Electric Generator
Key Notes:
Electric Generator
Introduction
- An electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.

- It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday.
- Generators are widely used in power plants, houses, and industries to produce electricity.
Principle
The electric generator works on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction:
- Whenever the magnetic flux linked with a coil changes, an EMF (Electromotive Force) is induced in the coil.
- The magnitude of the induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux.
The direction of the induced current is given by Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule.
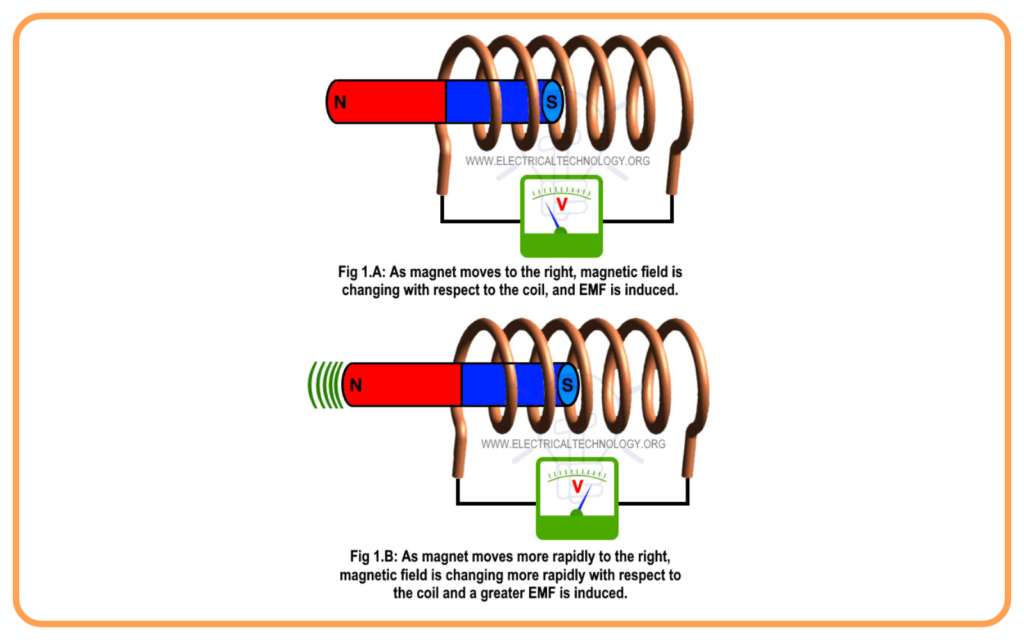
Types of Electric Generators
- AC Generator (Alternating Current Generator): Produces alternating current.
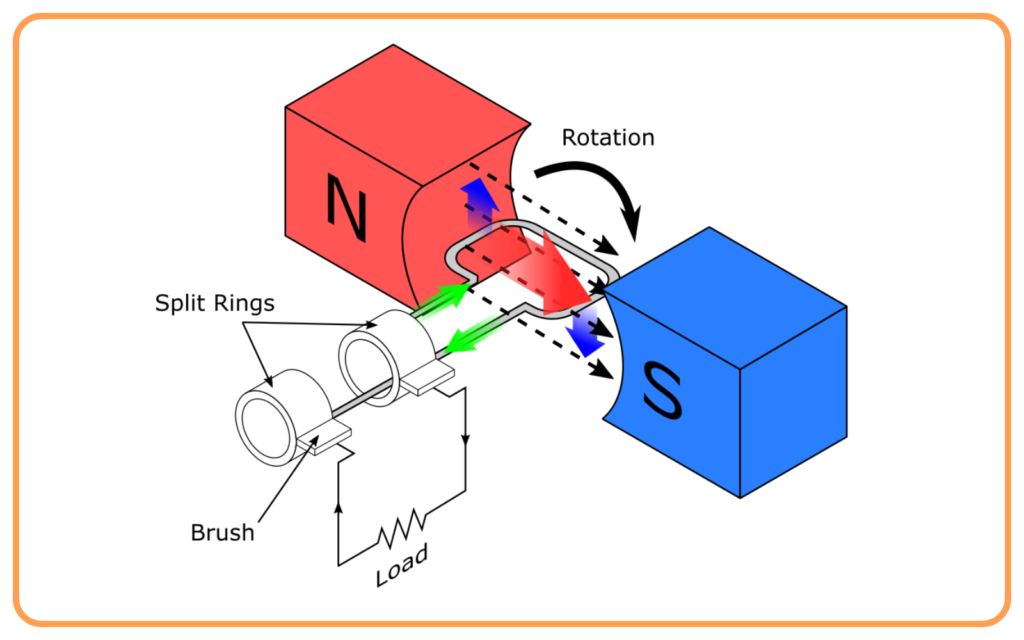
- DC Generator (Direct Current Generator): Produces direct current.
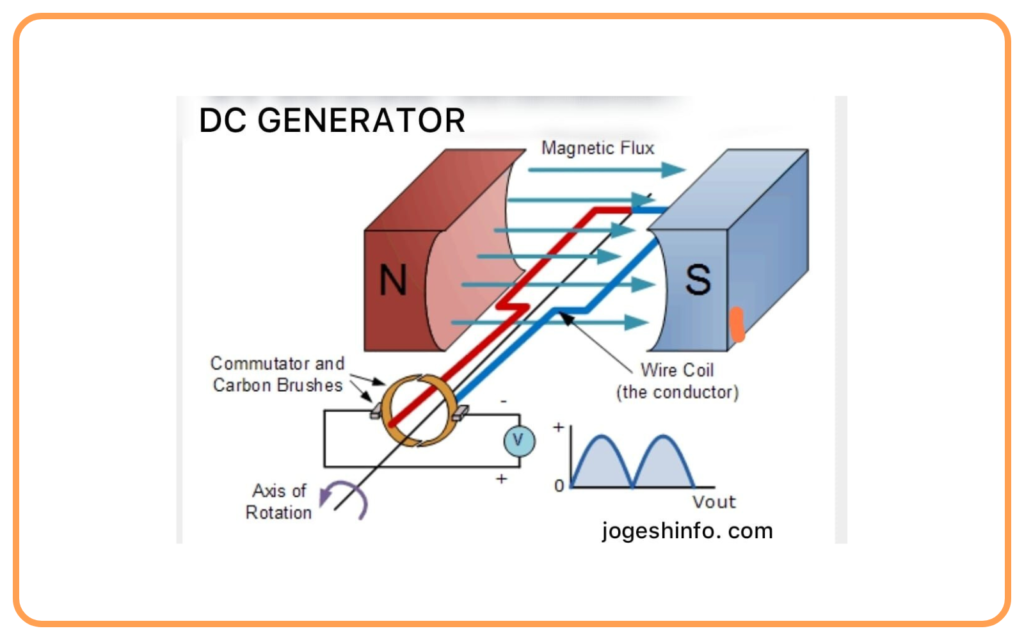
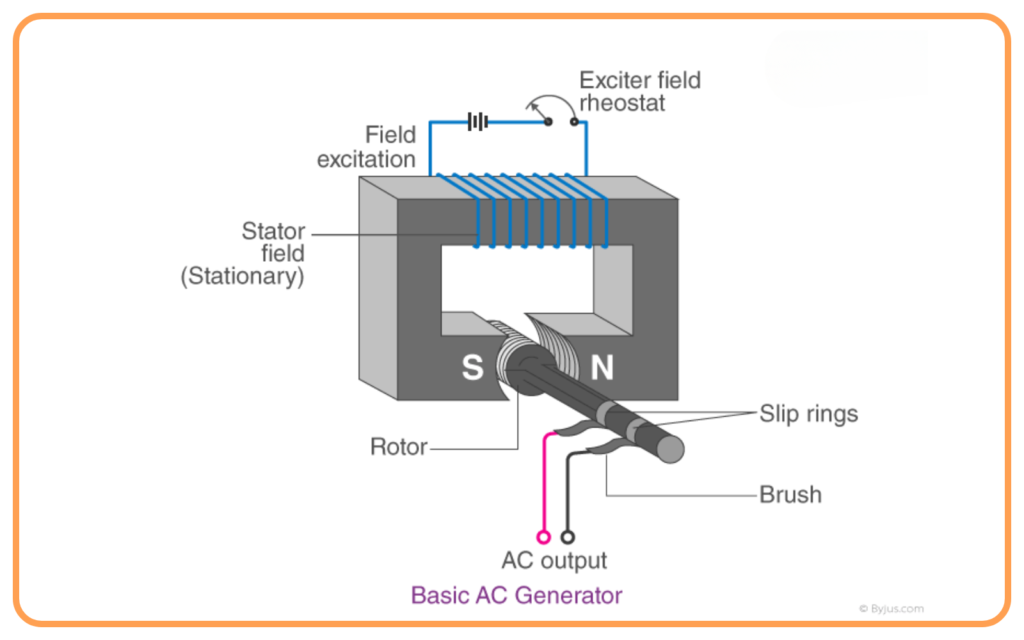
Construction of an AC Generator
The main parts of an AC generator are:
- Armature (Coil): A rectangular coil made of insulated copper wire that rotates in the magnetic field.
- Magnetic Field: Provided by strong magnets (electromagnets or permanent magnets).
- Slip Rings: Two rings connected to the ends of the coil. These rotate with the coil.
- Brushes: Carbon brushes press against the slip rings to transfer the current to the external circuit.
- Shaft: Rotates the coil using mechanical energy.

Working of an AC Generator
- The armature (coil) is rotated in the magnetic field using mechanical energy (from a turbine or engine).
- As the coil rotates, the magnetic flux linked with it changes continuously.
- According to Faraday’s Law, this change in magnetic flux induces an EMF in the coil.
- The direction of the induced current is determined by Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule.
- As the coil completes one rotation:
- The current reverses direction twice, producing an alternating current (AC).
- The slip rings ensure the ends of the coil remain connected to the external circuit.
Difference Between AC Generator and DC Generator
| Feature | AC Generator | DC Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Output Current | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Commutator | Uses slip rings | Uses split-ring commutator |
| Current Direction | Changes periodically | Flows in one direction |
Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule
To determine the direction of induced current:
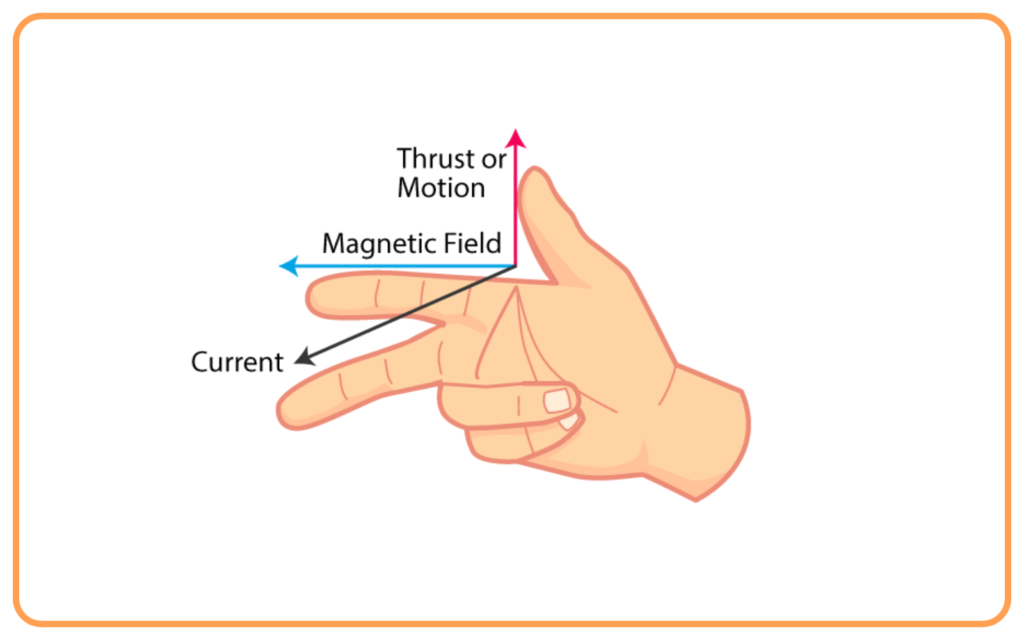
- Stretch your thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of the right hand at right angles to each other:
- Thumb → Direction of motion of the conductor.
- Forefinger → Direction of the magnetic field.
- Middle finger → Direction of the induced current.
Applications of Electric Generators
Electric generators are widely used in:
- Power Stations: To generate electricity for homes and industries.

- Backup Power Supply: Inverters and generators used during power cuts.
- Vehicles: To charge batteries in cars and trucks.
- Wind Turbines: To produce electricity using wind energy.

- Hydropower Plants: Converts the mechanical energy of water flow into electricity.

Key Points to Remember
- An electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
- Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule determines the direction of induced current.
- AC Generators produce alternating current, while DC Generators produce direct current.
- Generators are widely used to produce electricity in various sectors.
Diagram of an AC Generator
Ensure you practice and label a neat diagram of an AC generator, showing:
- Magnetic poles (N and S)
- Armature (coil)
- Slip rings
- Brushes
- Direction of motion and current
Conclusion
The electric generator is an essential device for producing electricity. It plays a crucial role in our daily lives by providing power for homes, industries, and transportation.
Let’s practice!

