Methods Of Mixtures
Key Notes:
Introduction to Mixtures
- A mixture is a combination of two or more substances where each substance retains its individual properties.
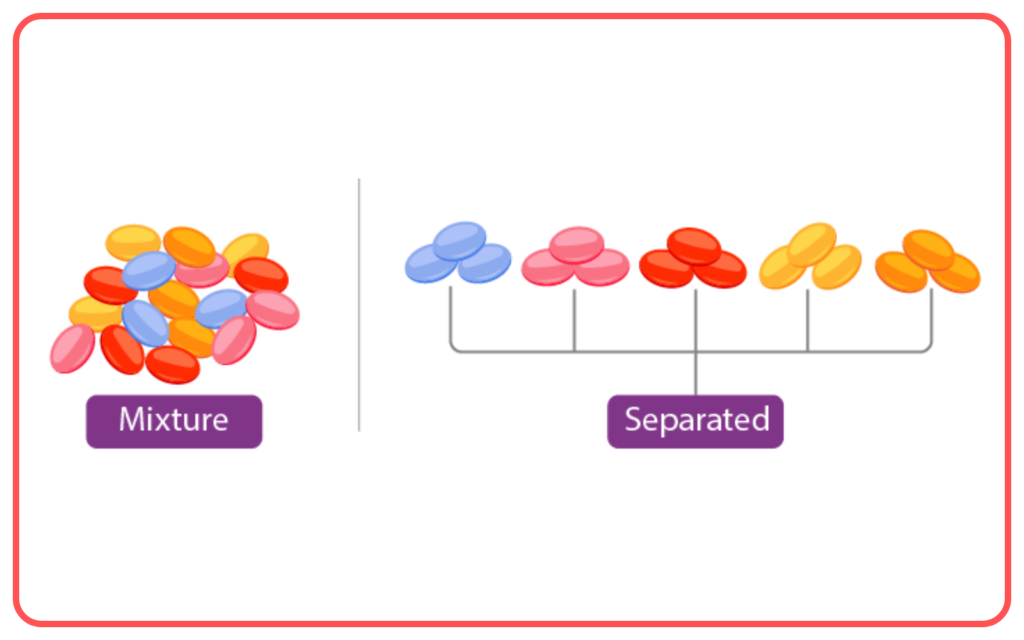
- Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition) or heterogeneous (non-uniform composition).
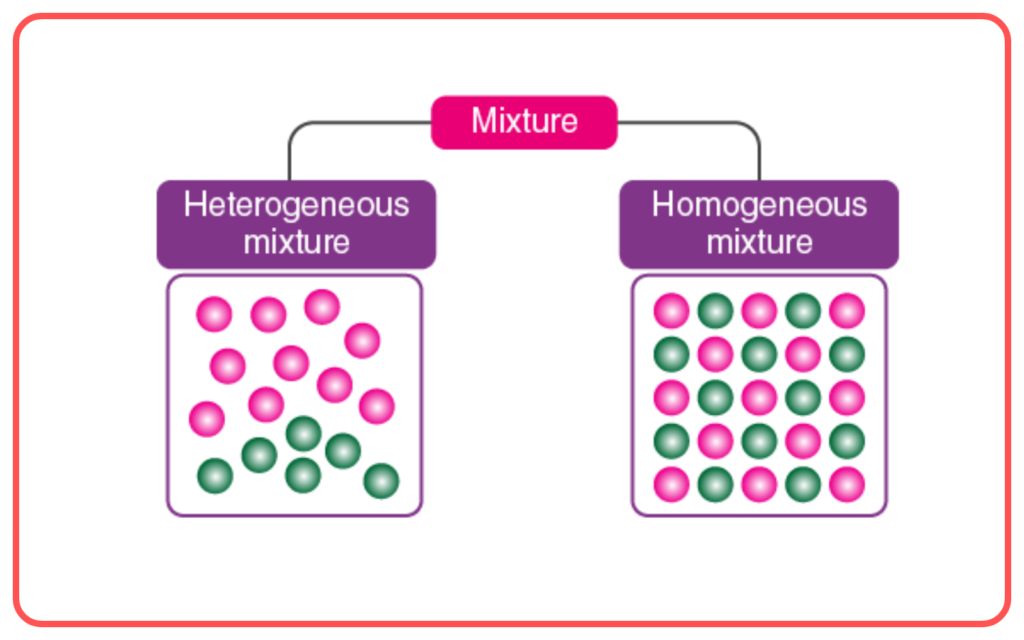
- In a homogeneous mixture, the substances are evenly distributed, such as in solutions.
- In a heterogeneous mixture, the substances remain distinct, like in salad or sand and salt.
Methods of Separation of Mixtures
There are several methods used to separate the components of a mixture, depending on the physical properties of the substances involved. The following are some common methods of separation:
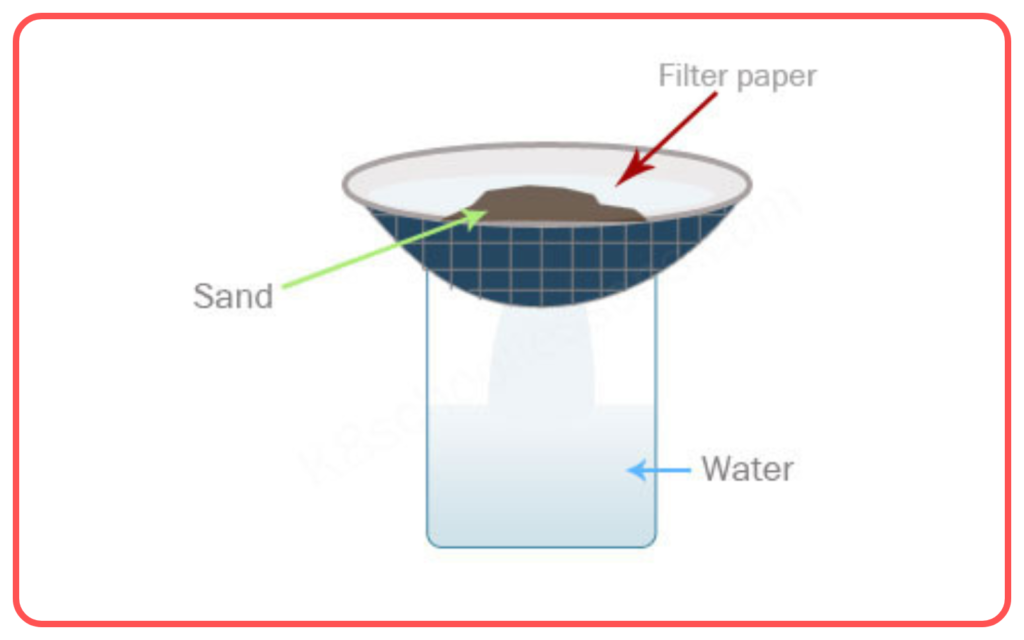
Filtration
- Filtration is used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid or gas.
- It involves passing the mixture through a filter paper that allows the liquid or gas to pass through, while the solid particles are left behind.
- Example: Separating sand from water.
- Used for: Separating solids from liquids, e.g., separating chalk powder from water.
Evaporation
- Evaporation is the process of heating a liquid to convert it into vapor, leaving behind any dissolved solid.
- This method is useful when the solid dissolved in the liquid has a higher boiling point than the liquid.
- Example: Evaporating water from saltwater to obtain salt.
- Used for: Separation of dissolved solids from liquids, e.g., separating salt from seawater.

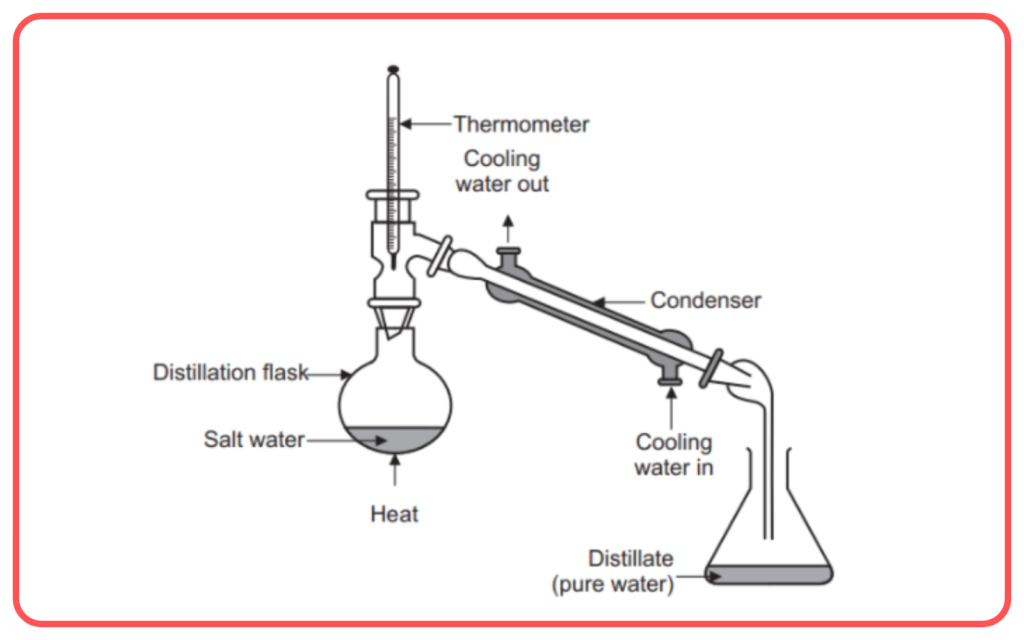
Distillation
- Distillation is a process used to separate a liquid mixture based on the difference in boiling points of its components.
- The mixture is heated, and the component with the lower boiling point vaporizes first. The vapor is then condensed into a liquid.
- Example: Distilling alcohol from a fermented mixture.
- Used for: Purification of liquids, separating liquids with different boiling points, e.g., distillation of water from saltwater.
Sublimation
- Sublimation is the process where a solid directly changes into a gas without passing through the liquid phase, or vice versa.
- This method is used to separate substances that sublime (transition from solid to gas) from those that do not.
- Example: The separation of iodine from a mixture of iodine and sand.
- Used for: Separating volatile solids (like iodine or naphthalene) from non-volatile substances.

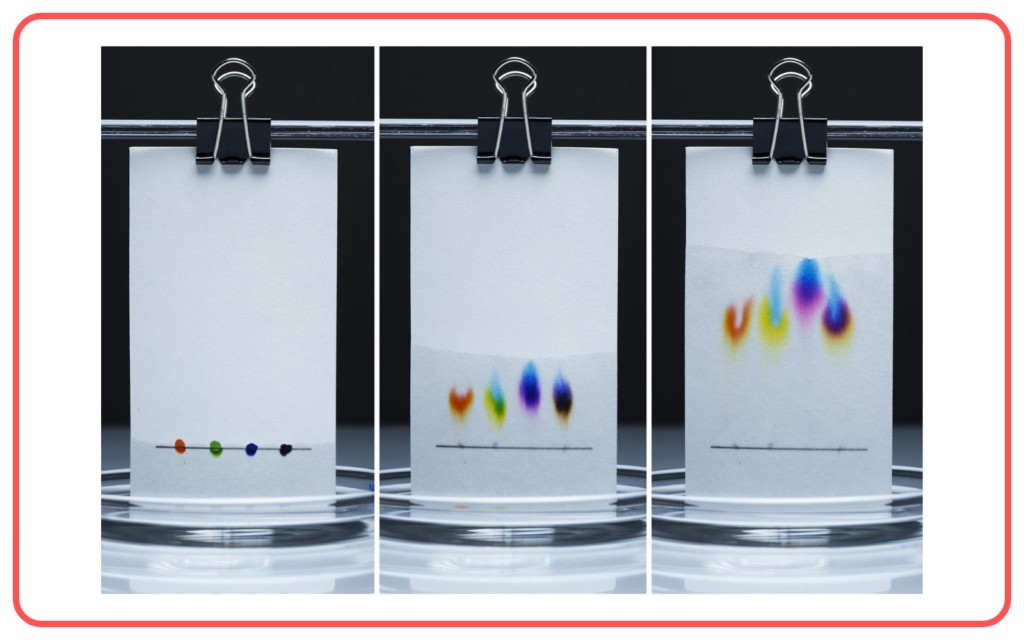
Chromatography
- Chromatography is used to separate components of a mixture based on their movement through a stationary phase (usually paper or a solid surface) and their affinity for a mobile phase (a liquid or gas).
- The components in the mixture move at different rates, allowing them to be separated.
- Example: Separating colors from ink or pigments in plants.
- Used for: Separation of complex mixtures like dyes or pigments.

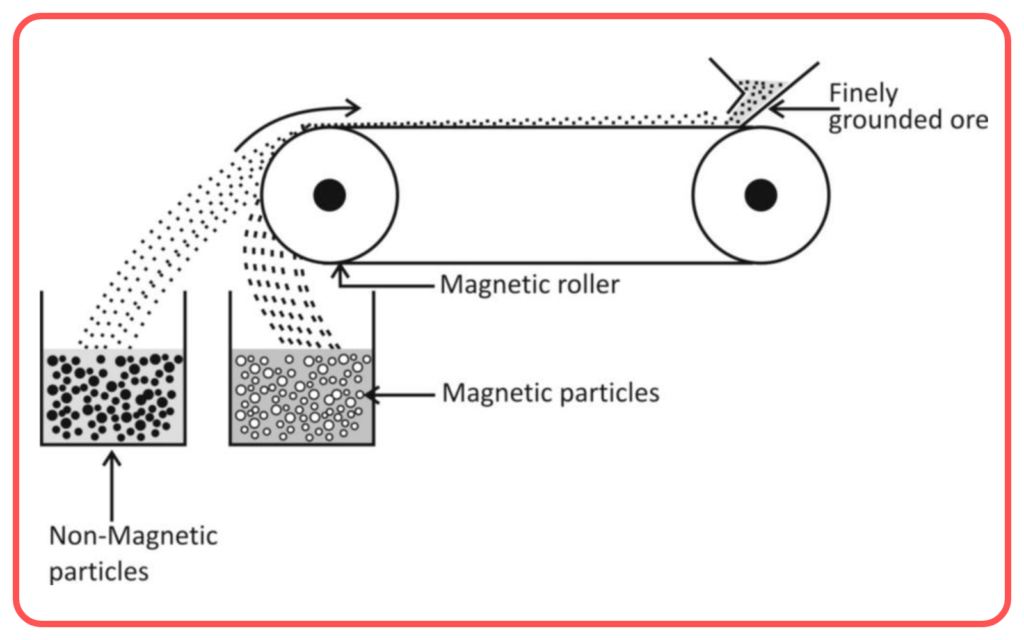
Magnetic Separation
- Magnetic separation is used to separate magnetic materials from non-magnetic ones.
- This method relies on the magnetic properties of the substances in the mixture.
- Example: Separating iron filings from a mixture of sand and iron.
- Used for: Separating magnetic materials (e.g., iron) from non-magnetic ones.
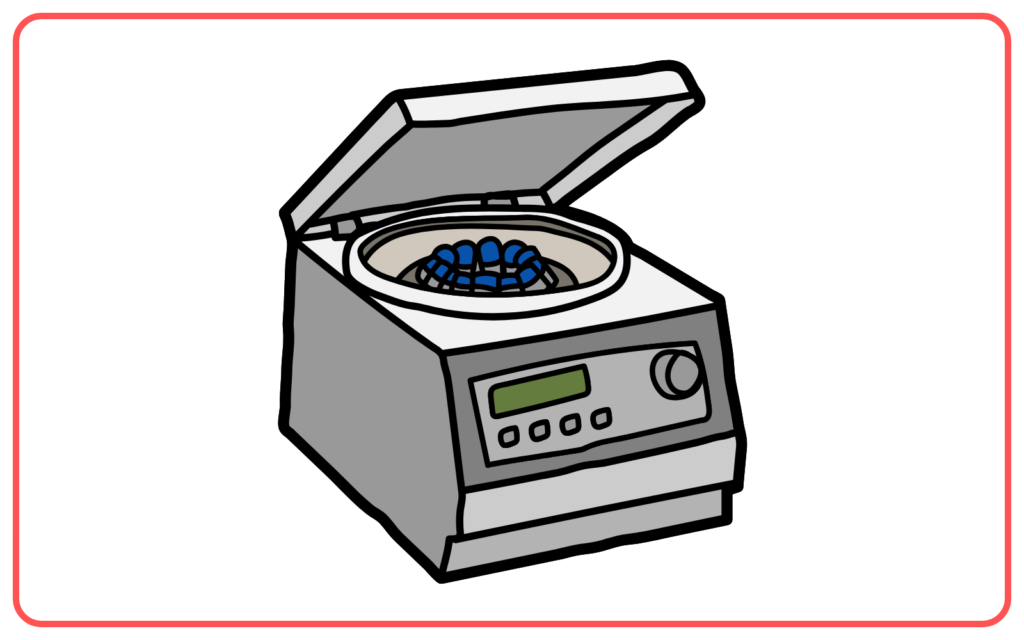
Centrifugation
- Centrifugation is used to separate components of a mixture based on their density by spinning the mixture at high speeds.
- The denser components move to the bottom, while the less dense components stay on top.
- Example: Separating cream from milk or blood components.
- Used for: Separation of mixtures with different densities, e.g., in the separation of blood into plasma and cells.
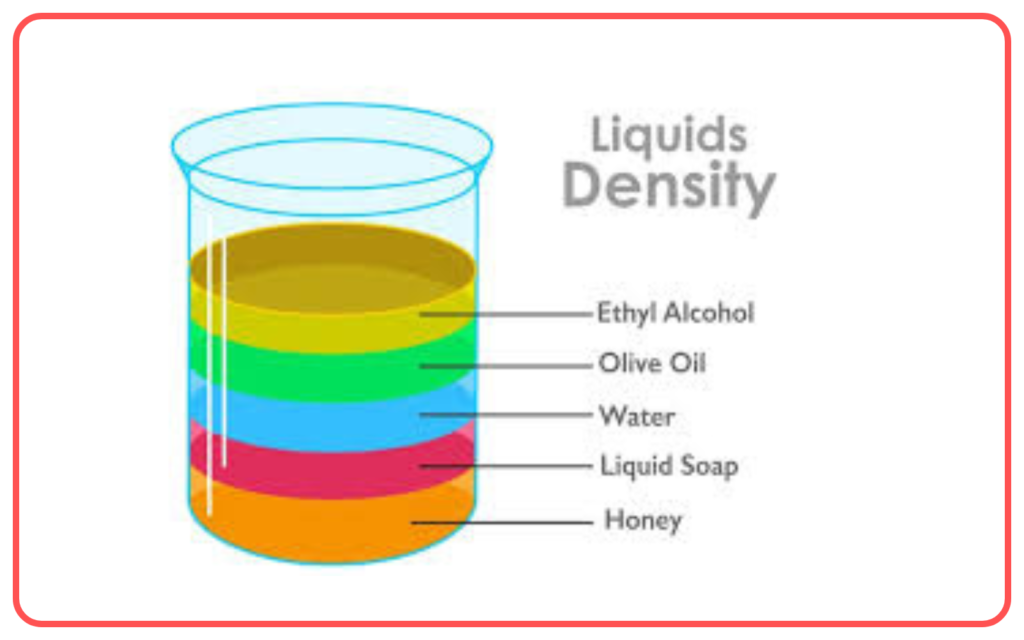
Separation by Density
- This method separates components of a mixture based on their different densities.
- When a mixture of substances with varying densities is placed in a liquid, the denser substances settle at the bottom, while the less dense substances float.
- Example: Separating oil from water.
- Used for: Separating immiscible liquids or components with different densities.
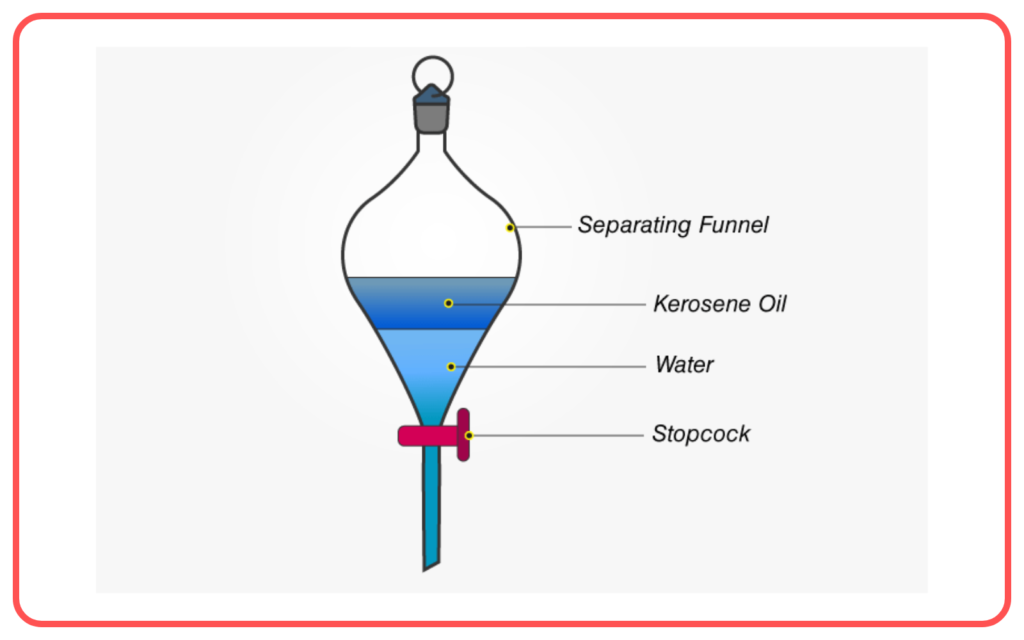
Decantation
- Decantation involves pouring off the liquid from a mixture after the solid has settled at the bottom due to gravity.
- It is a simple method used to separate liquids from solids or liquids with different densities.
- Example: Pouring water off sand or separating oil from water.
- Used for: Separating liquids from heavier solids (e.g., muddy water).
Conclusion
- The method of separation depends on the physical properties of the components in the mixture (such as size, solubility, boiling point, magnetic property, etc.).
- Filtration, distillation, evaporation, sublimation, and chromatography are commonly used methods to separate different types of mixtures in both scientific and everyday contexts.
- Understanding these separation methods is important in fields like chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
Let’s practice!

