Alternative Or Non Conventional Sources Of Energy
Key Notes:
Alternative or Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
Introduction
- Non-conventional sources of energy are those energy sources that are renewable and environmentally friendly.

- These sources are alternatives to conventional (fossil) fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are non-renewable and cause environmental harm.
- Non-conventional sources are sustainable and help in reducing pollution and combating global warming.
Types of Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
A. Solar Energy

- Solar energy is energy derived from the sunlight.
- Solar panels (photovoltaic cells) are used to convert sunlight into electricity.
- Advantages:
- Renewable and abundant.
- Reduces electricity bills.
- No pollution.
- Uses:
- Solar lights, heating, and electricity generation.
B. Wind Energy
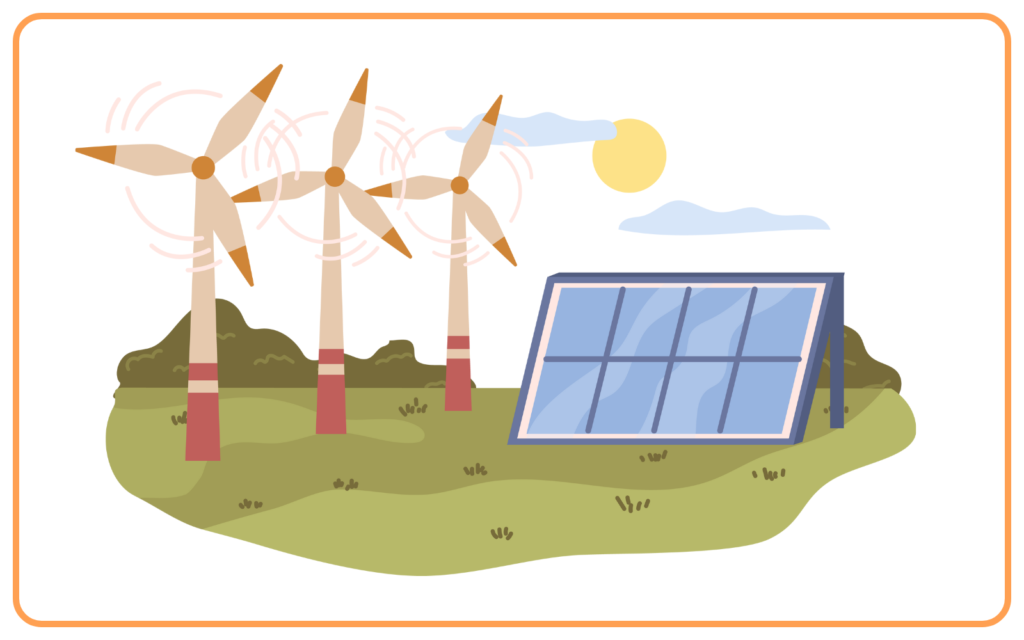
- Wind energy is generated using wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which is then converted to electricity.
- Advantages:
- Clean and renewable.
- Minimal environmental impact.
- Uses:
- Power generation in wind farms.
C. Hydroelectric Energy
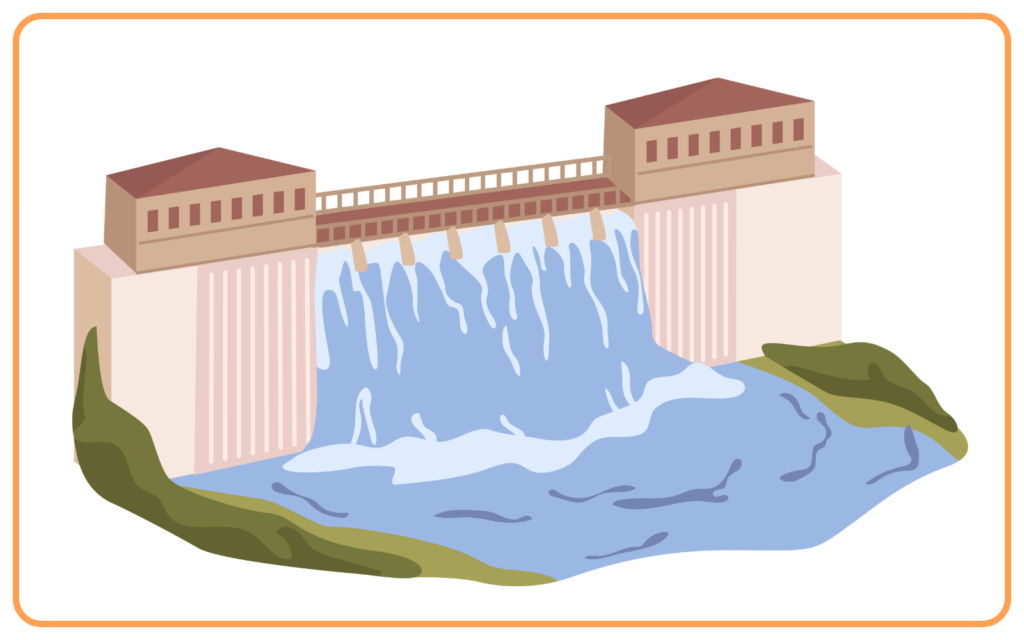
- Hydropower or hydroelectric energy uses the flow of water (rivers or dams) to generate electricity.
- Water flowing from a height is passed through turbines, generating mechanical energy which is then converted into electrical energy.
- Advantages:
- Renewable and reliable.
- Provides electricity to large areas.
- Uses:
- Large-scale electricity generation in hydroelectric plants.
D. Geothermal Energy
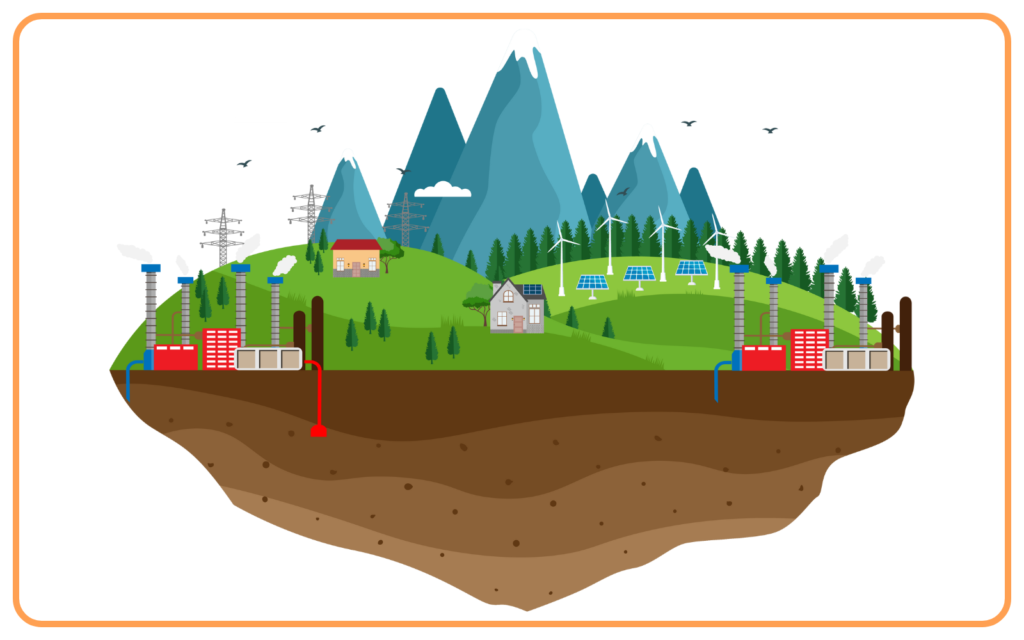
- Geothermal energy is heat derived from the Earth’s internal heat sources like hot springs, geysers, and geothermal reservoirs.
- This heat can be used to generate electricity or provide heating.
- Advantages:
- Continuous and reliable source of energy.
- Minimal environmental impact.
- Uses:
- Power plants and heating systems.
E. Biomass Energy
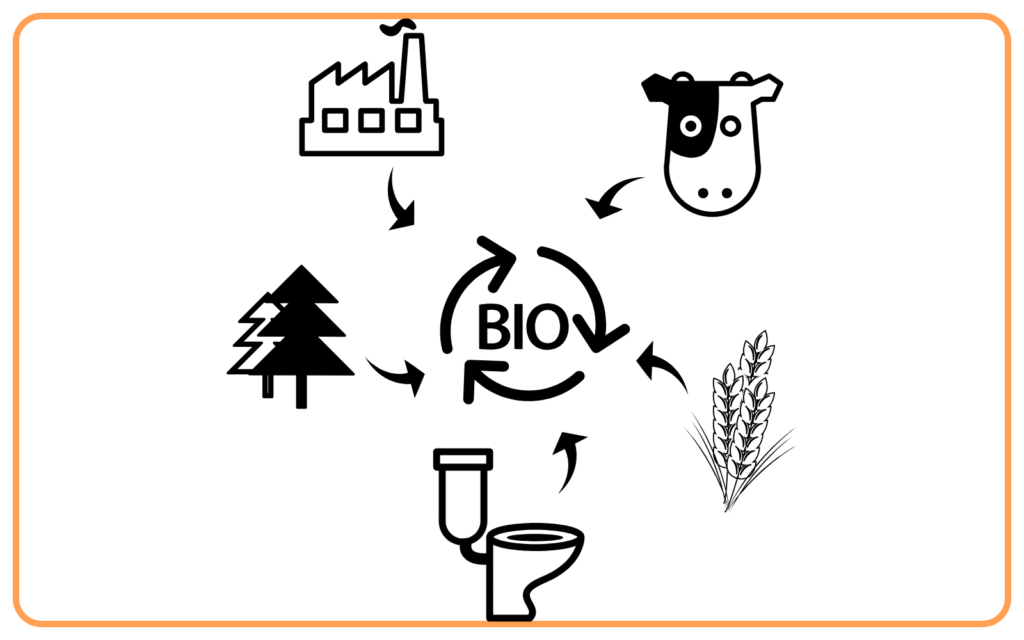
- Biomass energy comes from organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and animal waste.
- These materials are burned or decomposed to release energy, which can be used for heating or electricity generation.
- Advantages:
- Reduces waste.
- Can be used for heating and electricity.
- Uses:
- Biomass power plants, cooking stoves, and biogas generation.
F. Tidal Energy
- Tidal energy is produced from the movement of ocean tides.
- Tidal turbines or barrages are used to convert the kinetic energy of moving water into electricity.
- Advantages:
- Predictable and reliable source of energy.
- No pollution.
- Uses:
- Coastal regions for electricity generation.
Characteristics of Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
- Renewable: These sources can be replenished naturally and are not depleted when used.
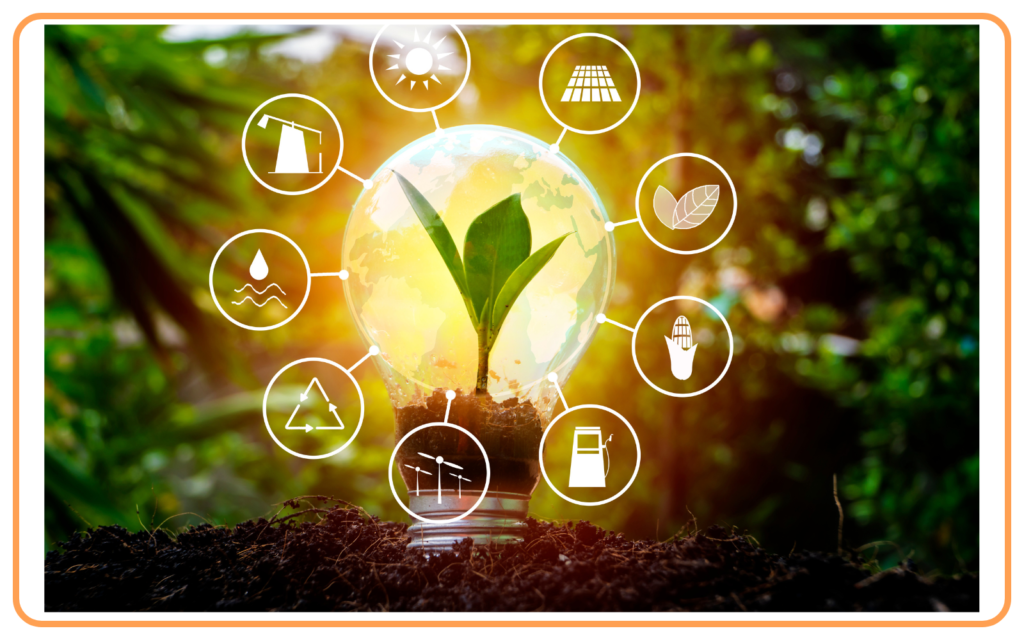

- Environmentally Friendly: They produce little or no pollution, making them clean alternatives to fossil fuels.

- Sustainable: Non-conventional energy sources can be used for the long term without the risk of running out.

- Abundant: Resources like sunlight, wind, and water are available in large quantities.

- Low Operating Costs: Once the infrastructure is set up, the operational costs for renewable sources are lower compared to fossil fuels.

Advantages of Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
- Sustainability: These sources provide energy without the fear of depleting natural resources.

- Environmentally Safe: They produce little to no greenhouse gases, reducing pollution and the effects of global warming.
- Economic Benefits: Reduced reliance on imported fuels, leading to energy security and economic independence.

- Job Creation: The development and maintenance of renewable energy projects can create jobs in various sectors, such as manufacturing and technology.

Disadvantages of Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
- High Initial Investment: The setup cost for renewable energy technologies (like solar panels, wind turbines) can be high.
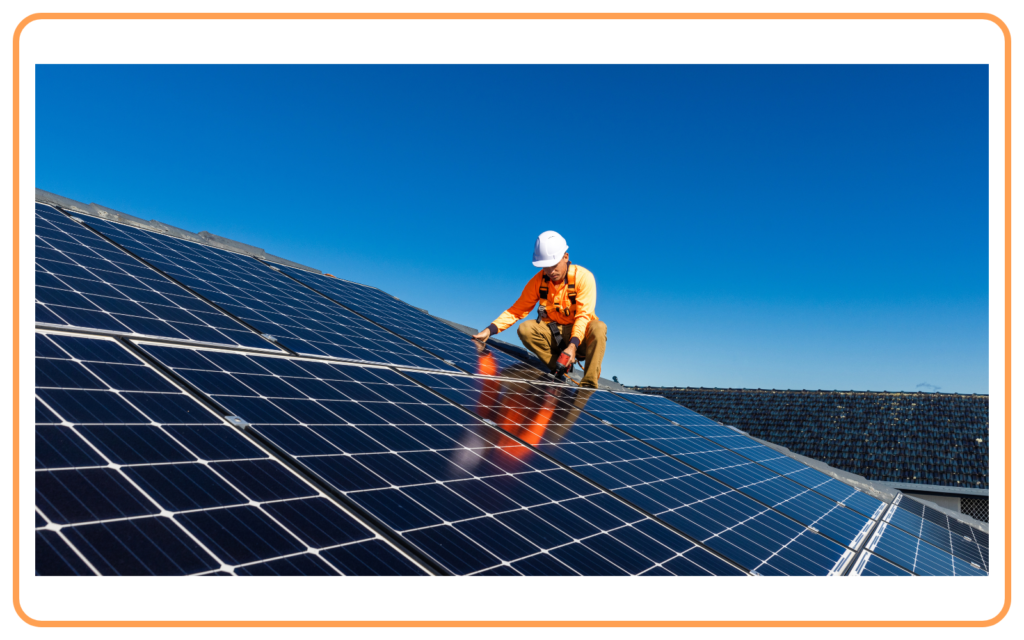

- Intermittency: Some renewable sources like solar and wind energy are intermittent, meaning they are dependent on weather conditions and time of day.
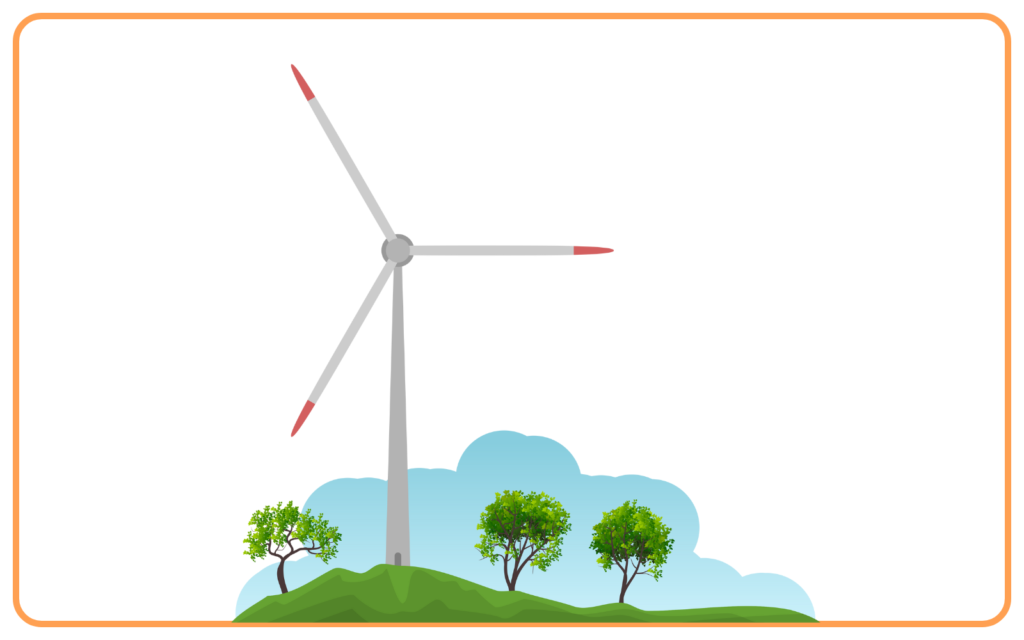

- Geographic Limitations: Certain sources like geothermal energy and hydropower are location-specific.
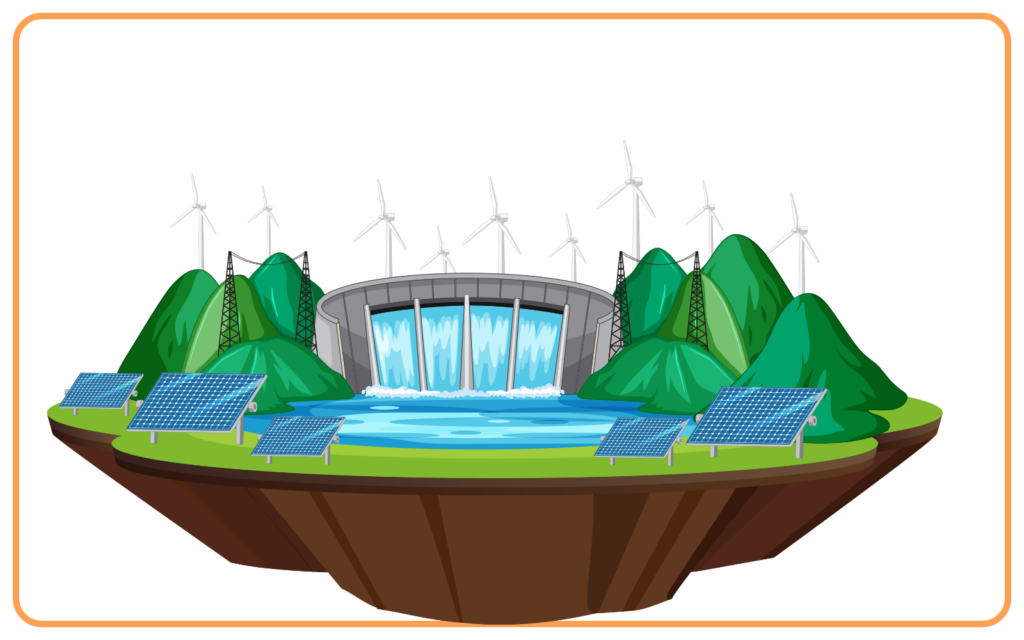

- Space Requirements: Wind farms and solar panels require a lot of space for effective energy generation.
Comparison of Conventional and Non-Conventional Energy Sources
| Criteria | Conventional Sources | Non-Conventional Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Limited (non-renewable) | Abundant (renewable) |
| Pollution | High | Low or no pollution |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High initial setup cost |
| Sustainability | Unsustainable | Sustainable |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate to High |
Future of Non-Conventional Energy Sources
- With advancements in technology and increased awareness of environmental concerns, the use of renewable energy is expected to grow rapidly.

- Governments and industries are investing in research and development to make renewable energy more efficient, affordable, and accessible.
- The shift to non-conventional sources is essential to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate environmental damage.
Conclusion
- Non-conventional energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, biomass, and tidal energy are sustainable, environmentally friendly, and renewable.
- Though there are some challenges, the advantages of these sources outweigh their drawbacks, making them crucial for a cleaner, more sustainable future.
- Transitioning to non-conventional sources of energy is vital for reducing the harmful effects of fossil fuel consumption and ensuring long-term energy security.
Let’s practice!

