Ecosystem-What Are Its Components
Key Notes:
Introduction to Ecosystem:
- An ecosystem is a community of living organisms (biotic factors) and their non-living environment (abiotic factors) interacting as a functional unit.

- Ecosystems can be found in various forms, such as forests, grasslands, oceans, and even urban areas.
Components of an Ecosystem:
- Biotic Components:
- These are the living organisms within an ecosystem.
- They include plants, animals, microorganisms, and humans.
- Biotic components interact with each other through various relationships like predation, competition, and symbiosis.
- Abiotic Components:
- These are the non-living factors in an ecosystem.
- Abiotic components include soil, water, air, temperature, sunlight, and nutrients.
- These factors influence the distribution and behavior of biotic components.

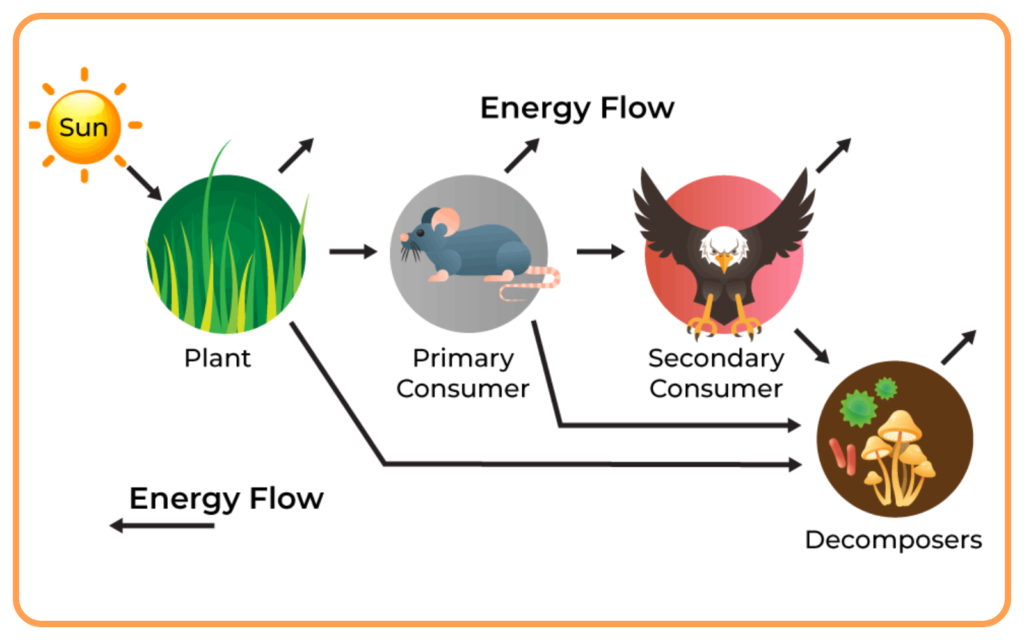
Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers:
- Producers are autotrophic organisms (e.g., plants) that produce their own food through photosynthesis.

- Consumers are heterotrophic organisms (e.g., herbivores, carnivores) that obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
- Decomposers (e.g., bacteria, fungi) break down dead organisms and organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Food Chains and Food Webs:
- Food chains represent the flow of energy from one organism to another as they consume each other.
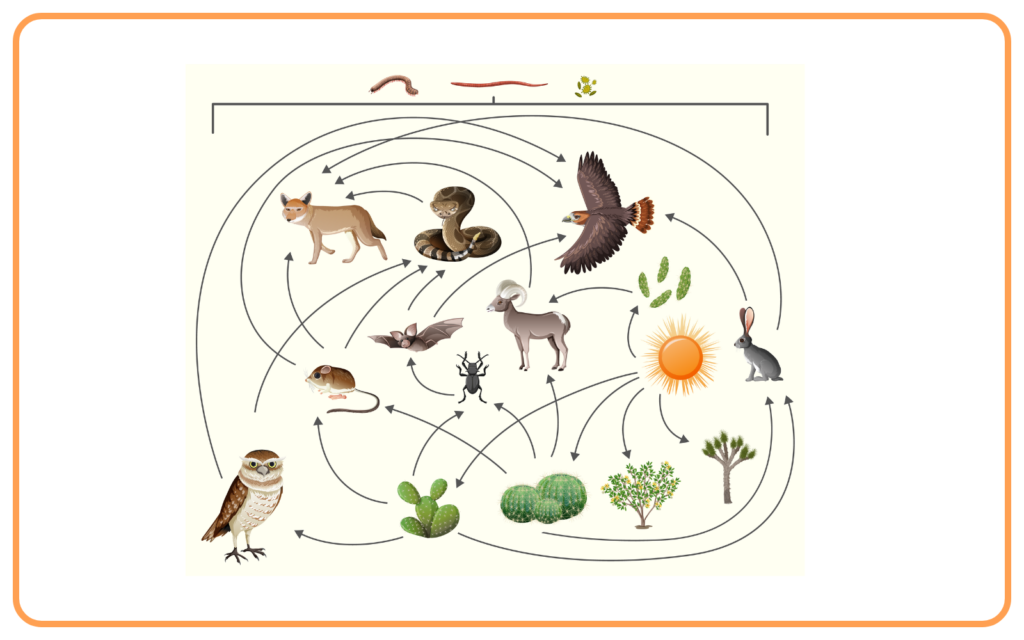
- Food webs are more complex and show interconnected food chains in an ecosystem, illustrating the diverse relationships between organisms.
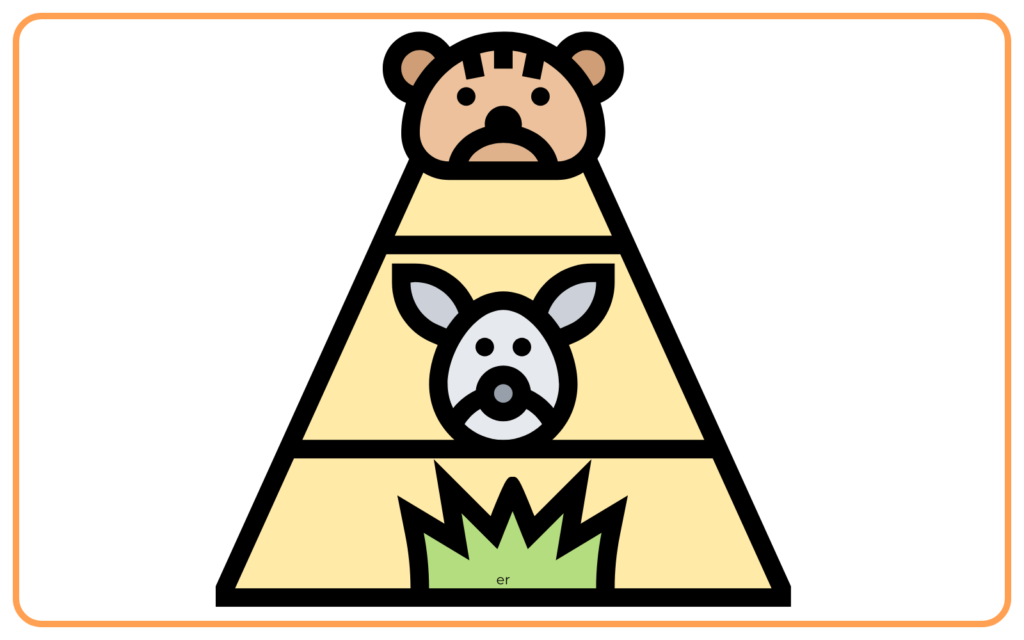
Trophic Levels:
- Trophic levels are the hierarchical levels in a food chain or food web, including producers (1st level), primary consumers (2nd level), secondary consumers (3rd level), and so on.
- Energy is transferred from one trophic level to another, with energy loss occurring at each level.
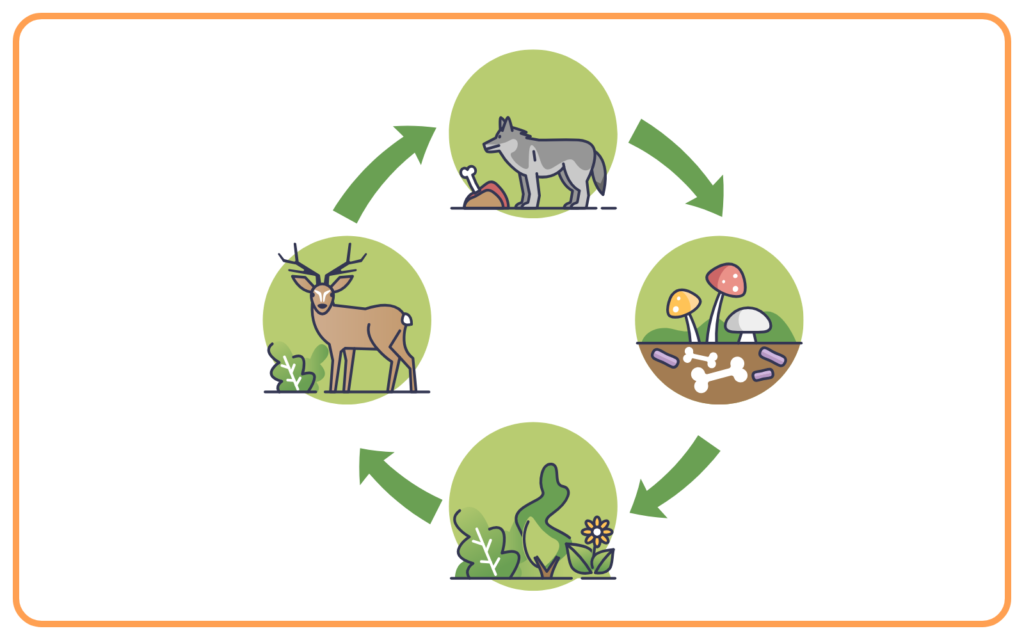
Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling:
- Energy flows through ecosystems in a unidirectional manner, while nutrients are cycled within the ecosystem.
- Decomposers play a crucial role in breaking down dead organisms, returning nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus to the soil or water for reuse.
Habitat and Niche:
- A habitat is the physical environment where an organism lives.
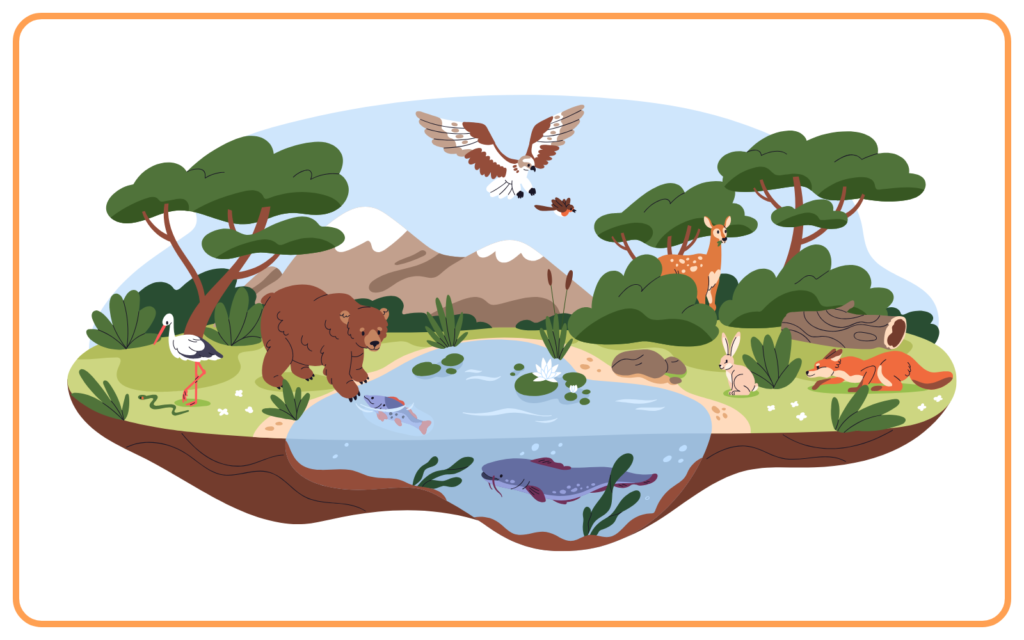

- A niche refers to an organism’s role and position within the ecosystem, including its interactions with other species and its specific adaptations.
Human Impact on Ecosystems:
- Human activities such as deforestation, pollution, habitat destruction, and over-exploitation of resources can disrupt ecosystems and lead to biodiversity loss.

Conclusion:
- Ecosystems are complex and dynamic systems consisting of both living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components.
- Understanding the components and interactions within ecosystems is crucial for conserving biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance.
Let’s practice!

