Magnetic Field Due To Straight Current Carrying Conductor
Key Notes:
What is a Magnetic Field?
- A magnetic field is a region around a magnet or a current-carrying conductor where a magnetic force can be experienced.
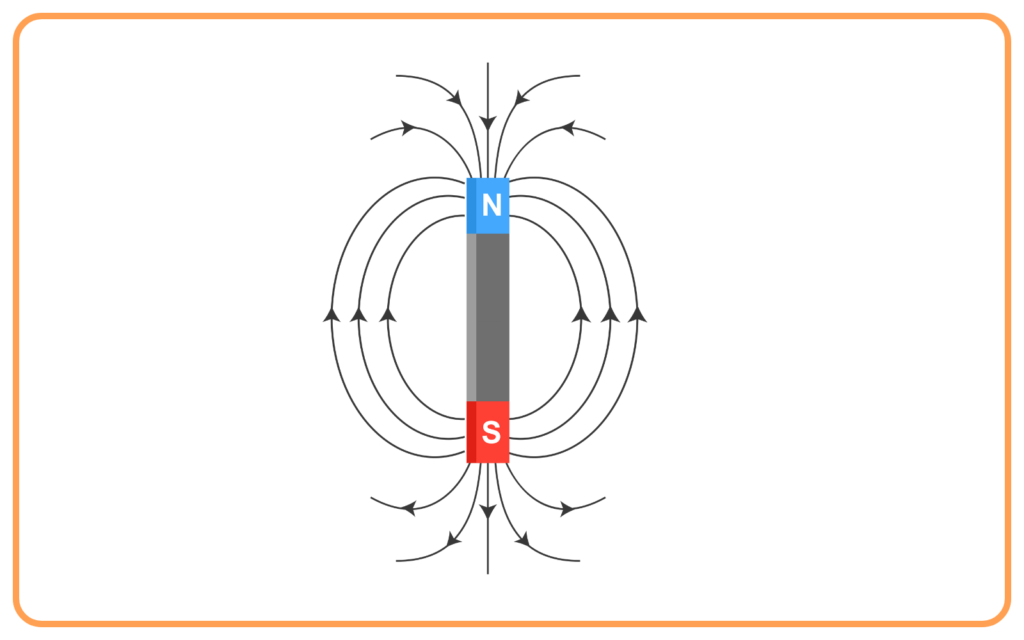
- It’s invisible, but we can visualize it using magnetic field lines. These lines are imaginary curves that show the direction and strength of the magnetic field at different points.
Magnetic Field Around a Straight Conductor
- When an electric current flows through a straight conductor, it creates a magnetic field around it.
- The magnetic field lines form concentric circles around the conductor.
Direction of the Magnetic Field
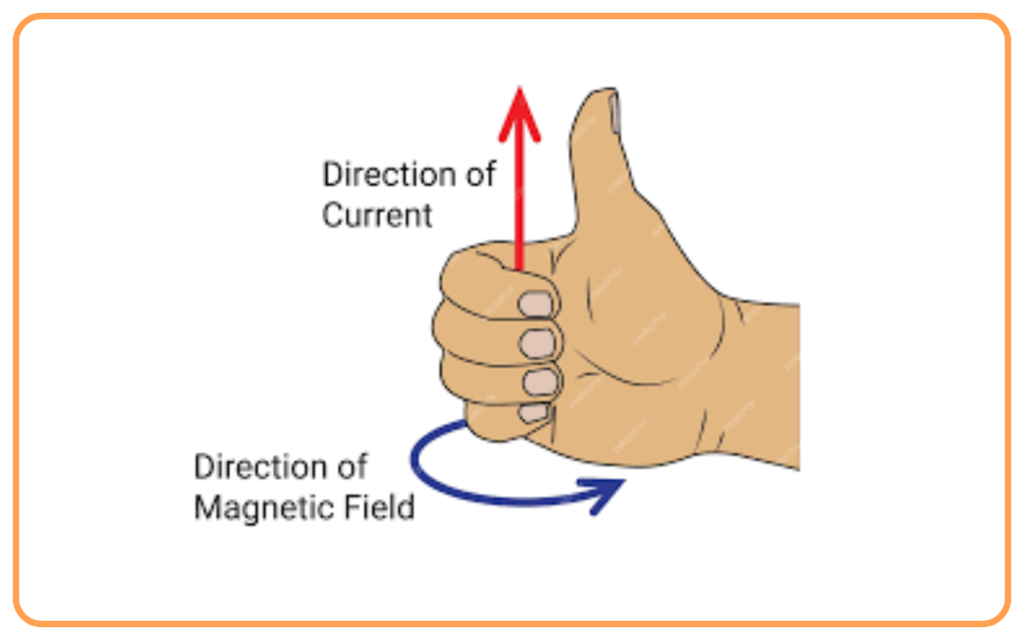
- Right-Hand Thumb Rule:
- Hold the current-carrying conductor with your right hand.
- Point your thumb in the direction of the current flow.
- Curl your fingers around the conductor.
- The direction of your curled fingers indicates the direction of the magnetic field.
Strength of the Magnetic Field
- The strength of the magnetic field at a point depends on:
- Magnitude of the current: A stronger current produces a stronger magnetic field.
- Distance from the conductor: The closer you are to the conductor, the stronger the magnetic field.
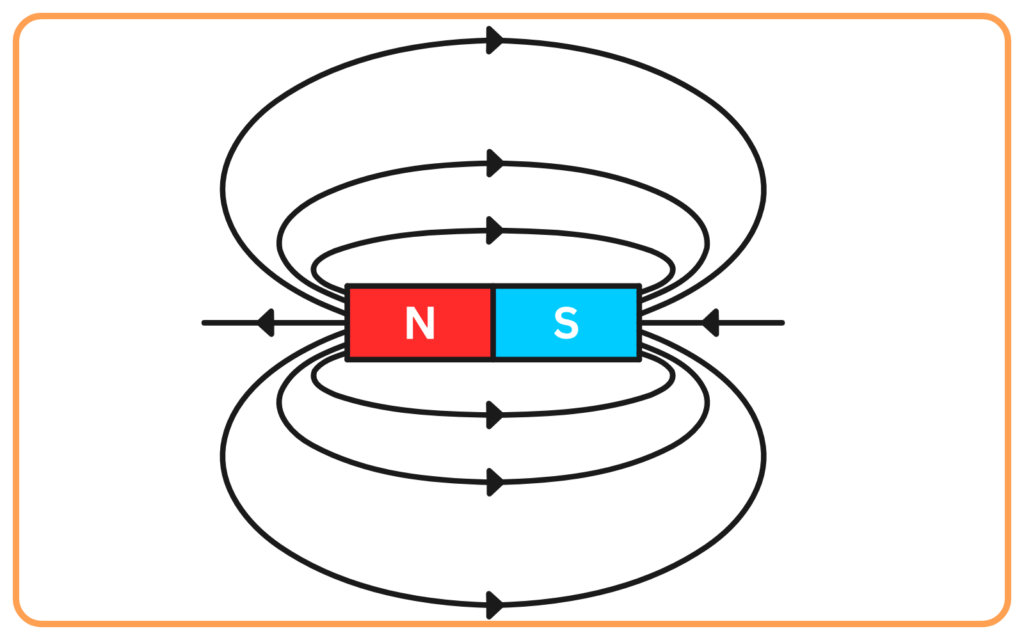
Magnetic Field Formula
- The magnetic field (B) at a distance (r) from a straight, infinitely long current-carrying conductor is given by:
B = (μ₀ * I) / (2πr)where:- B is the magnetic field strength in Tesla (T)
- μ₀ is the permeability of free space (4π × 10^-7 T m/A)7
- I is the current in Amperes (A)
- r is the distance from the conductor in meters (m)
Applications of Magnetic Fields
- Electromagnets: Used in various devices like motors, relays, and transformers.
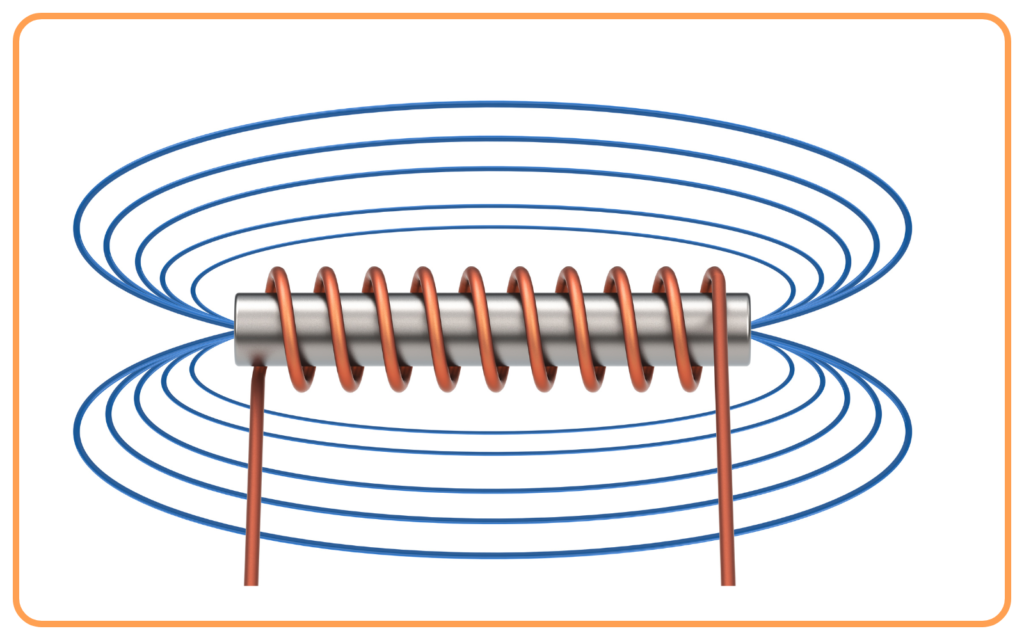
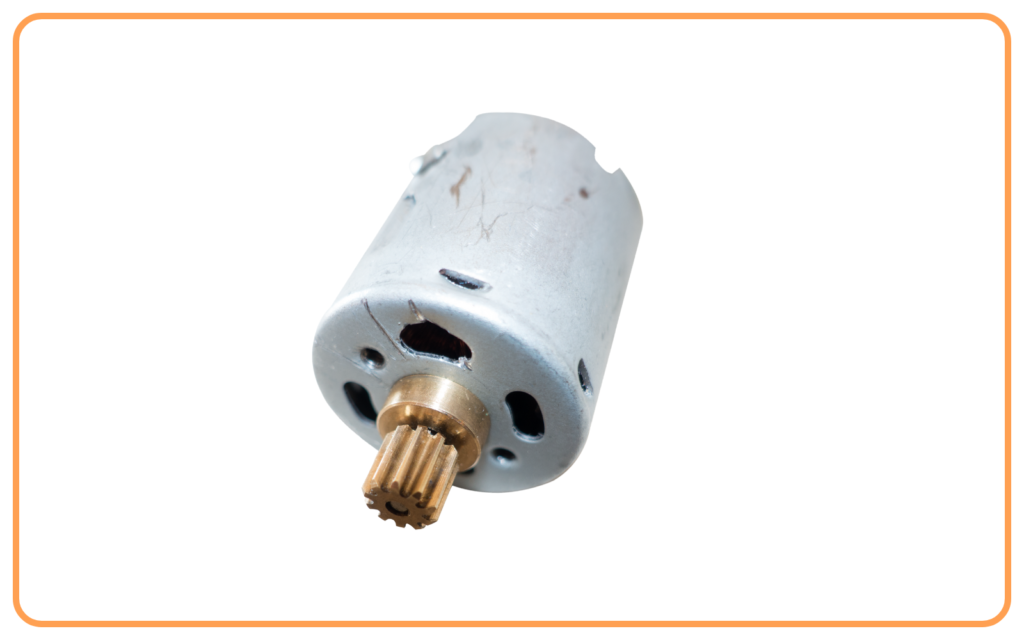
- Electric Motors: Convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.

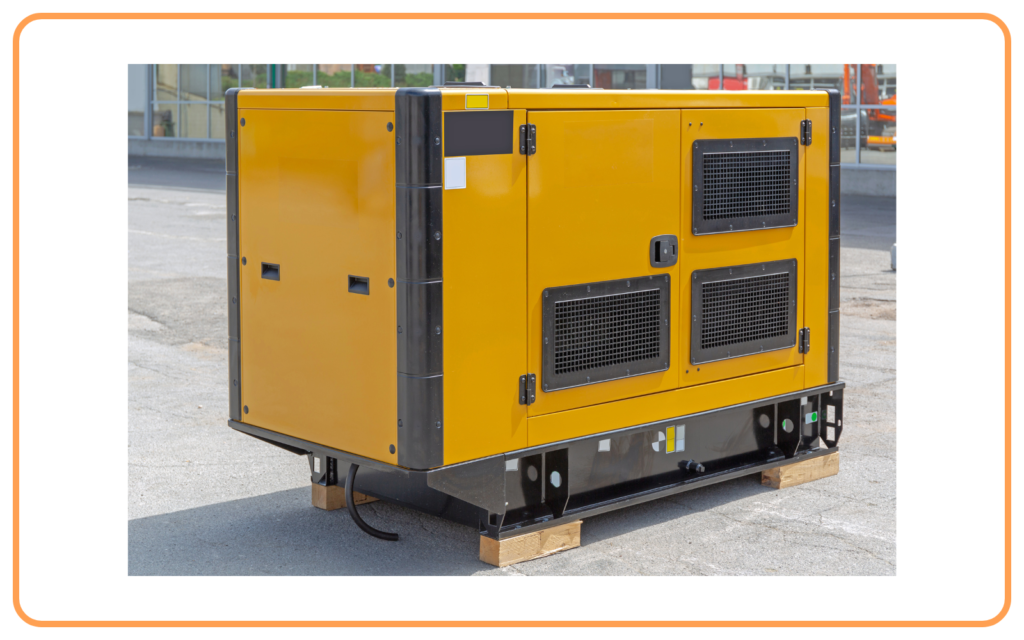
- Generators: Convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.

- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Used in medical diagnosis.
Let’s practice!

