Forests And Wildlife
Key Notes:
Forests and Wildlife
Introduction
- Forests are large areas covered chiefly with trees, and they provide numerous resources like wood, fruits, and medicinal plants.

- Wildlife refers to the wild animals, birds, insects, and other organisms living in their natural habitats, including forests, grasslands, and oceans.
- The preservation of forests and wildlife is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring sustainable development.
Importance of Forests
A. Ecological Benefits
- Biodiversity: Forests support a wide variety of life forms, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. They are home to more than half of the world’s species.

- Oxygen Production: Trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis, maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere.

- Climate Regulation: Forests play a significant role in controlling global climate by regulating temperature and moisture levels.

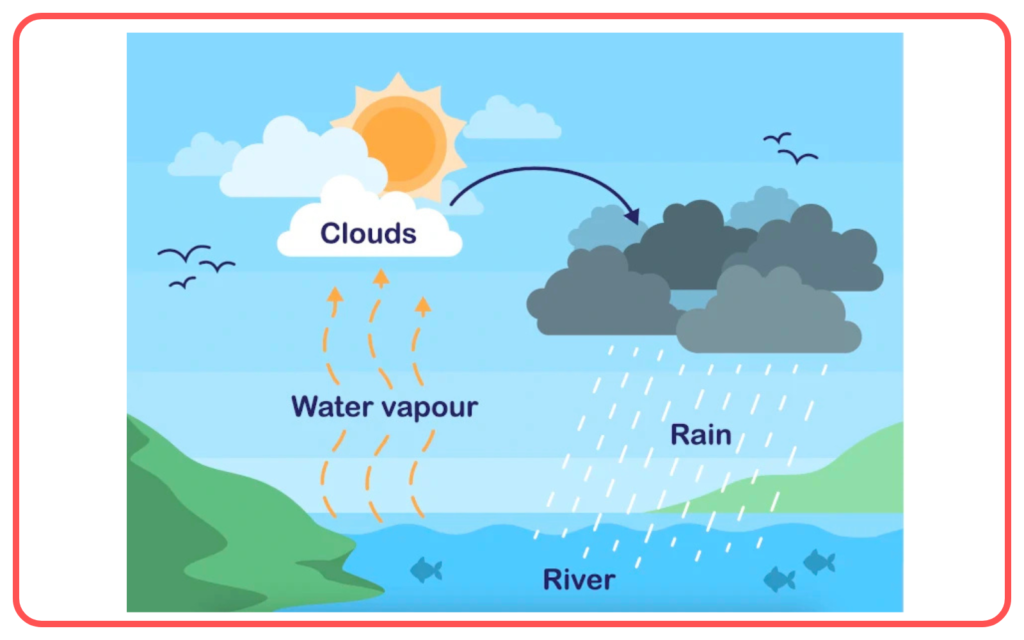
- Water Cycle: Forests help in the recharge of groundwater and regulate precipitation by releasing water vapor into the atmosphere.
B. Economic Benefits
- Forests provide timber, fuelwood, medicinal plants, fruits, and other non-timber forest products. These resources are essential for the economy and livelihood of millions of people.

- They contribute to tourism, with national parks and wildlife sanctuaries attracting eco-tourists.
C. Soil Conservation
- Tree roots help in preventing soil erosion and maintaining soil fertility. Forests also reduce the risk of flooding by absorbing excess water during heavy rains.

Importance of Wildlife
A. Ecological Role
- Wildlife plays a crucial role in pollination, seed dispersal, and maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
- Example: Bees pollinate plants, while bats help control insect populations.

- Animals contribute to the food chain by maintaining the population of other species and ensuring the stability of ecosystems.

B. Medicinal and Economic Value
- Many medicinal plants and animals have been used in the development of life-saving drugs.
- Example: Snakes and frogs provide toxins that are used in pharmaceuticals.
- Wildlife tourism is a significant source of income for many countries through the establishment of national parks, zoos, and wildlife sanctuaries.
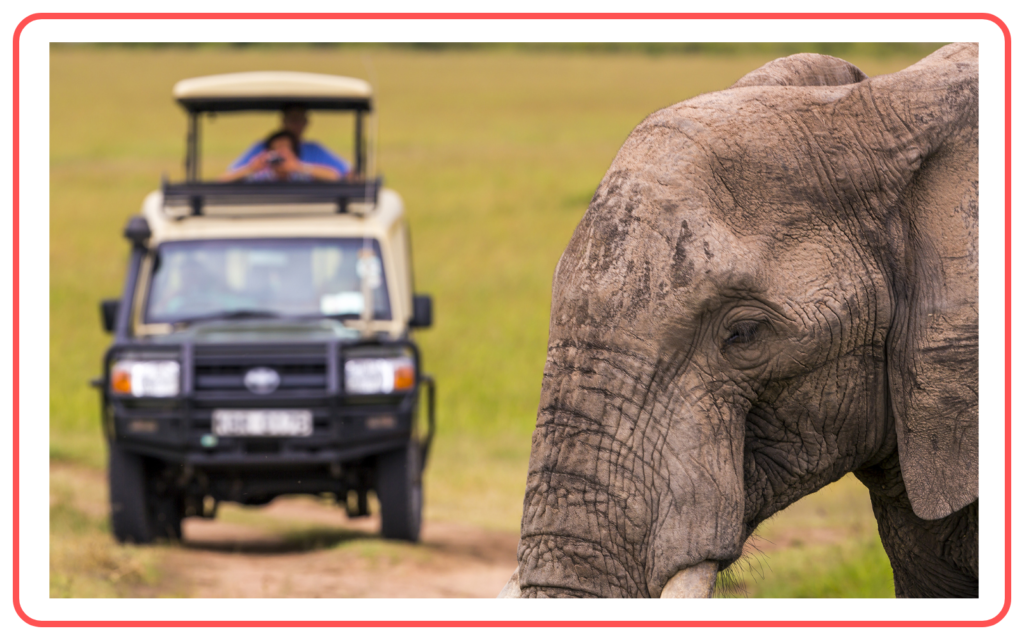

C. Aesthetic and Cultural Value
- Wildlife and forests provide aesthetic value, inspiring art, literature, and spiritual beliefs.
- Many indigenous cultures have deep connections with wildlife and forests, and their cultures and traditions depend on the conservation of these resources.
Threats to Forests
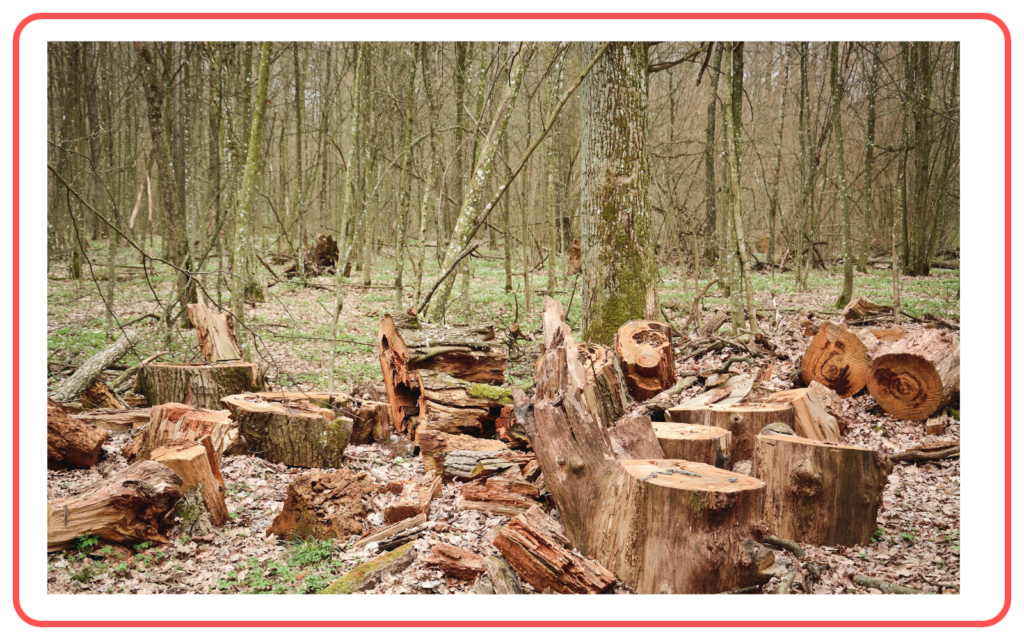
A. Deforestation
- Deforestation is the large-scale removal of forests for agricultural activities, urbanization, and industrialization.
- Causes of deforestation include:
- Commercial logging: Trees are cut down for timber and paper.
- Agricultural expansion: Forests are cleared for farming and grazing land.
- Urbanization: Expansion of cities leads to the loss of forested areas.
- Deforestation causes the loss of biodiversity, increases soil erosion, and contributes to climate change by releasing carbon dioxide stored in trees.

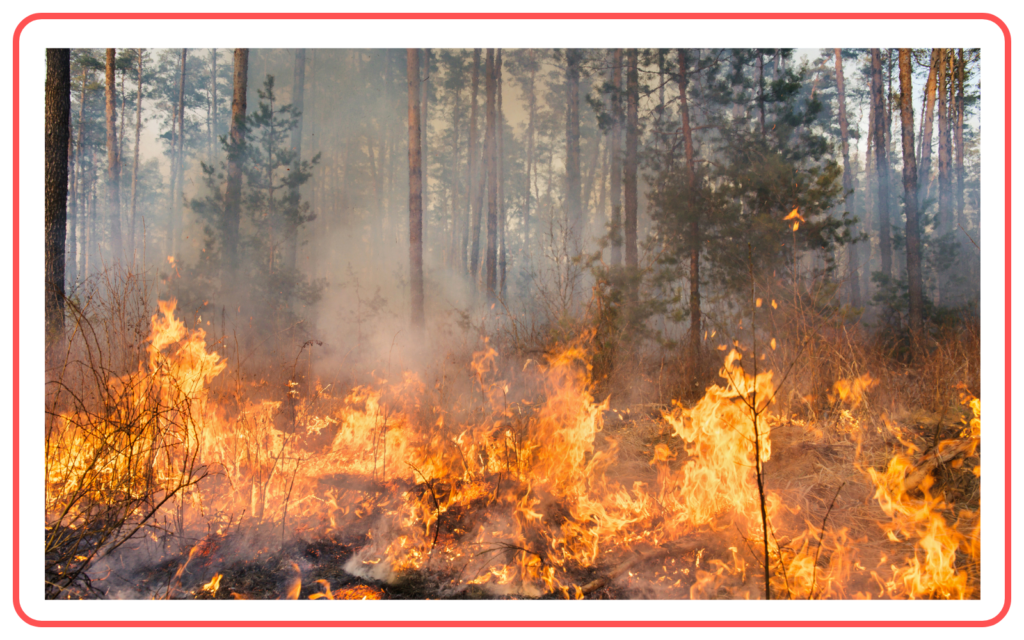
B. Forest Fires
- Forest fires, whether natural or man-made, destroy large areas of forest, contributing to the loss of habitats, soil fertility, and oxygen production.

C. Overgrazing and Pollution
- Overgrazing by livestock damages vegetation and prevents the regeneration of trees and plants.

- Pollution, including air, water, and soil pollution, impacts forest ecosystems and wildlife health.

Threats to Wildlife
A. Habitat Destruction
- Destruction of forests, wetlands, and grasslands due to human activities forces wildlife out of their natural habitats, leading to species extinction.

- Urban sprawl and deforestation are major causes of habitat loss for many species.
B. Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
- Poaching involves hunting wildlife illegally for their skins, tusks, horns, and other body parts.

- The illegal trade of wildlife products, such as ivory, rhino horns, and tiger skins, threatens the survival of species like tigers, elephants, and rhinos.

C. Pollution
- Chemical pollutants like pesticides and industrial waste harm wildlife by contaminating food sources, water, and habitats.
- Plastic waste in oceans and rivers causes harm to marine life and other species.

D. Climate Change
- Climate change alters habitats and disrupts food chains, affecting species’ migration, reproduction, and survival.
- Example: Rising temperatures can affect the breeding cycles of certain species, while others may not survive in the altered conditions.

Conservation of Forests and Wildlife
A. Afforestation and Reforestation
- Afforestation is the process of planting trees in an area where there were no forests, while reforestation is the replanting of trees in deforested areas.

- Governments and organizations promote afforestation through tree plantation drives to increase the forest cover.

B. Wildlife Protection Laws
- Many countries have enacted wildlife protection laws and established national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves to protect endangered species.
- Example: Project Tiger in India aims to protect tiger populations by creating reserves and promoting conservation efforts.

C. Community Participation
- Involving local communities in forest management, conservation, and wildlife protection programs is essential.

- Eco-tourism promotes the conservation of wildlife by generating income for local communities, helping them become stakeholders in conservation.
D. Reducing Pollution
- Waste management, reducing carbon emissions, and avoiding harmful chemicals can help reduce the pollution that negatively affects forests and wildlife.
Conclusion
- Forests and wildlife are crucial for the balance of nature, economic well-being, and cultural heritage.
- Conservation efforts are necessary to prevent further damage to these resources, and sustainable management is the key to their long-term survival.
- It is important to raise awareness and take collective action to ensure the protection of forests and wildlife for future generations.
Let’s practice!

