Occurrence Of The Metals In Nature
Key Notes:
Forms of Metals in Nature:
- Native State: Some metals like gold, silver, and platinum occur in a free state because they are unreactive and resist oxidation or corrosion.
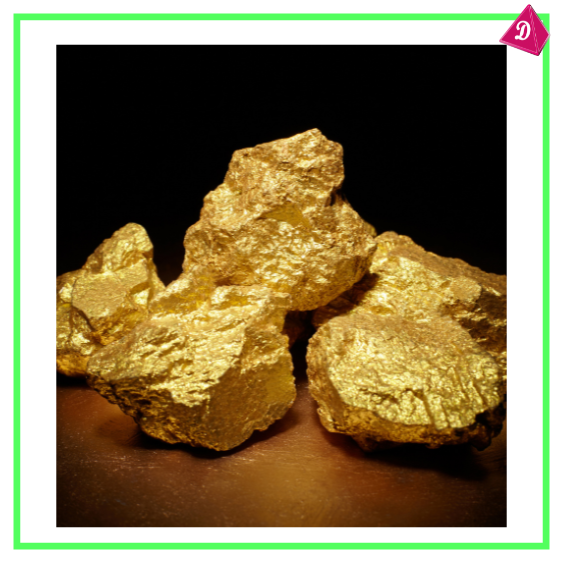

- Combined State: Most metals occur as compounds in the form of oxides, sulfides, carbonates, and chlorides due to their reactivity.

Ores and Minerals:
- Minerals: Naturally occurring substances in the Earth’s crust containing metals.

- Ores: Minerals from which metals can be profitably extracted.

- Examples:
- Iron: Found as hematite (Fe₂O₃), magnetite (Fe₃O₄).

- Aluminium: Found as bauxite (Al₂O₃·2H₂O).

- Copper: Found as chalcopyrite (CuFeS₂), cuprite (Cu₂O).

Distribution in Earth’s Crust:
- Metals constitute about 25% of the Earth’s crust.
- Abundant metals include aluminium, iron, and magnesium.
- Rare metals like gold and platinum are sparsely distributed.
Reactivity and Occurrence:
- Highly Reactive Metals: Like sodium, potassium, and calcium occur in combined states (as compounds).

- Moderately Reactive Metals: Like iron and zinc occur as oxides, sulfides, or carbonates.

- Low Reactive Metals: Like gold and platinum occur in native states.

Extraction of Metals:
- Metals are extracted based on their reactivity and the nature of the ore.
- Methods include:
- Physical Processes: Crushing, grinding, and washing.
- Chemical Processes: Reduction of ores by carbon or electrolysis.
Importance of Metals:
- Metals are crucial for industrial applications, including construction, transportation, electronics, and more.

- The abundance and ease of extraction influence the cost and utility of metals.
Environmental Impact:
- Mining and extraction of metals can lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution.

- Sustainable practices and recycling are essential to mitigate environmental damage.

