Boiling
Key Notes:
Definition:
- Boiling is a phase transition from a liquid to a gas that occurs when a substance’s temperature reaches its boiling point under normal atmospheric pressure.
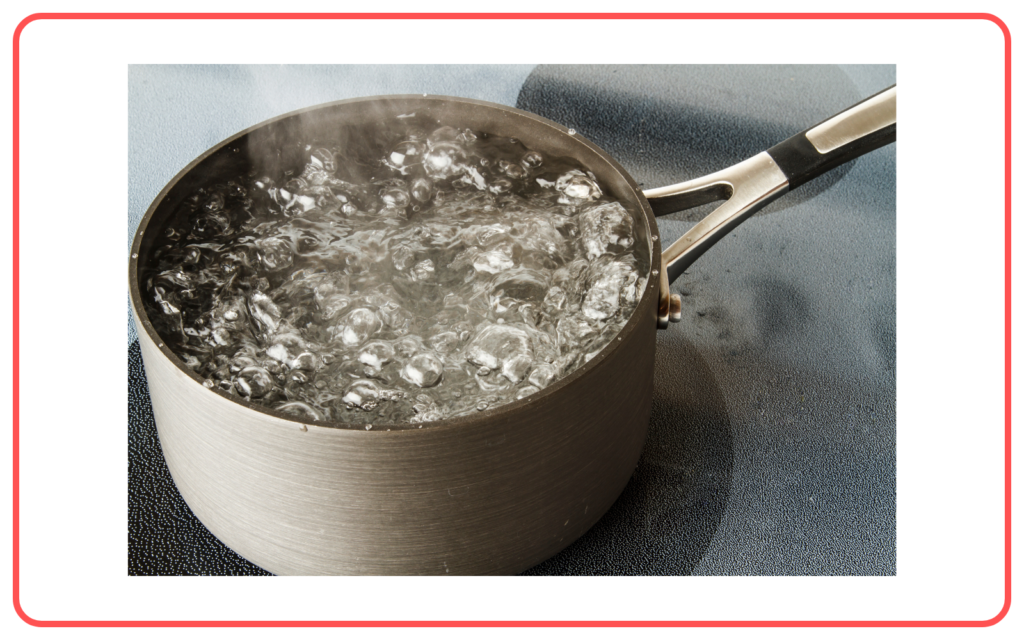

Boiling Point:
- The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure, causing it to boil.
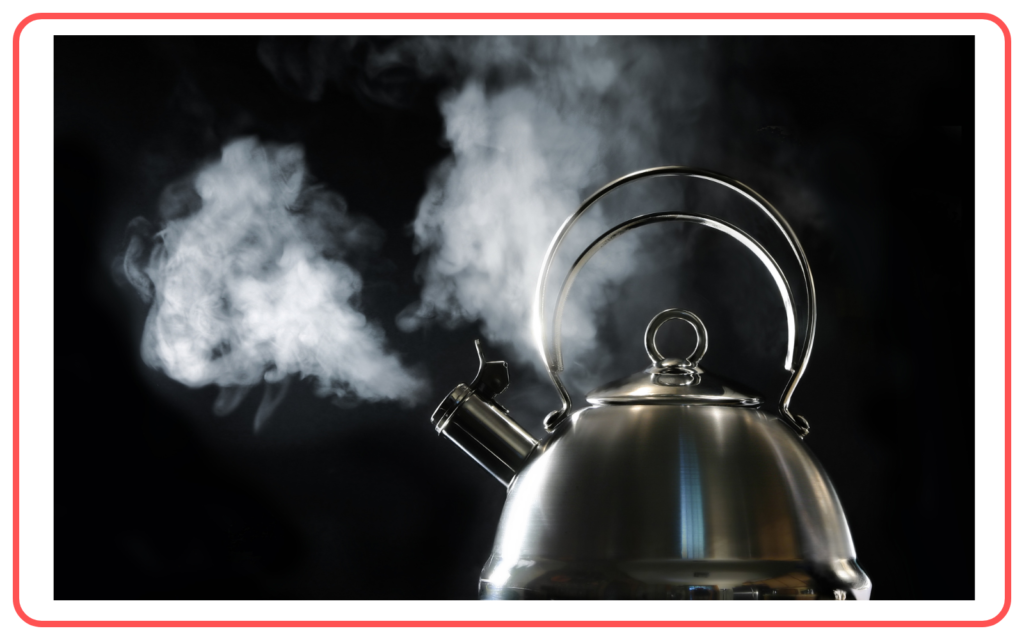

- Different substances have different boiling points due to variations in intermolecular forces.
Factors Affecting Boiling Point:
- Atmospheric pressure: Higher pressure can raise the boiling point, while lower pressure can lower it.
- Type of substance: The strength of intermolecular forces (e.g., hydrogen bonding) affects boiling points. Substances with stronger forces typically have higher boiling points.
Boiling Process:
- As a liquid is heated, its temperature increases until it reaches the boiling point.
- At the boiling point, the liquid absorbs heat energy, but its temperature remains constant until all of it is converted into vapor.
- Once all the liquid has vaporized, further heating causes the temperature of the vapor to rise.
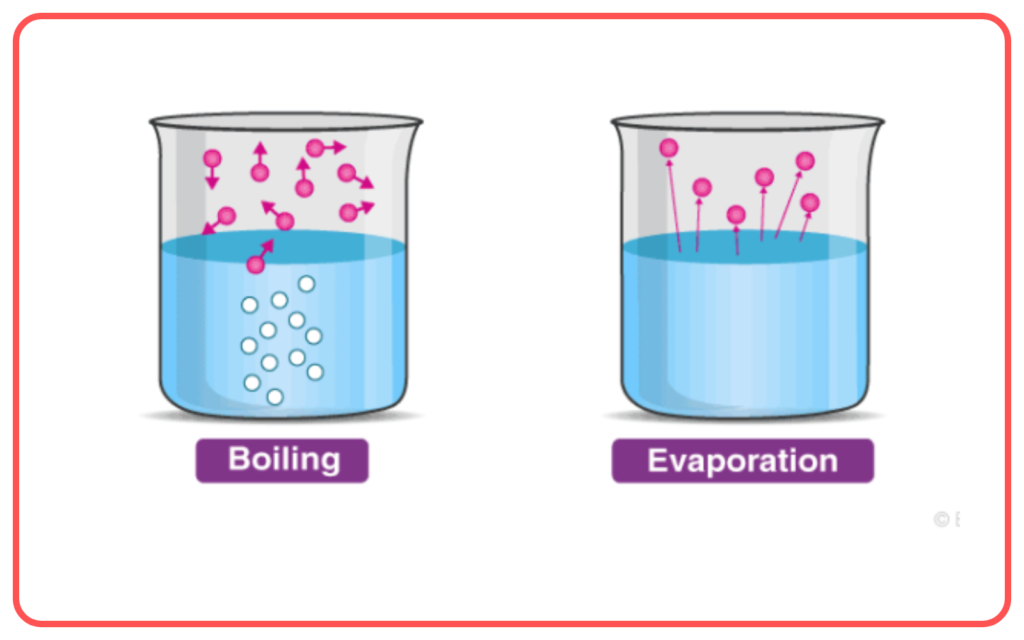
Vaporization vs. Boiling:
- Vaporization is the general process of a substance changing from a liquid to a gas, which includes both boiling and evaporation.
- Evaporation occurs at the surface of a liquid at temperatures below the boiling point, while boiling happens throughout the liquid at the boiling point.
Uses of Boiling:
- Cooking: Boiling is commonly used for cooking various food items, such as pasta, vegetables, and eggs.
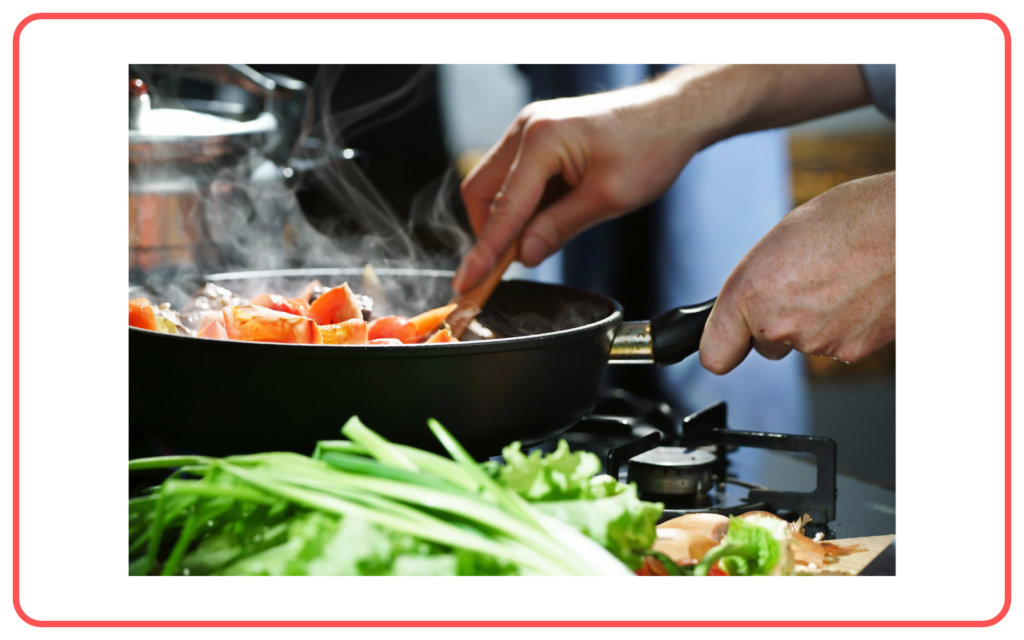

- Sterilization: Boiling water can be used to sterilize drinking water, medical instruments, and baby bottles.

- Chemical Reactions: Boiling is used in chemistry for various reactions and separations.

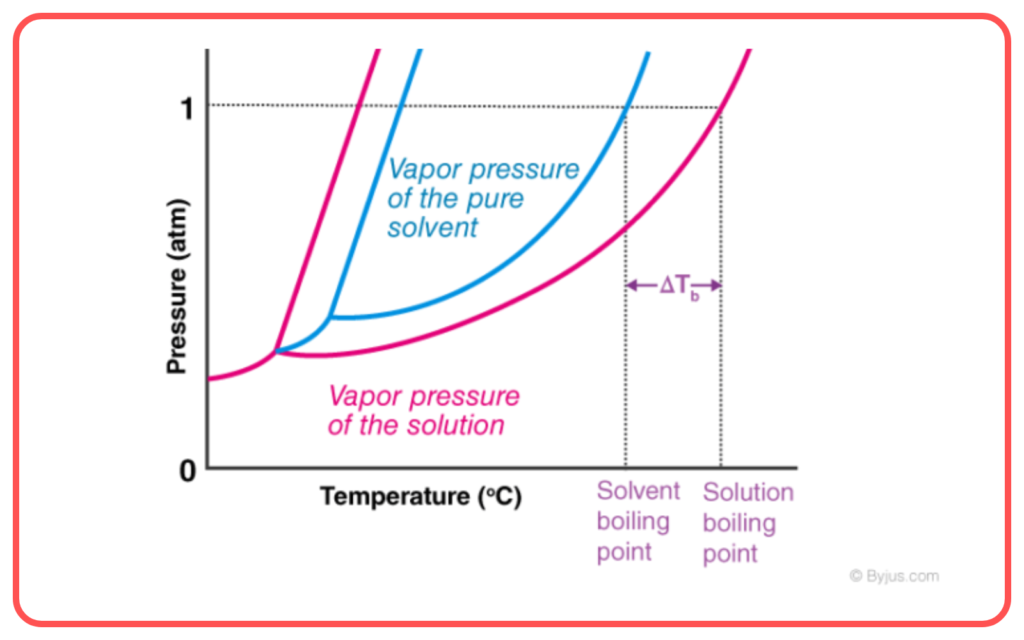
Boiling Point Elevation and Depression:
- Adding solutes (like salt) to a solvent (like water) can raise the boiling point (boiling point elevation) or lower it (boiling point depression).
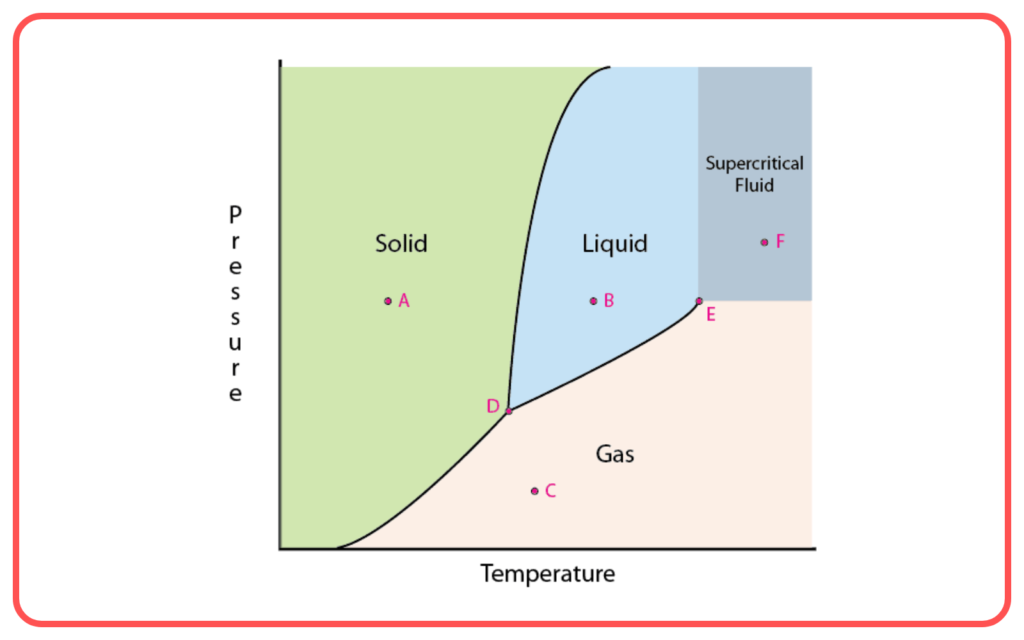
Phase Diagrams:
- Phase diagrams illustrate the relationship between temperature, pressure, and the states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) for a substance.
Importance of Boiling:
- Boiling is crucial in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and petrochemicals, for purification, separation, and product formation.
Let’s practice!

