Bohr’s Model Of Hydrogen Atom And Its Limitations
Key Notes:
Introduction to Bohr’s Model
- Proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913 to explain the structure of the hydrogen atom.
- Combined concepts of classical physics and quantum theory.

Postulates of Bohr’s Model
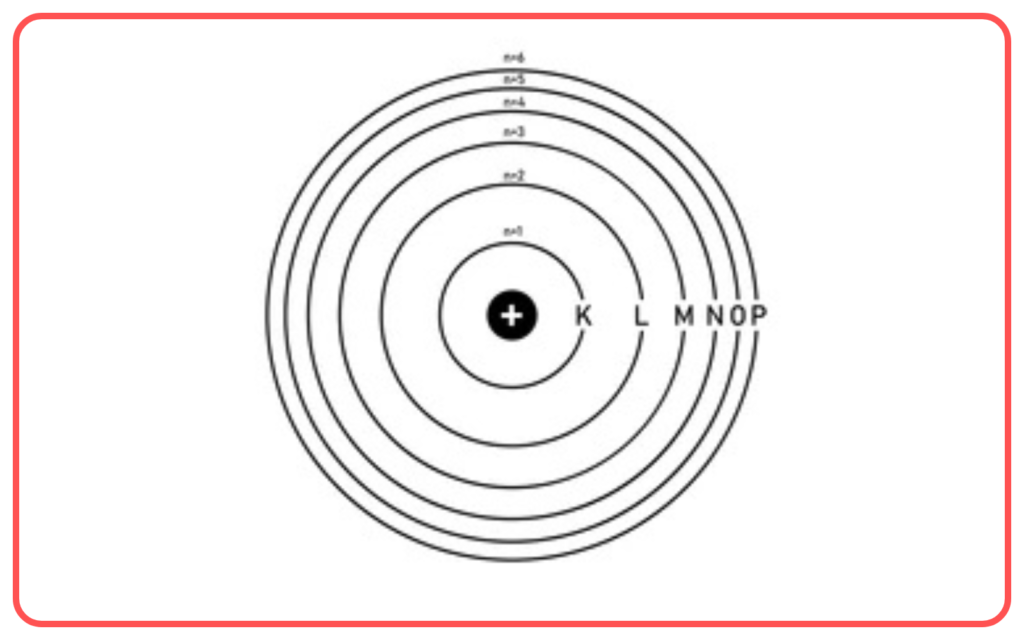
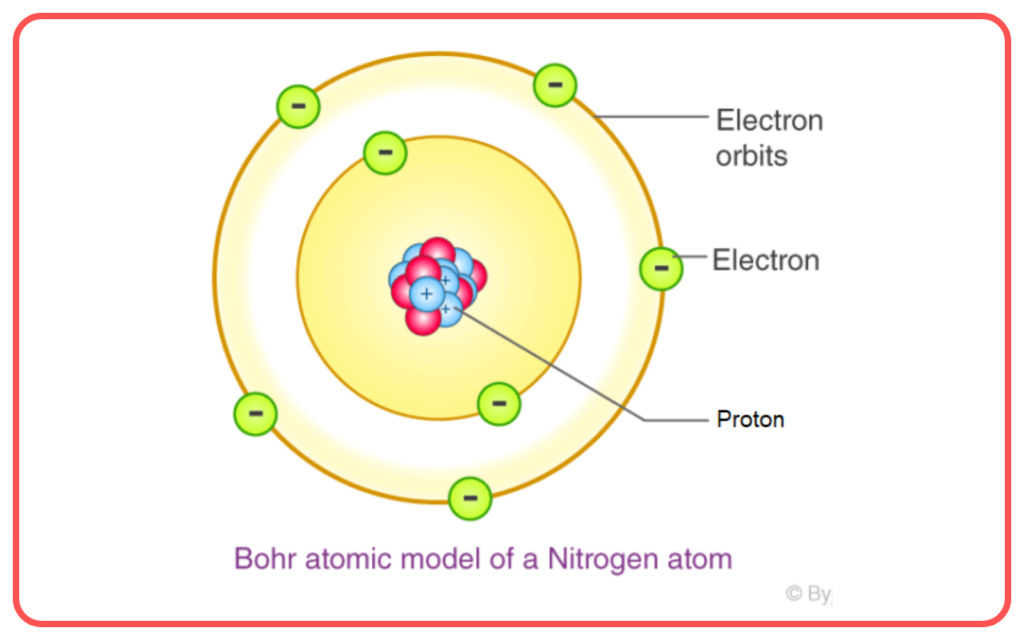
- Stationary Orbits
- Electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific circular orbits called stationary orbits.
- Each orbit corresponds to a fixed energy level, so electrons do not radiate energy while in these orbits.
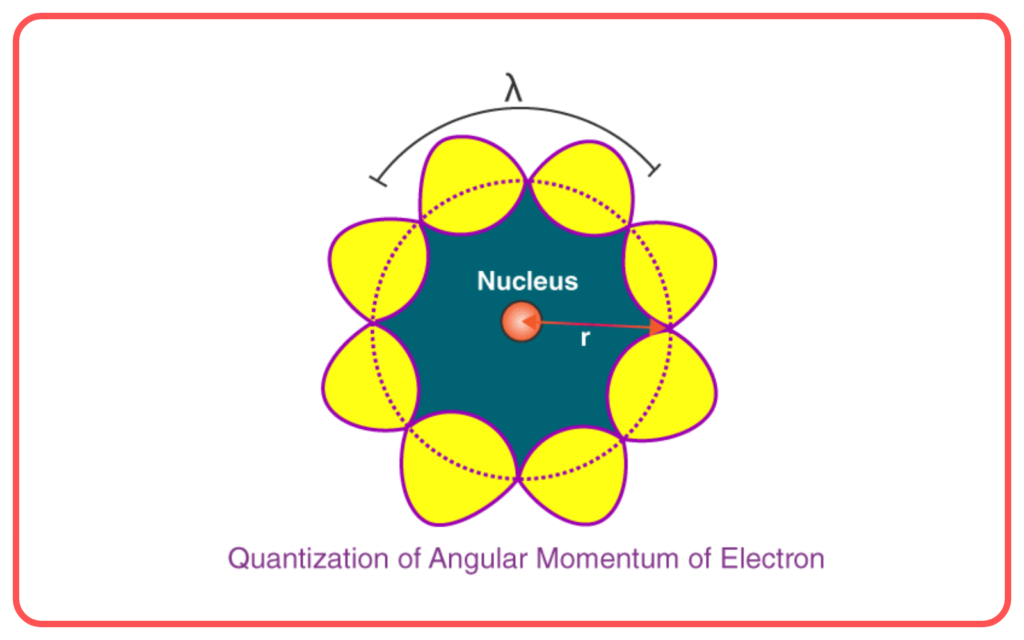
- Quantization of Angular Momentum
- The angular momentum of an electron in orbit is quantized: L=nℏ=nh/2π, where n is the principal quantum number, ℏ is the reduced Planck’s constant.
- Energy Levels
- Electrons can move between orbits by absorbing or emitting energy: ΔE=E₂−E₁=hν
- h= Planck’s constant, ν = frequency of emitted/absorbed radiation.
- Electrons can move between orbits by absorbing or emitting energy: ΔE=E₂−E₁=hν
- Radiation of Energy
- When an electron jumps from a higher energy orbit (n₂) to a lower energy orbit (n₁), it emits energy as photons.
Key Features of Bohr’s Model
- Energy Levels
- The energy of the electron is inversely proportional to the square of the orbit number (n): Eₙ=(−13.6/n²)eV
- Negative sign indicates the electron is bound to the nucleus.
- The energy of the electron is inversely proportional to the square of the orbit number (n): Eₙ=(−13.6/n²)eV
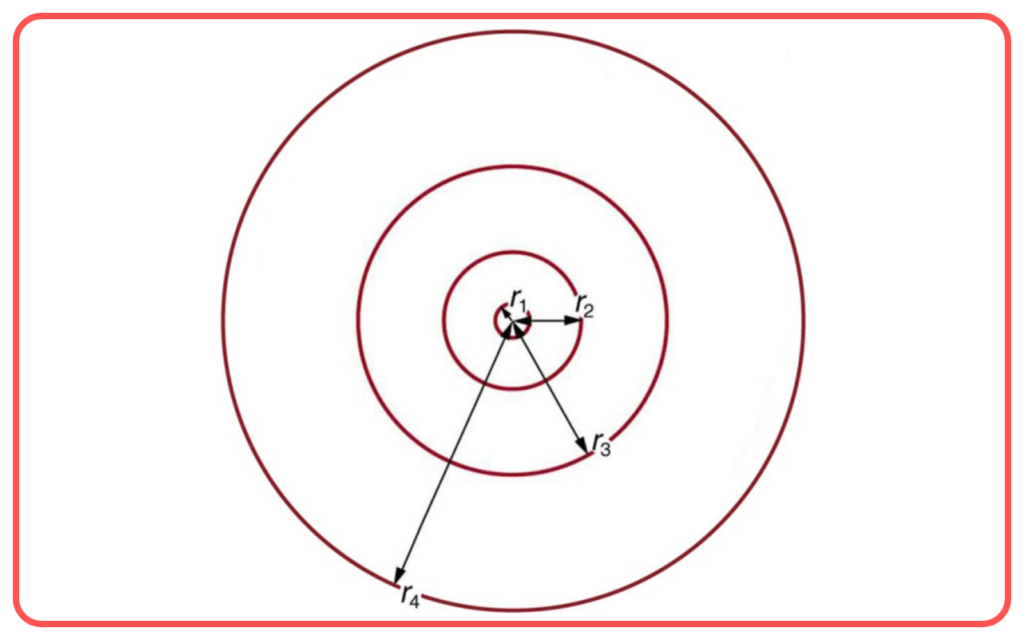
- Radius of Orbits
- The radius of the nth orbit is proportional to rₙ=n²×r₁
- r₁=0.53 A˚(Bohr radius).
- The radius of the nth orbit is proportional to rₙ=n²×r₁
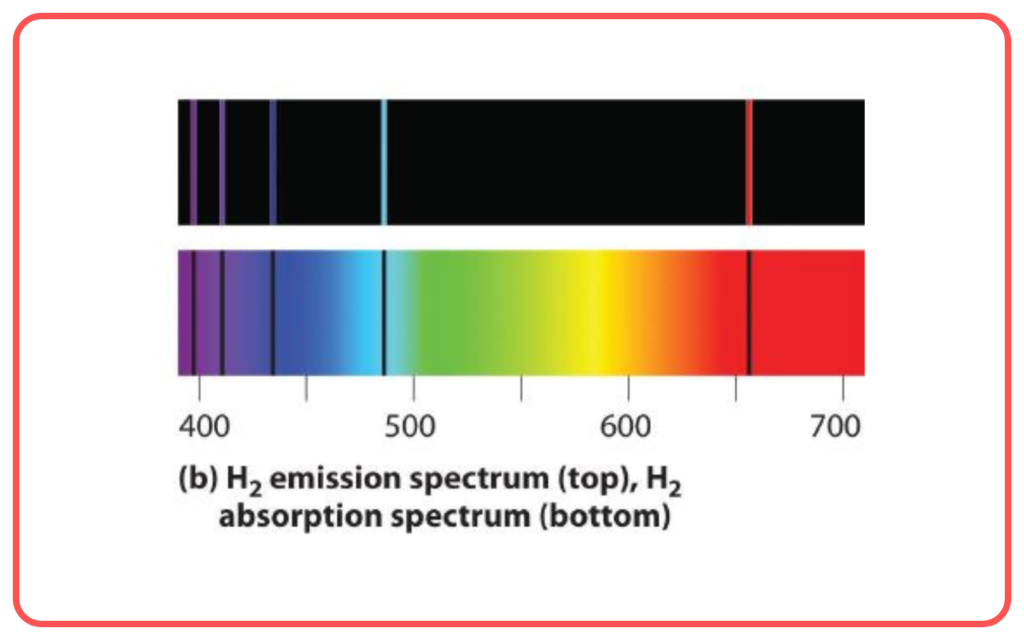
- Hydrogen Spectrum
- Explained the emission spectrum of hydrogen (Lyman, Balmer, Paschen, etc.).
Achievements of Bohr’s Model
- Successfully explained the spectral lines of hydrogen.
- Introduced the concept of quantized energy levels.
- Laid the foundation for modern atomic physics.
Limitations of Bohr’s Model
- Applicable Only to Hydrogen-like Atoms
- Could not explain spectra of atoms with more than one electron (e.g., Helium, Lithium).
- No Explanation for Spectral Line Splitting
- Could not explain the fine structure (splitting of spectral lines in magnetic/electric fields) observed in the Zeeman and Stark effects.
- Fails to Address Wave-Particle Duality
- Does not consider the wave-like nature of electrons (proposed later by de Broglie).
- Violation of Uncertainty Principle
- Assumes precise paths (orbits) for electrons, contradicting Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle.
- No Explanation for Chemical Bonding
- Fails to account for the behavior of electrons in chemical bonding.
Bohr’s Model and Modern Atomic Theory
- Bohr’s model was replaced by the Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom, which incorporates wave-particle duality and probability distributions of electrons.
Conclusion
- Bohr’s model was a significant step in understanding atomic structure and paved the way for further advancements in quantum mechanics.
Let’s practice!

