Conventional Sources Of Energy
Key Notes:
Conventional Sources of Energy
Introduction
- Conventional sources of energy are those which have been used for a long time.
- These include fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, natural gas) and biomass.

- They are primarily non-renewable and are being depleted with excessive use.
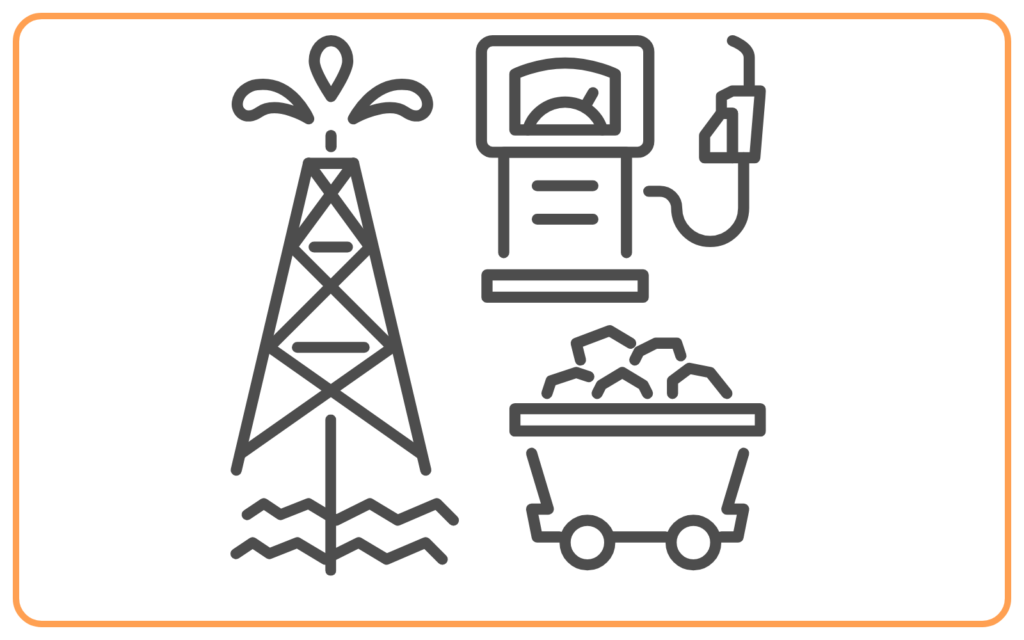
Types of Conventional Sources of Energy
A. Fossil Fuels
- Formed from the remains of dead plants and animals buried under the Earth’s surface for millions of years.
- Examples: Coal, Petroleum, and Natural Gas.
- Coal:
- A solid fossil fuel used for cooking, industrial processes, and electricity generation.
- It is a major source of thermal energy.
- Disadvantages: Causes air pollution and releases carbon dioxide (CO₂), contributing to global warming.

- Petroleum (Crude Oil):
- A liquid fossil fuel used to produce petrol, diesel, kerosene, and LPG.
- Major use: Transportation and domestic fuel.
- Disadvantages: Limited availability and causes oil spills and pollution.

- Natural Gas:
- A clean-burning fuel used for cooking, heating, and electricity generation.
- Example: CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas).
- Advantages: Cleaner compared to coal and petroleum.

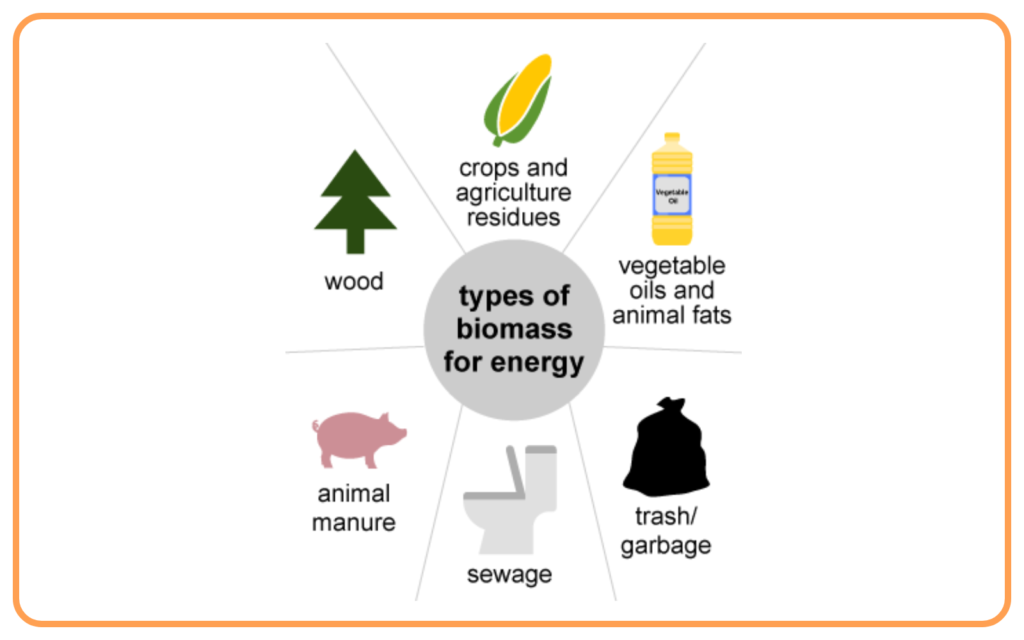
B. Biomass
- Biomass refers to energy derived from organic matter like wood, agricultural waste, and animal dung.
- It is commonly used in rural areas for cooking and heating.
- Biogas:
- Produced through the decomposition of organic waste (e.g., animal dung) in a biogas plant.
- Components: Methane (CH₄), which is a flammable gas.
- Advantages:
- Produces clean energy.
- Reduces dependence on wood.
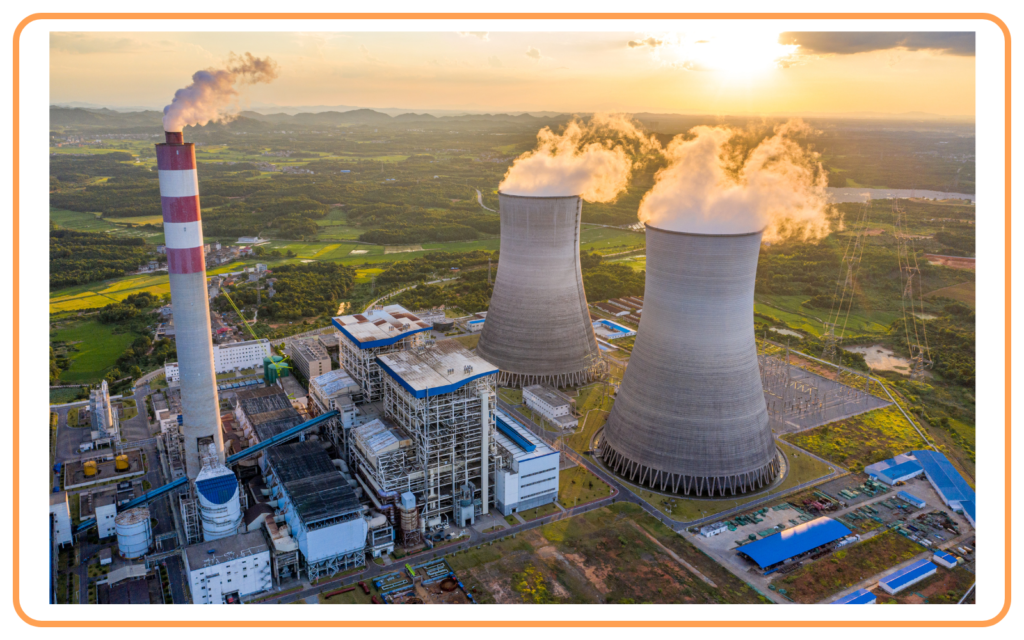
C. Thermal Power Plants
- Fossil fuels like coal are burned to produce thermal energy that is used to generate electricity.
- Example: Steam turbines in thermal power plants.
- Disadvantages:
- Causes air pollution.
- Releases large amounts of greenhouse gases.

Characteristics of Conventional Energy Sources
- Non-Renewable:
- These sources are finite and will run out if used excessively.
- Widely Used:
- Fossil fuels are the primary sources for electricity, transportation, and industry.

- Environmental Impact:
- They cause air pollution, global warming, and acid rain.

- High Energy Output:
- Fossil fuels release large amounts of energy upon combustion.
Environmental Problems Due to Fossil Fuels
- Air Pollution:
- Burning coal and petroleum releases carbon dioxide (CO₂), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and other pollutants.
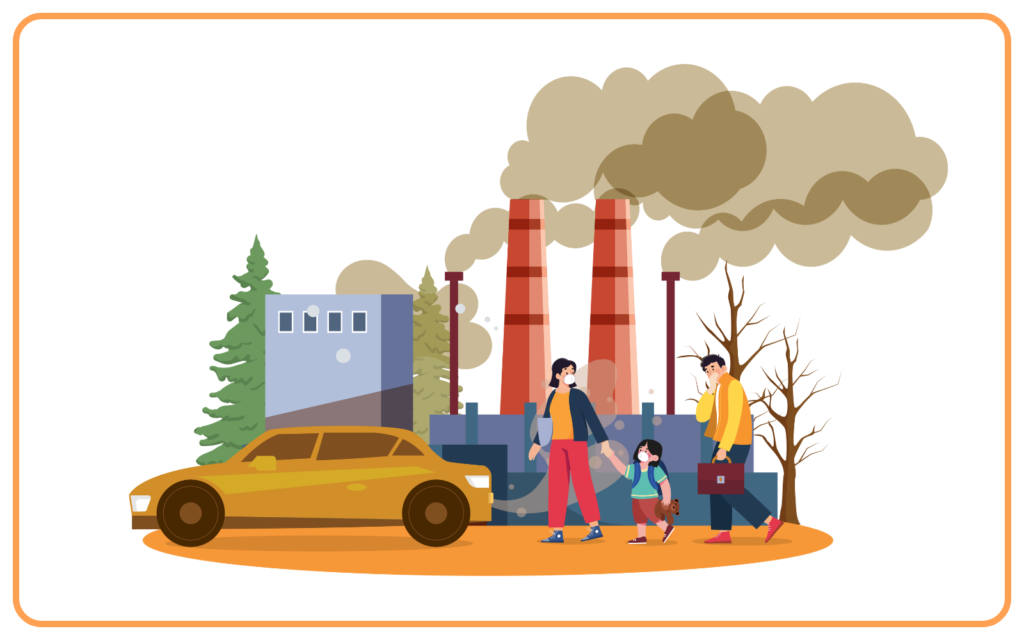

- Global Warming:
- Excessive CO₂ emissions trap heat, causing climate change.

- Acid Rain:
- Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine with rainwater to form acid rain, which harms crops and water bodies.

- Depletion of Resources:
- Fossil fuels take millions of years to form and are being consumed rapidly.
Comparison of Conventional Sources
| Energy Source | Availability | Usage | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | Plentiful but depleting | Electricity, industries | Air pollution, global warming |
| Petroleum | Limited | Transport, fuel | Pollution, oil spills |
| Natural Gas | Limited | Cooking, electricity | Less polluting but finite |
| Biomass | Renewable (limited) | Cooking, rural usage | Low efficiency, indoor smoke |
Importance of Saving Conventional Energy Sources
- Non-renewable Nature: Once exhausted, they cannot be replenished.

- Environmental Damage: Reducing dependence can control pollution and climate change.

- Energy Crisis: Conserving energy ensures availability for future generations.
Measures to Conserve Conventional Energy Sources
- Use energy-efficient appliances (e.g., LED lights).

- Opt for public transport or carpooling to reduce fuel consumption.

- Promote the use of renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy.
- Reduce wastage of energy in households and industries.
Key Terms to Remember
- Fossil Fuels: Coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
- Biomass: Energy derived from organic matter.
- Biogas: A clean fuel produced from decomposed organic waste.
- Thermal Power: Electricity generation by burning fossil fuels.
- Air Pollution: Contamination caused by harmful gases released during combustion.
Conclusion
Conventional sources of energy like fossil fuels and biomass have powered the world for centuries. However, their depletion and environmental impact emphasize the urgent need for energy conservation and the adoption of renewable energy sources.
Let’s practice!

