Properties Of Ionic And Covalent Compounds
Key Notes:
Introduction
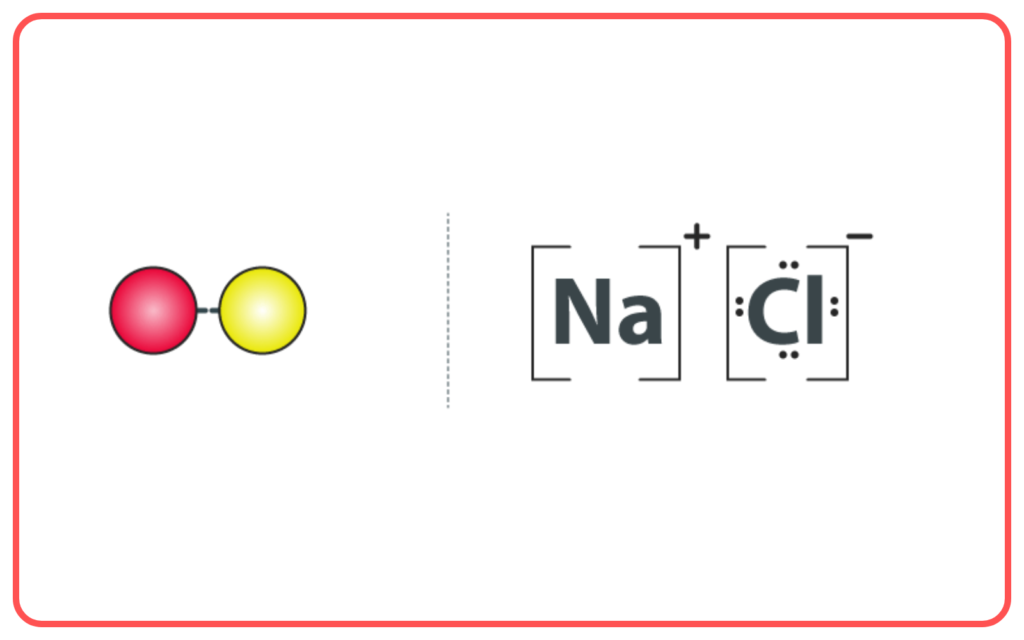
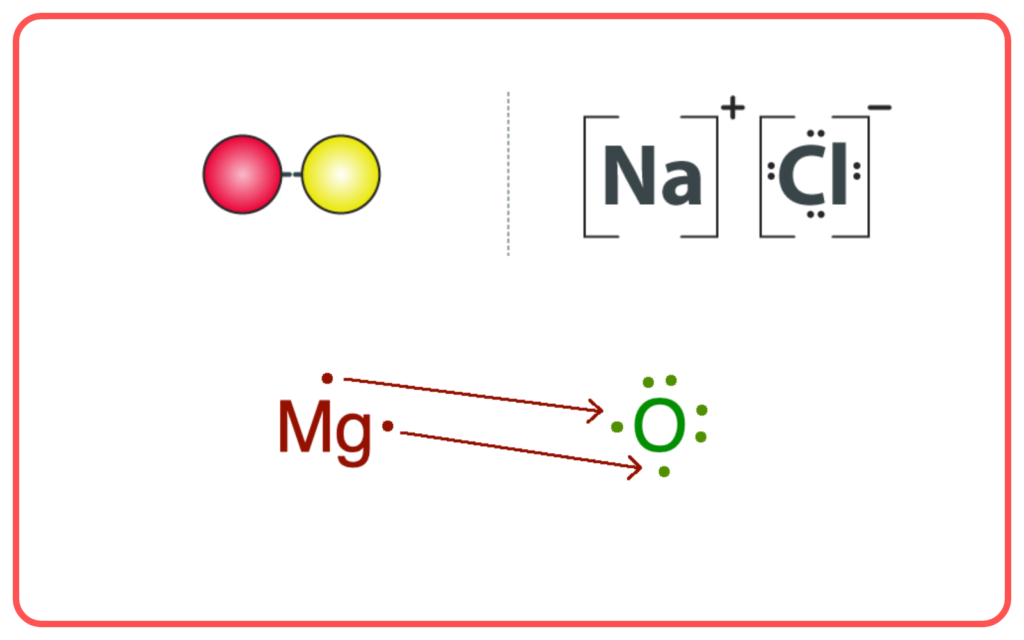
- Ionic Compounds: Formed by the transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals, resulting in ions held together by strong electrostatic forces.
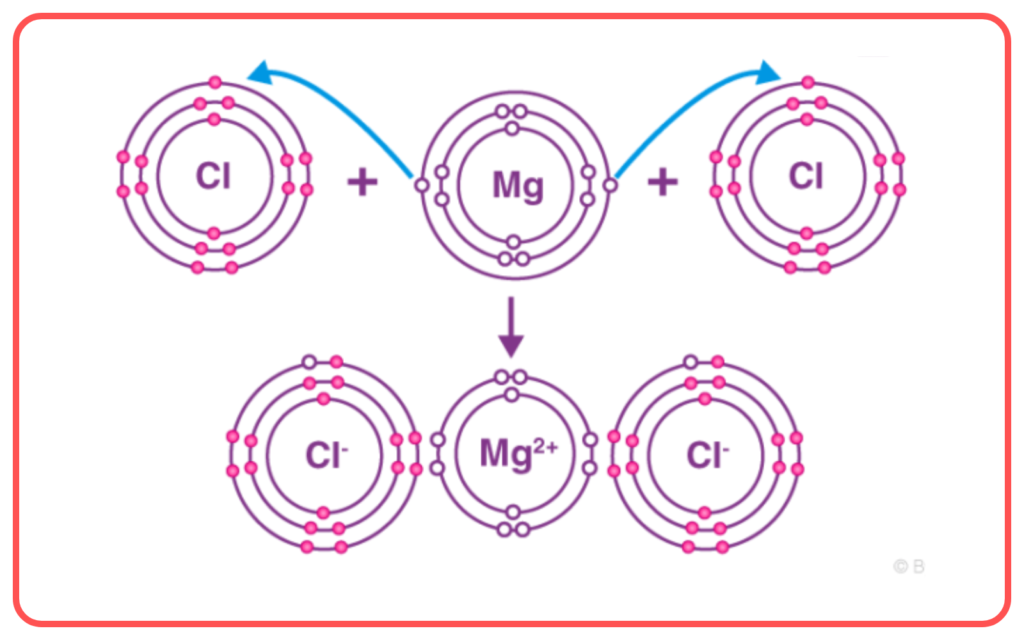
- Example: Sodium chloride (NaCl).
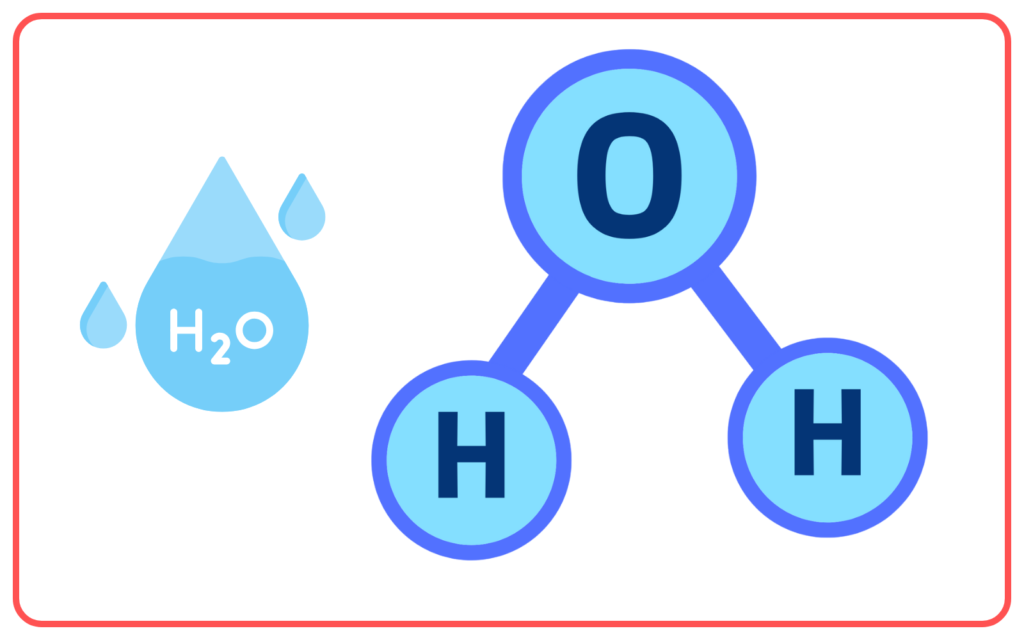
- Covalent Compounds: Formed by the sharing of electrons between two non-metals.
- Example: Water (H₂O).
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Physical State:
- Usually solid at room temperature.
- Have a crystalline structure.
- Melting and Boiling Points:
- High melting and boiling points due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction between ions.
- Solubility:
- Soluble in polar solvents like water.
- Insoluble in non-polar solvents like benzene.

- Electrical Conductivity:
- Conduct electricity in molten or aqueous state due to free-moving ions.
- Do not conduct electricity in solid state as ions are fixed in the lattice.
- Strength of Bonds:
- Ionic bonds are strong, resulting in a rigid and brittle structure.
- Examples:
- NaCl, MgO, CaCl₂.
Comparison of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
| Property | Ionic Compounds | Covalent Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Transfer of electrons | Sharing of electrons |
| Bond Type | Ionic bond (electrostatic force) | Covalent bond |
| Melting/Boiling Points | High | Low |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, insoluble in non-polar solvents | Soluble in non-polar solvents, insoluble in water |
| Electrical Conductivity | Conduct in molten/aqueous state | Non-conductors |
| Physical State | Solid | Solid, liquid, or gas |
Key Differences
- Nature of Bonding:
- Ionic compounds form strong electrostatic bonds.
- Covalent compounds form shared electron pairs.
- Behavior in Water:
- Ionic compounds dissociate into ions.
- Covalent compounds do not dissociate easily.
- Hardness:
- Ionic compounds are hard but brittle.
- Covalent compounds are softer.
Examples in Daily Life
- Ionic Compounds:
- Common salt (NaCl) used in cooking.
- Baking soda (NaHCO₃) used in baking.

- Covalent Compounds:
- Sugar (C₆H1₁₂O₆) in food.
- Water (H₂O) essential for life.

Conclusion
Understanding the properties of ionic and covalent compounds helps explain their different uses and behaviors in real-life applications. The type of bonding significantly influences a compound’s physical and chemical properties.
Let’s practice!

