Feeling Hungry
Key Notes:
Understanding Hunger:
- Hunger is the body’s signal that it requires energy to function.
- It is regulated by hormones like ghrelin, which stimulates appetite, and leptin, which suppresses it.

Causes of Hunger:
- Physiological Reasons: Lack of food intake or extended gaps between meals.

- Psychological Factors: Emotional states like stress, boredom, or sadness can trigger cravings.

- Environmental Cues: The sight, smell, or thought of food can stimulate hunger.

Types of Hunger:
- Physical Hunger: A biological need for energy and nutrients.

- Emotional Hunger: Driven by feelings rather than physical needs.

Importance of Balanced Nutrition:
- Eating a well-balanced diet ensures the body gets all the necessary nutrients.
- Skipping meals can lead to overeating later or poor concentration in studies.

Role of Nutrients:
- Carbohydrates: Provide immediate energy.

- Proteins: Help in growth and repair of tissues.

- Fats: Offer long-term energy storage.

- Vitamins and Minerals: Support metabolic processes and overall health.

Consequences of Ignoring Hunger:
- Prolonged fasting can lead to low blood sugar, fatigue, and difficulty focusing.

- Chronic malnutrition can impact growth and immunity.
Healthy Eating Practices:
- Eat at regular intervals.
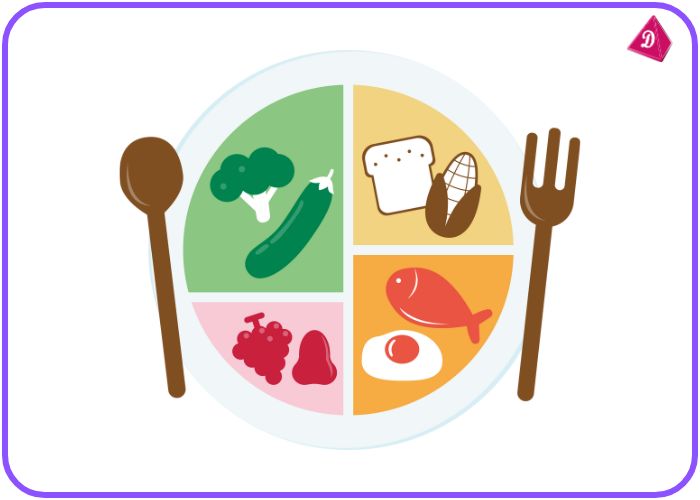

- Include diverse food groups in meals.

- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.

Awareness and Responsibility:
- Understanding global issues like food insecurity and malnutrition.

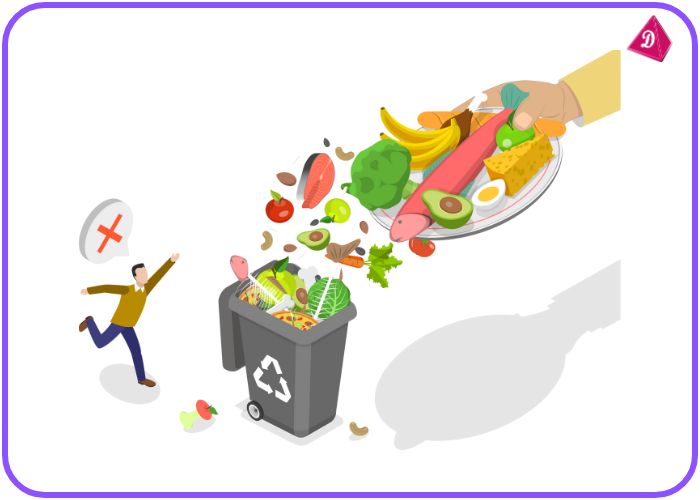
- The importance of reducing food wastage and helping the needy

Let’s practice!

