Spectrum
Key Notes:
Definition of Spectrum
The spectrum refers to the band of colors or wavelengths obtained when light is dispersed through a prism or diffraction grating.

Types of Spectrum
- Continuous Spectrum
- Contains all wavelengths without any gaps.
- Example: Sunlight, which gives a rainbow of colors (red to violet).

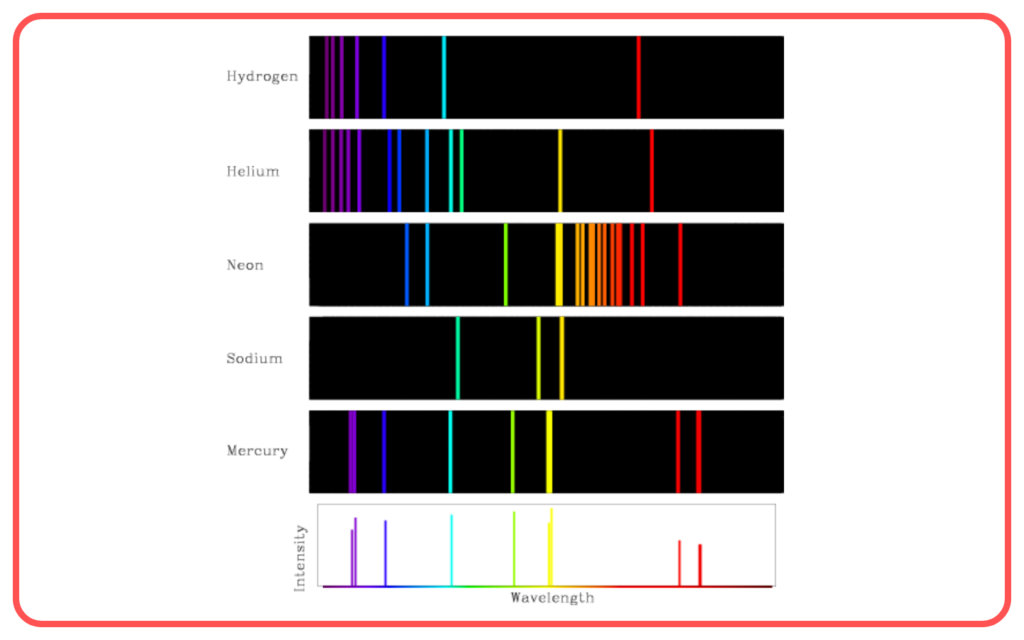
- Emission Spectrum
- Produced by a hot gas or excited atoms.
- Appears as bright lines on a dark background.
- Example: Hydrogen emission spectrum.
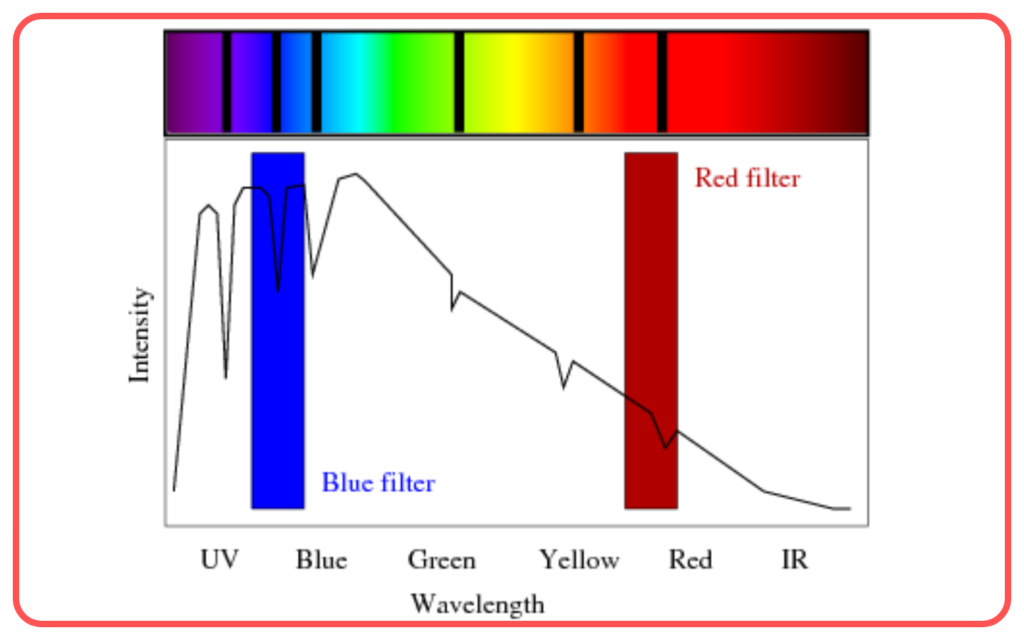
- Absorption Spectrum
- Produced when light passes through a cooler gas or medium.
- Appears as dark lines on a continuous spectrum background.
- Example: Solar spectrum.
Formation of Spectrum
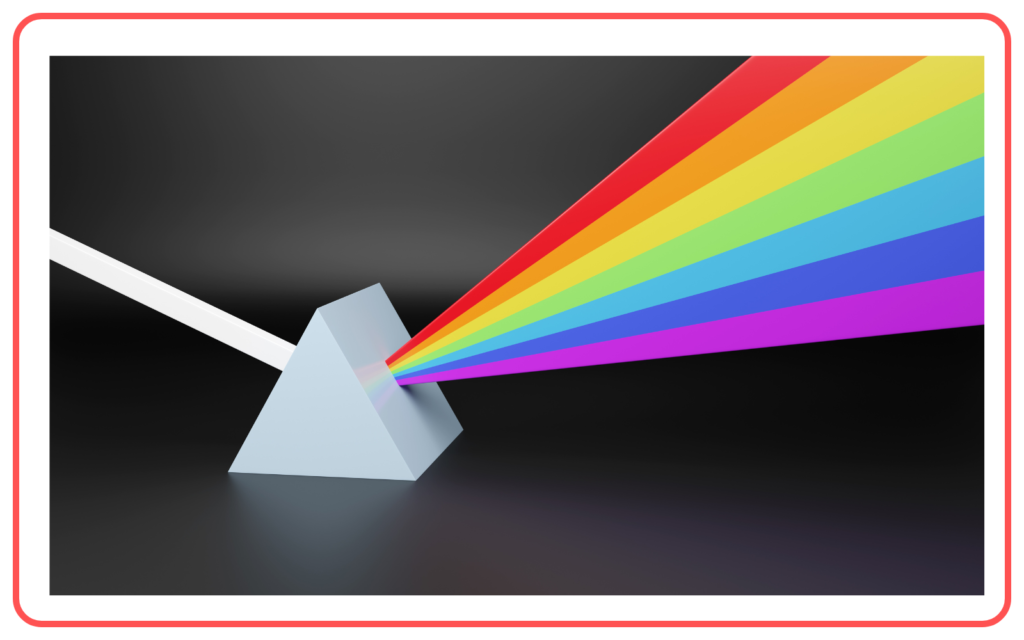
- Dispersion of Light:
When light passes through a prism, it splits into its constituent colors due to differences in the bending (refraction) of each wavelength.
Order of Colors (VIBGYOR): Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red.
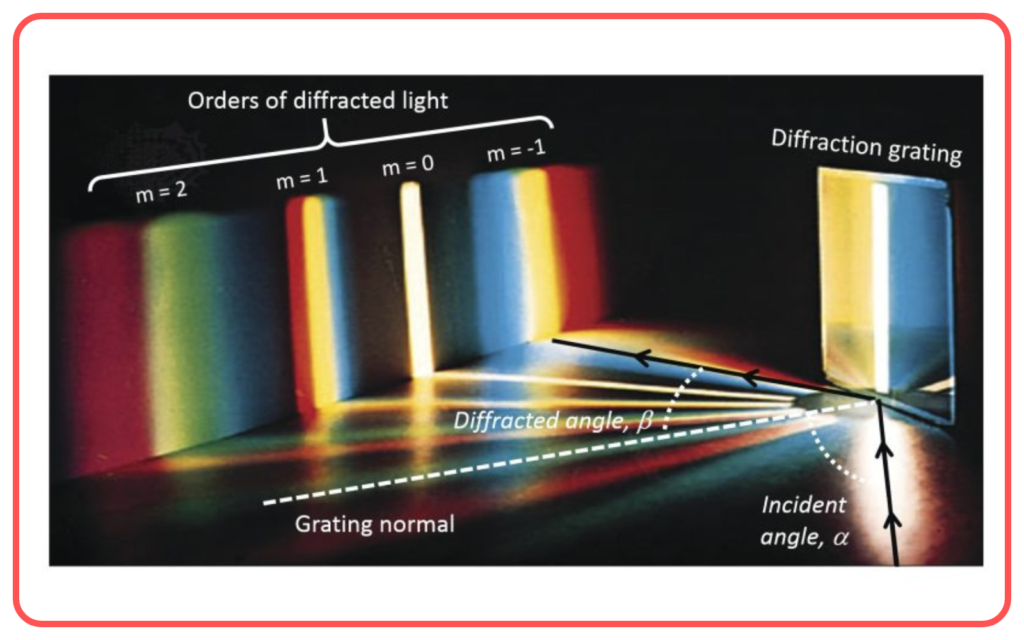
- Diffraction Grating:
A device used to separate light into its components more precisely using the principle of diffraction.
Important Terms
- Wavelength (λ): The distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs in a wave.
- Frequency (f): The number of wave cycles passing a point per second.
- Energy (E): Related to wavelength and frequency (E=hf, where h is Planck’s constant).
Applications of Spectrum
- Astronomy:
- Study of stars and planets using absorption and emission spectra.
- Identification of elements in celestial bodies.

- Spectroscopy:
- Analysis of chemical substances by studying their spectra.

- Communication:
- Use of electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves) in telecommunication.

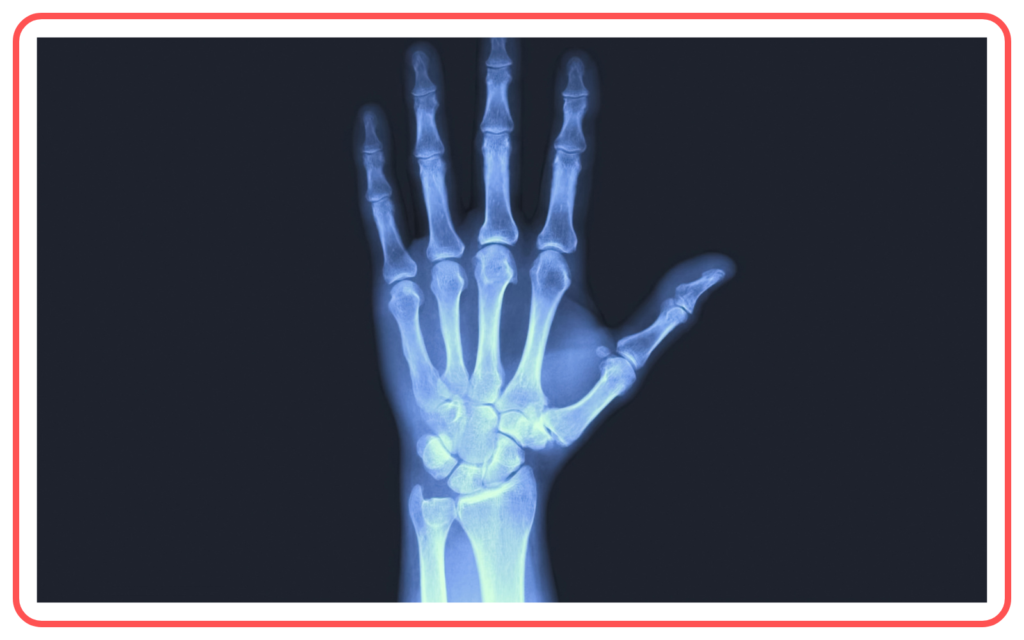
- Medical:
- X-rays (part of the spectrum) are used in diagnostics.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
- A broader classification of waves includes visible light, radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
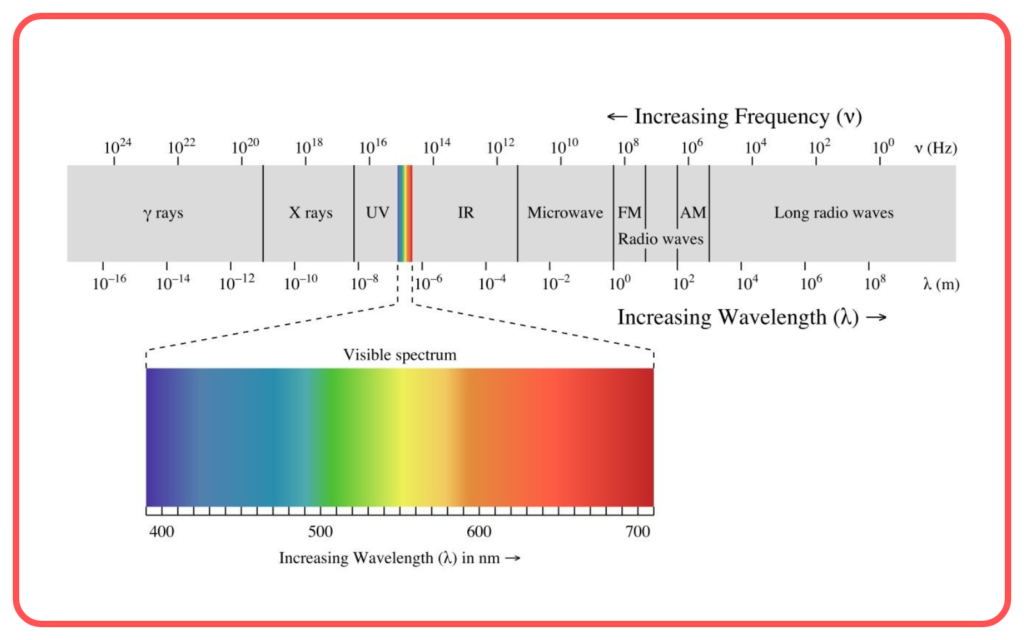
- Order of Wavelength:
Radio waves > Microwaves > Infrared > Visible Light > Ultraviolet > X-rays > Gamma rays.
Characteristics of Light Spectrum
- Dispersion: Separation of light into its components.

- Refraction: Bending of light when passing from one medium to another.

- Diffraction: Spreading of light when it encounters an obstacle or slit.
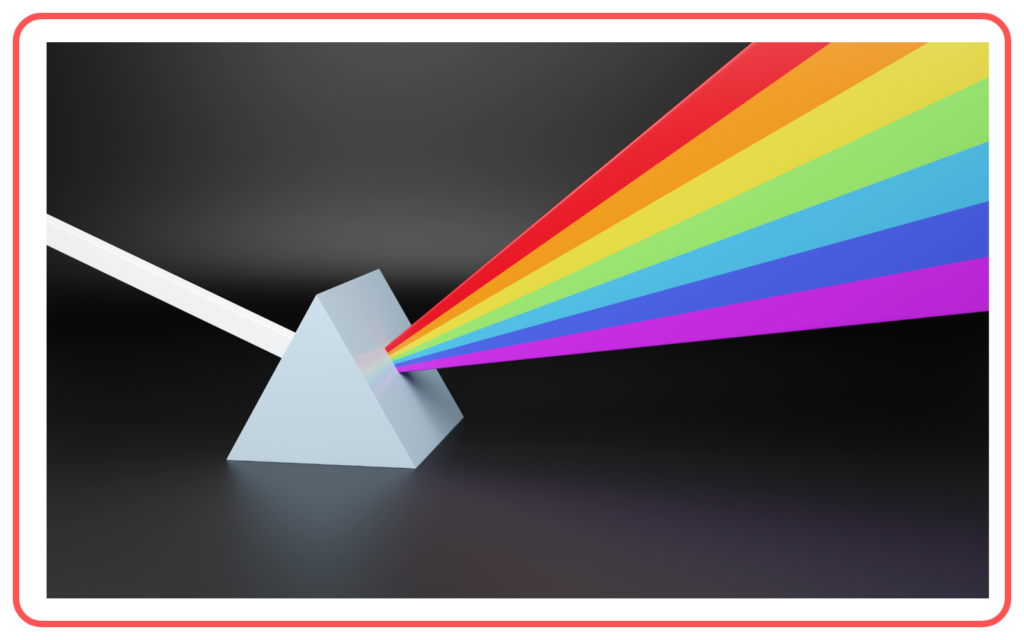
Newton’s Experiment
- Newton demonstrated the dispersion of white light into its constituent colors using a prism, proving that light is a mixture of colors.
Significance in Science
- Provides insights into the composition, temperature, and motion of celestial objects.
- Helps in understanding the wave-particle duality of light.
Let’s practice!

