Domestic Electric Circuits
Key Notes:
Domestic Electric Circuits
Introduction
- A domestic electric circuit is the network of electrical wiring and devices used to distribute electric power to different appliances in homes.
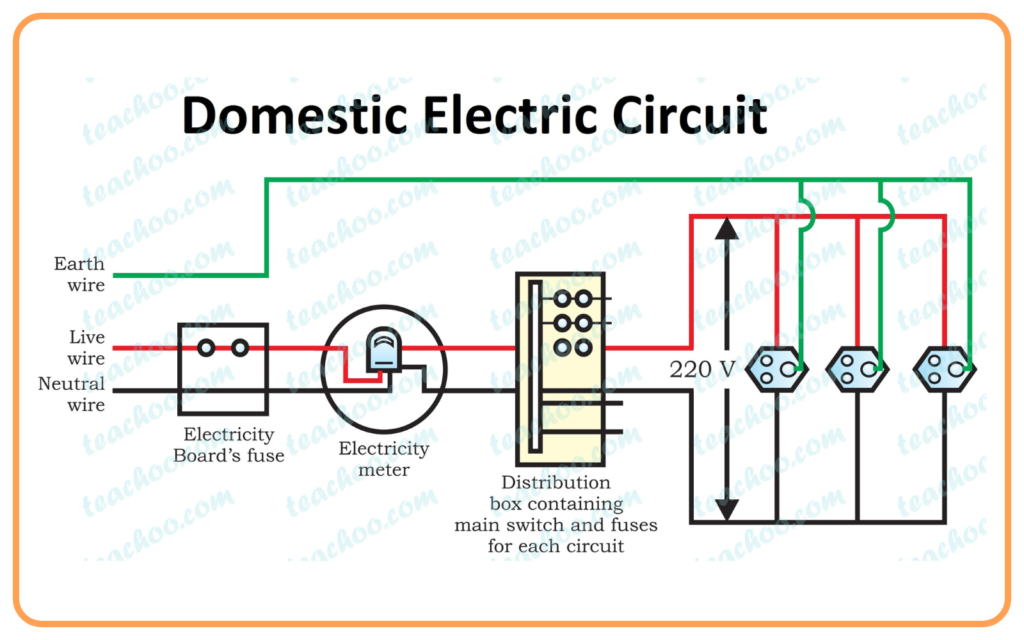
- It ensures the safe and efficient supply of electricity.
Key Components of Domestic Electric Circuits
- Main Supply:
- Electricity is supplied to houses through the mains supply (usually 220V AC in India).
- The supply enters the house through service wires.
- Electric Meter:
- It measures the amount of electrical energy consumed in the house.
- The reading is in kilowatt-hours (kWh), also called units of electricity.
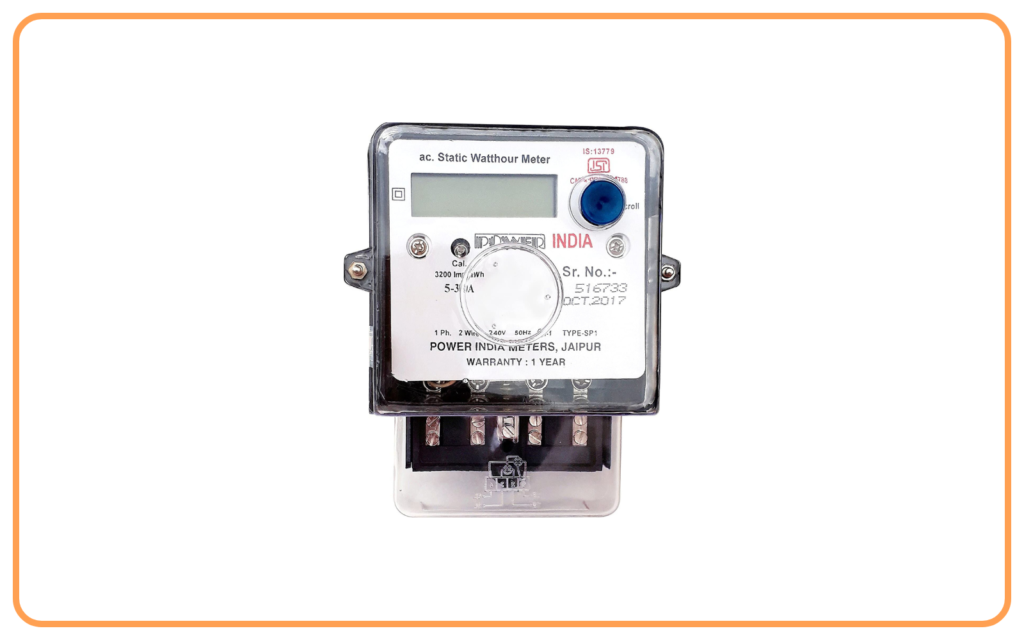

- Main Fuse (Main Switch):
- The main fuse protects the entire electrical system from overloading or short circuits.
- It disconnects the supply if the current exceeds a safe limit.
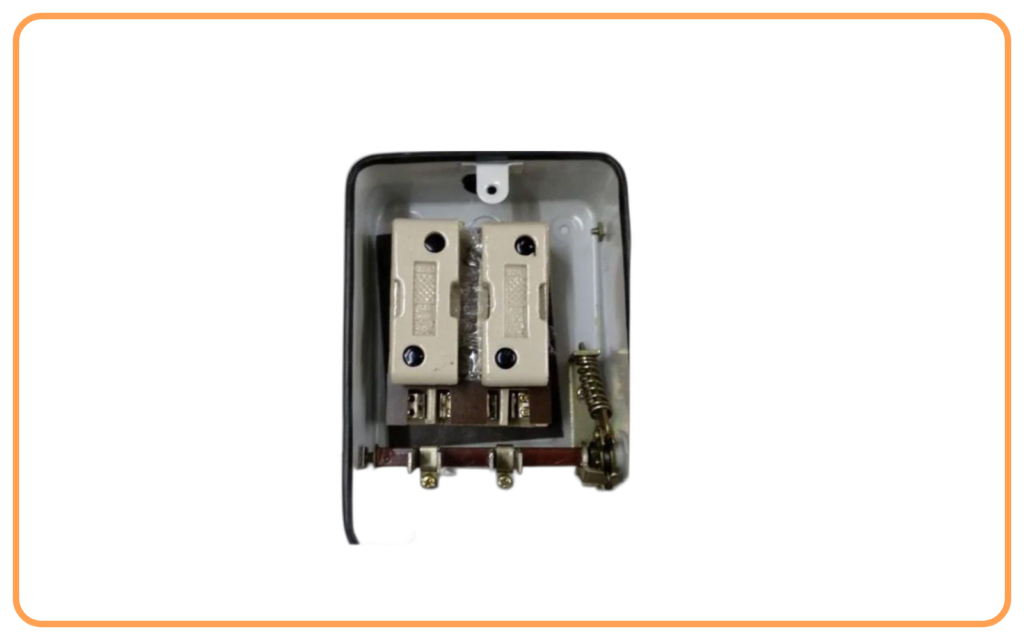

- Distribution Board:
- Contains circuit breakers or fuses for different sections of the house.
- Modern homes use Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) instead of traditional fuses.
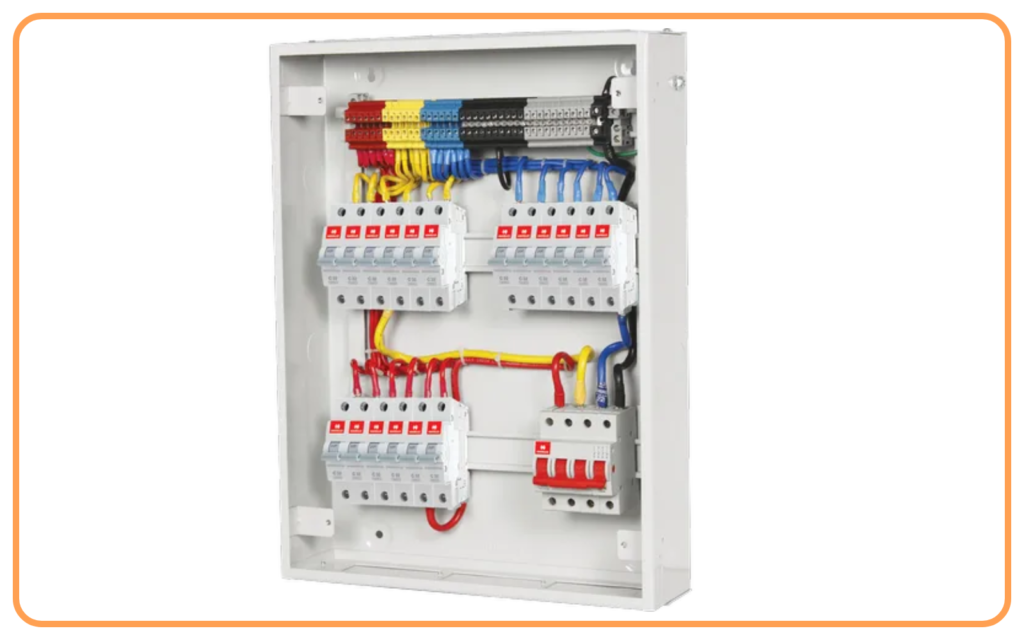

- Wiring:
- Wiring distributes power to different parts of the house.
- Common types of wiring are parallel wiring and series wiring.
- Domestic circuits use parallel wiring for uniform voltage across all devices.

- Switches:
- Used to connect or disconnect appliances from the power supply.

- Sockets and Plugs:
- Electrical appliances are connected to the circuit using sockets and plugs.

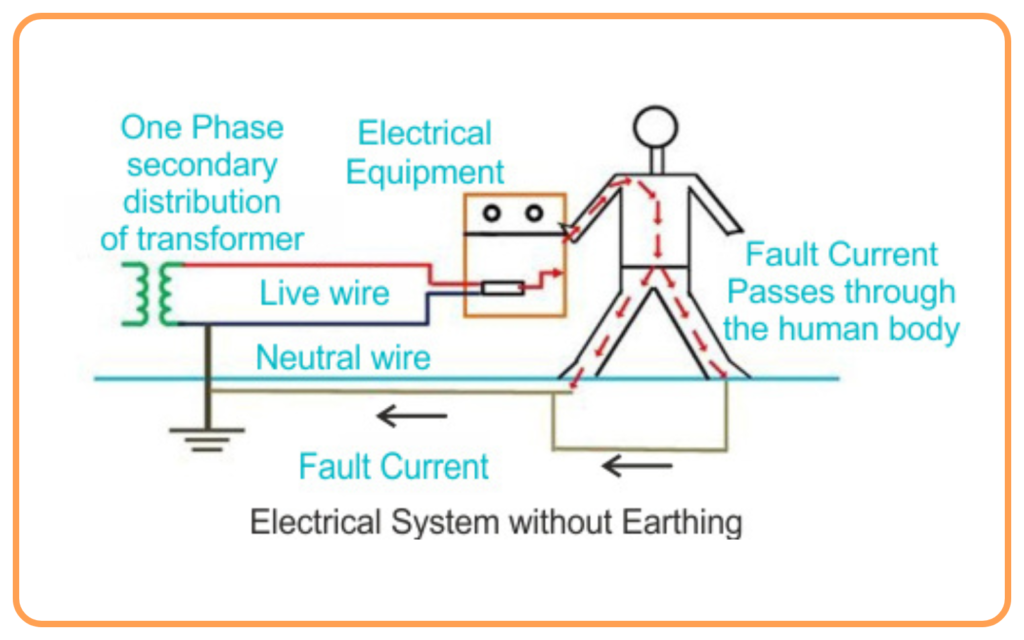
- Earth Wire (Grounding):
- A safety wire connected to the ground to prevent electric shocks in case of leakage of current.
Features of Domestic Electric Circuits
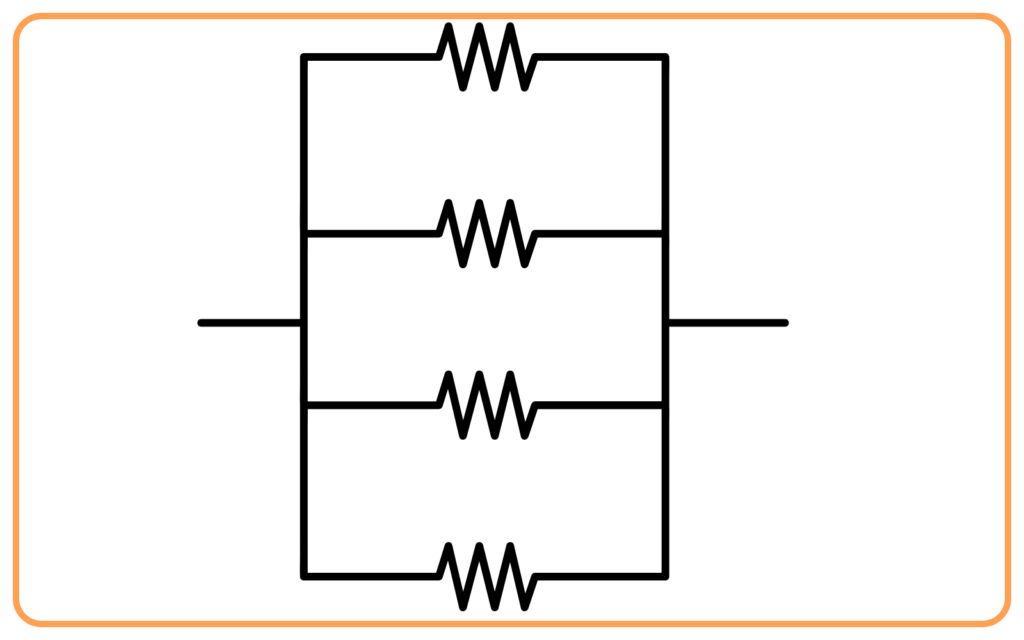
- Parallel Connection:
- In domestic wiring, all appliances are connected in parallel to ensure:
- Equal voltage (220V) across all devices.
- Independent operation of appliances.
- In domestic wiring, all appliances are connected in parallel to ensure:
- Two-Way Supply:
- The supply is through two wires:
- Live wire (Phase, Red): Carries current to appliances.
- Neutral wire (Black): Completes the circuit back to the supply.
- Earth wire (Green): Provides safety during current leaks.
- The supply is through two wires:
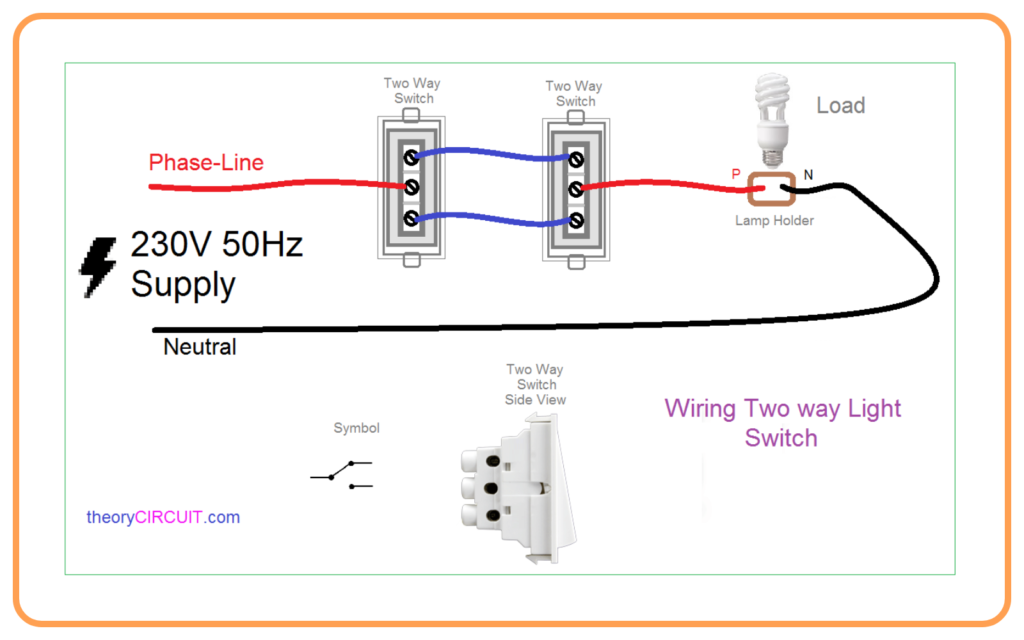
- Safety Devices:
- Devices like fuses and MCBs protect the system from:
- Overloading: When the current exceeds the safe limit.
- Short Circuit: When live and neutral wires touch each other, causing a sudden increase in current.
- Devices like fuses and MCBs protect the system from:
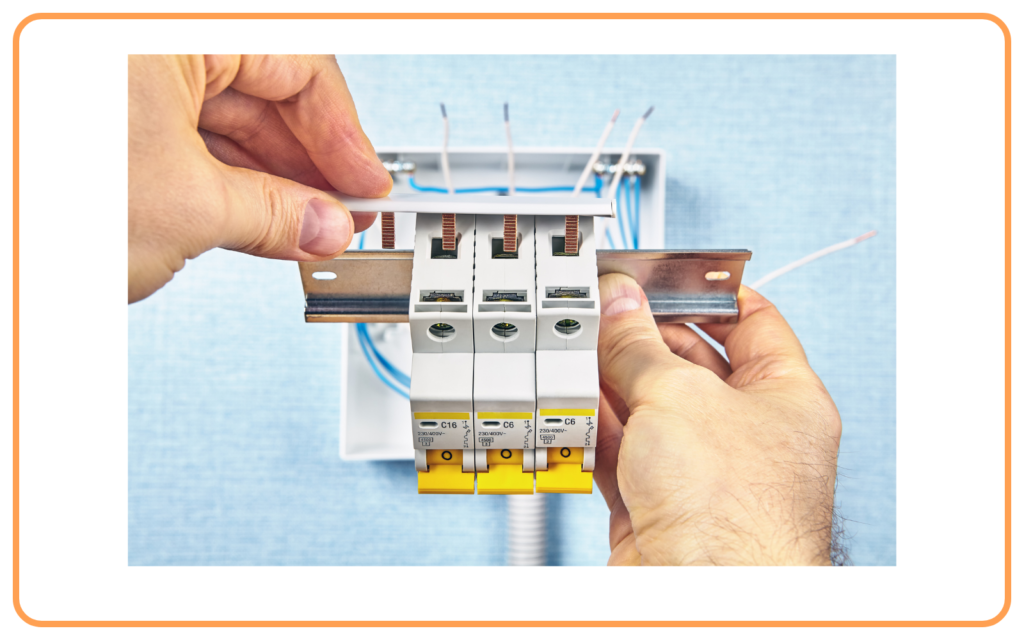
Overloading and Short Circuiting
- Overloading:
- When too many appliances are connected to the same circuit, it draws a large current.
- This can heat the wires and damage the insulation, causing fires.
- Short Circuit:
- Happens when the live wire and neutral wire come into contact directly.
- This results in a sudden flow of high current, damaging the circuit.
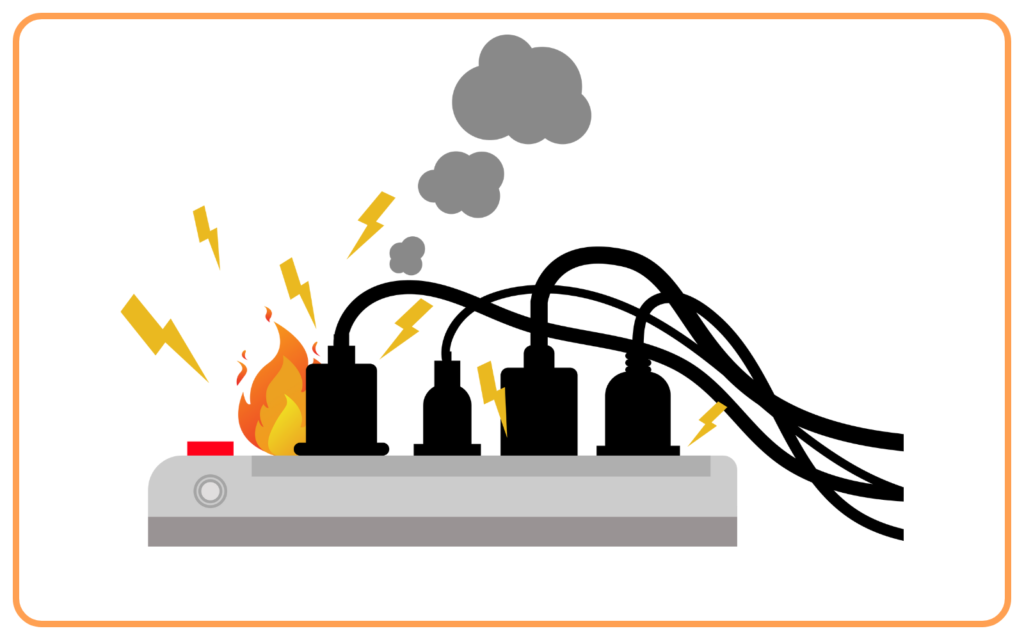
Solution: Use fuses or MCBs to protect against overloading and short circuits.
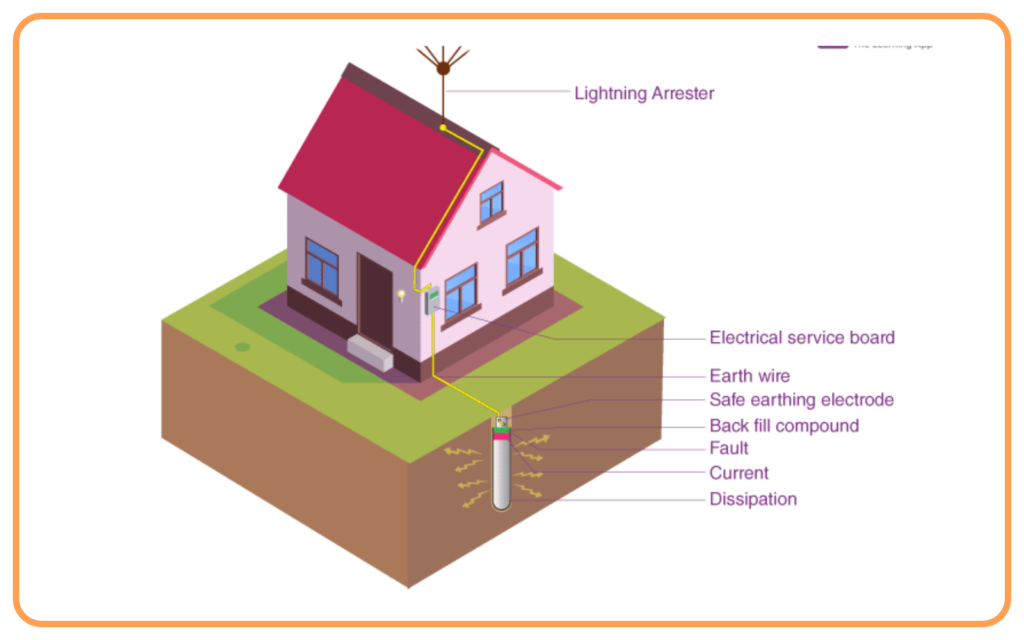
Earthing
- Earthing is the process of connecting the metal body of an appliance to the ground through an earth wire.
- It protects users from electric shocks by:
- Redirecting leaked current to the ground.
- Preventing the appliance from becoming live.
Example: Refrigerator and washing machine bodies are earthed for safety.
Fuse and MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
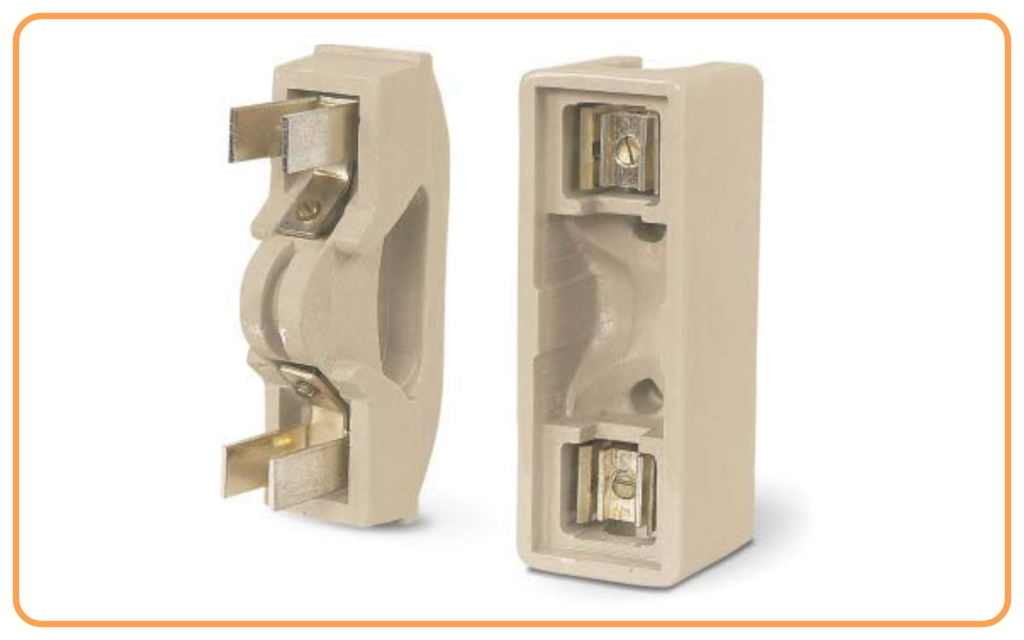
- Electric Fuse:
- A fuse is a safety device that breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a safe limit.
- It has a thin wire that melts when overheated.

- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker):
- An MCB is an automatic switch that turns off the supply when excessive current flows through the circuit.
- It is more reliable and convenient than a fuse.
Important Safety Tips
- Always use properly rated fuses and MCBs.
- Never overload the circuit by connecting too many devices.
- Use earthing for all metal appliances.
- Use insulated wires to prevent electric shocks.
- Avoid handling electrical appliances with wet hands.
Advantages of Parallel Wiring in Domestic Circuits
- Constant Voltage: Each appliance receives the same voltage (220V).
- Independent Control: Each appliance can be switched on/off independently.
- Safe and Efficient: Prevents overloading and short circuits more effectively.
Key Terms to Remember
- Live Wire: Carries current from the supply (Red).
- Neutral Wire: Returns current to the supply (Black).
- Earth Wire: Provides safety during faults (Green).
- Overloading: Excessive current in a circuit.
- Short Circuit: Direct contact between live and neutral wires.
- Fuse/MCB: Protects the circuit from damage.
Conclusion
Domestic electric circuits ensure the safe and efficient distribution of electricity in homes. The use of safety devices like fuses, MCBs, and earthing is essential to prevent accidents.
Let’s practice!

