The Arrangement Of Ions In Ionic Compounds
Key Notes:
Ionic Compounds:
- Formed by the transfer of electrons between metals (which form cations) and non-metals (which form anions).
- Held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
Crystal Lattice Structure:
- Ionic compounds arrange in a three-dimensional lattice structure to minimize energy and maximize stability.
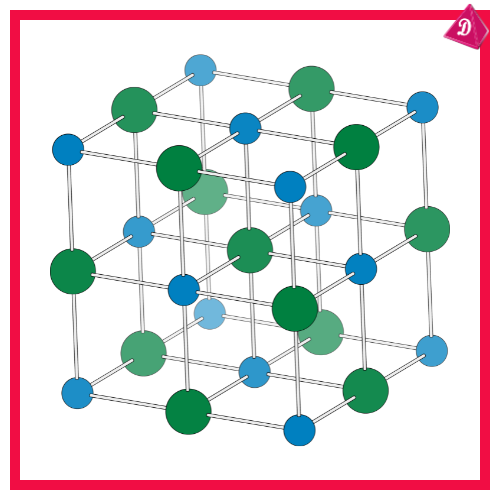
- The structure ensures a balanced charge with alternating positive and negative ions.
Examples of Ionic Compounds:
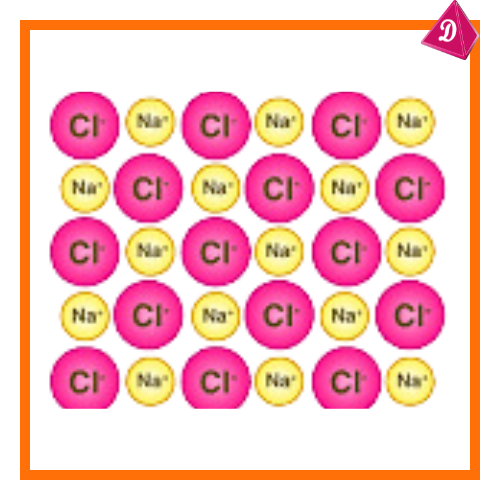
- Sodium chloride (NaCl): Each Na⁺ ion is surrounded by six Cl⁻ ions and vice versa in a cubic lattice.

- Magnesium oxide (MgO): Arranged in a similar lattice with higher attraction due to 2+ and 2− charges.

Key Properties of Ionic Arrangement:
- High Melting and Boiling Points: Strong ionic bonds in the lattice require significant energy to break.
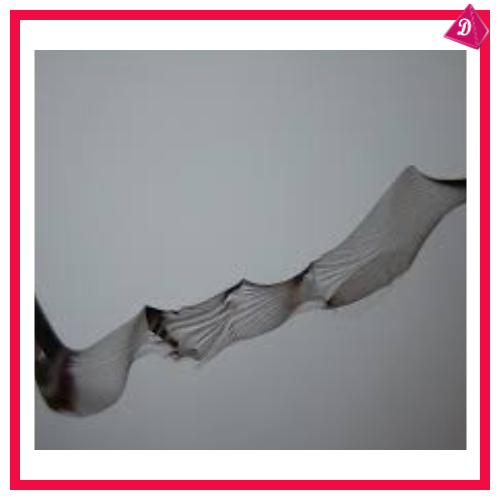
- Brittleness: When force is applied, ions of like charge come closer, causing repulsion and fracture.

- Electrical Conductivity: Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten or aqueous states due to the free movement of ions.
Coordination Number:
- Represents the number of oppositely charged ions surrounding a given ion.
- Example: In NaCl, the coordination number is 6.
Factors Influencing Arrangement:
- Ionic Size: Smaller ions pack more tightly.
- Ionic Charge: Higher charges create stronger attractions and tighter lattices.
- Ration of Ion Sizes: Determines the type of lattice (e.g., cubic, hexagonal).
Lattice Energy:
- The energy released when one mole of an ionic compound forms from its gaseous ions.
- Determines the stability of the crystal lattice.

Importance of Lattice Structures:
- Explains properties like solubility, hardness, and conductivity.
Let’s practice!

