Electric Potential And Potential Difference
Key Notes:
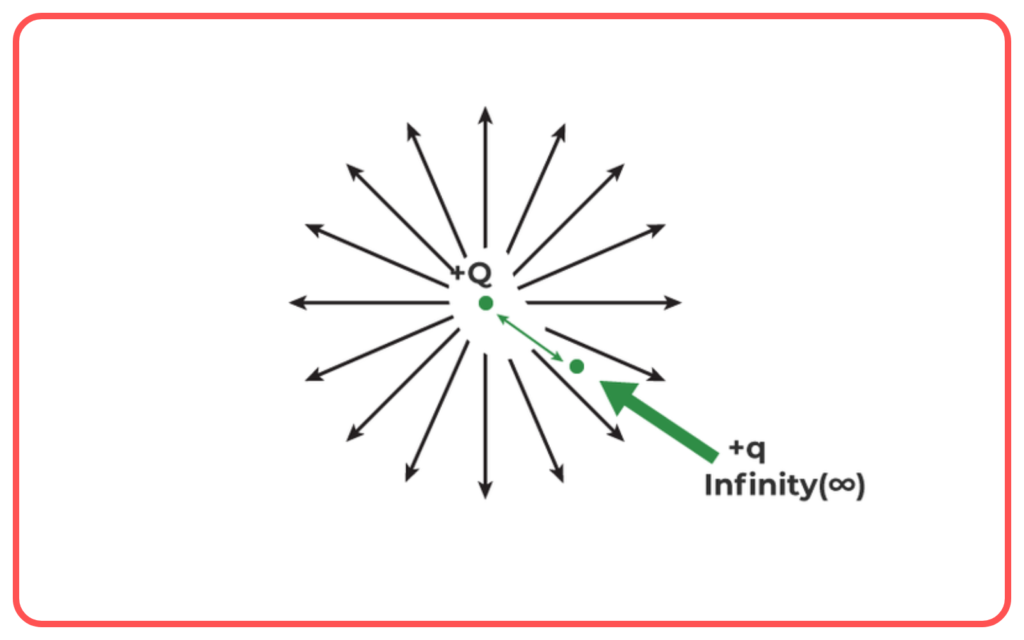
Electric Potential
- Definition: Electric potential at a point is the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge at that point.
- Formula: V = W/q, where:
- V is the electric potential (in volts),
- W is the work done (in joules) to move the charge,
- q is the charge (in coulombs).
- Unit: The unit of electric potential is volt (V), where 1 volt = 1 joule/coulomb.
- Concept: Electric potential tells us how much work would be needed to move a charge from infinity to a specific point in an electric field without changing its kinetic energy.
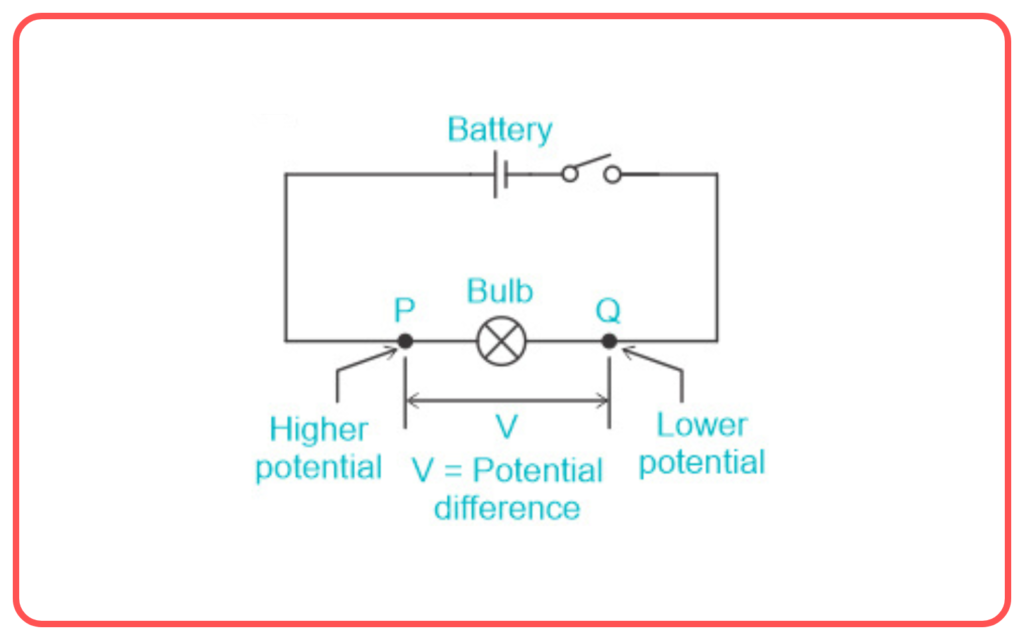
Potential Difference
- Definition: The potential difference between two points is the work done to move a unit charge from one point to another.
- Formula: V=W/q , where:
- V is the potential difference,
- W is the work done to move the charge,
- q is the charge.
- Unit: Measured in volts (V), similar to electric potential.
- Concept: The potential difference between two points drives the flow of electric charge (current) in a circuit.
Work Done in Moving a Charge
- To move a charge q across a potential difference V, the work done is given by W = qV.
- Work is measured in joules (J), where 1 J = 1 C × 1 V.
Electric Circuit and Potential Difference
- In an electric circuit, the battery or power source creates a potential difference, which causes the flow of current.
- The potential difference across components like resistors determines how much energy per charge is used in that part of the circuit.
Electrostatic Potential Energy
- The potential energy stored in an electric charge due to its position in an electric field.
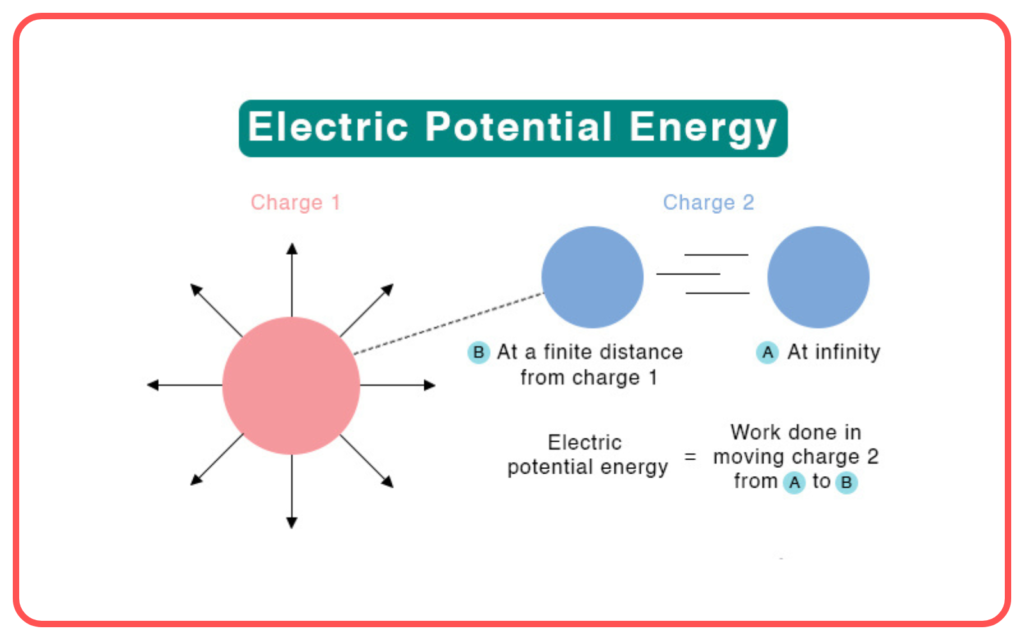
- Related to electric potential but dependent on the amount of charge and the position in the field.
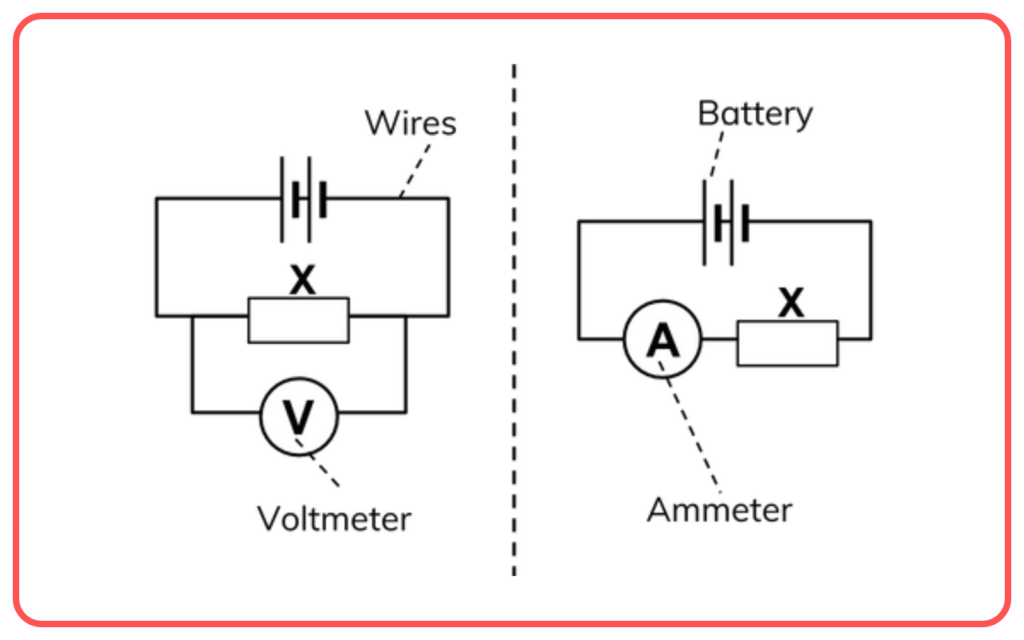
Measurement of Potential Difference
- A device called a voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference between two points in a circuit.
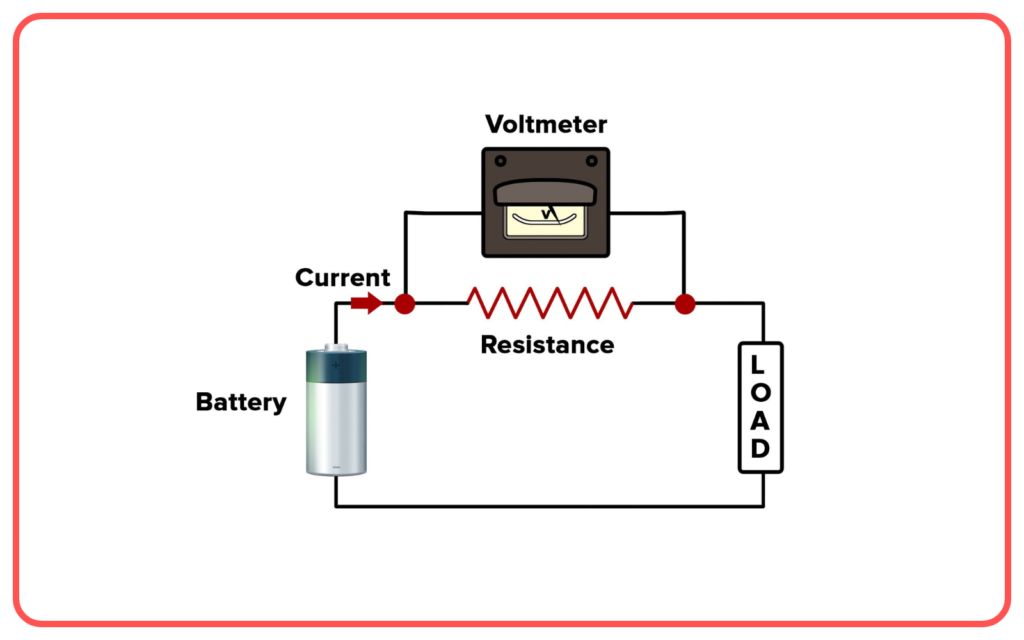
- It is always connected in parallel to the circuit elements.
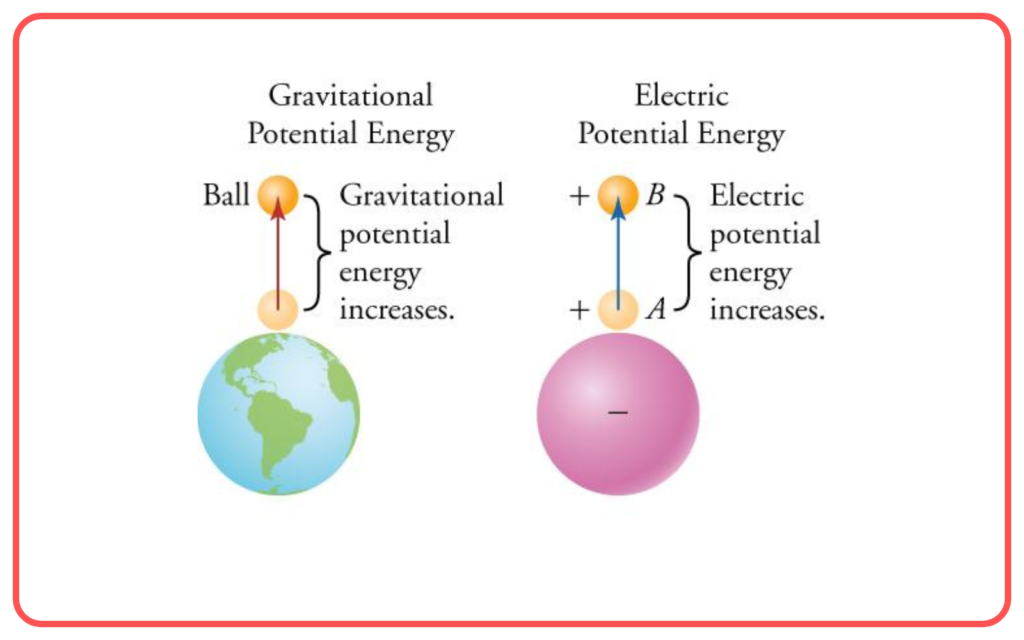
Analogy with Gravitational Potential
- Electric potential is similar to gravitational potential: just as work is done to lift an object against gravity, work is done to move a charge against the electric field.
Let’s practice!

