of the substance’s appearance.

- State of Matter: Whether a substance is solid, liquid, or gas.
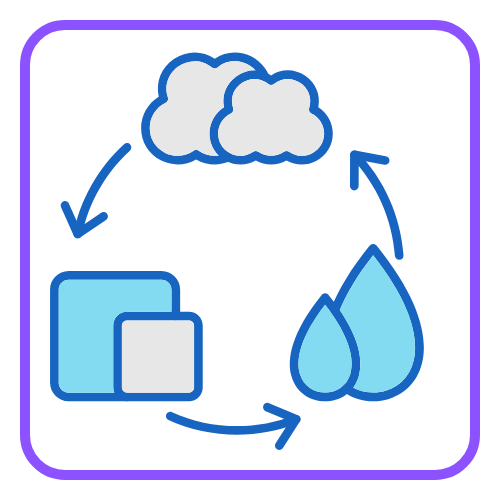
- Melting Point: The temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid.

- Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.

- Density: The mass per unit volume of a substance.

- Solubility: The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.

- Conductivity: The ability to conduct heat or electricity.

Measuring Physical Properties:
- Mass: Measured using a balance (grams or kilograms).
- Volume: Measured using graduated cylinders, beakers, or formulas (liters or cubic centimeters).

- Temperature: Measured using a thermometer (Celsius, Fahrenheit, or Kelvin).

Importance of Physical Properties:
- Helps in identification of substances.
- Predicts behavior in different environments (e.g., knowing the boiling point helps in understanding phase changes).
- Plays a role in material selection for various applications.
Changes in Physical Properties:
- Physical changes affect physical properties (e.g., changes in state) but do not alter the chemical composition of the substance.
Let’s practice!

