Scattering Of Light
Key Notes:
What is Scattering of Light?
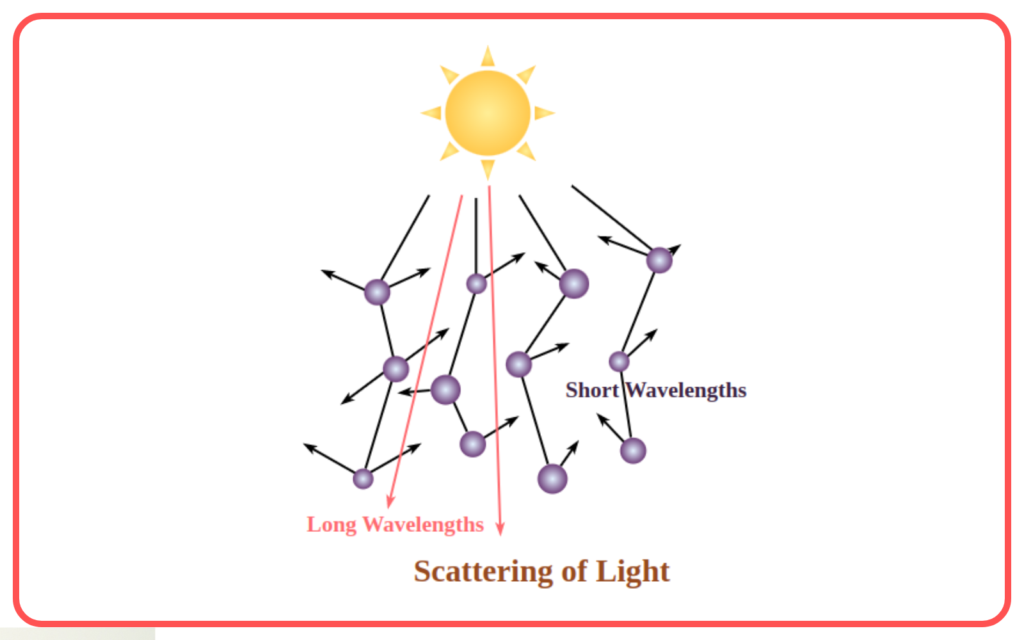
- Scattering of light refers to the phenomenon in which light rays change direction when they interact with particles or obstacles in its path.
Why Does Scattering Occur?
- Scattering occurs because light is made up of tiny particles called photons, which interact with other particles, causing them to change direction.
Types of Scattering:
- Rayleigh Scattering: This type of scattering occurs when light interacts with particles much smaller than the wavelength of light. It’s responsible for the blue color of the sky.
- Mie Scattering: This occurs when light interacts with particles similar in size to the wavelength of light. It’s responsible for the white appearance of clouds.
- Non-selective Scattering: This happens when light interacts with larger particles or irregular surfaces, causing light to scatter in all directions. It’s responsible for the diffuse reflection of light.
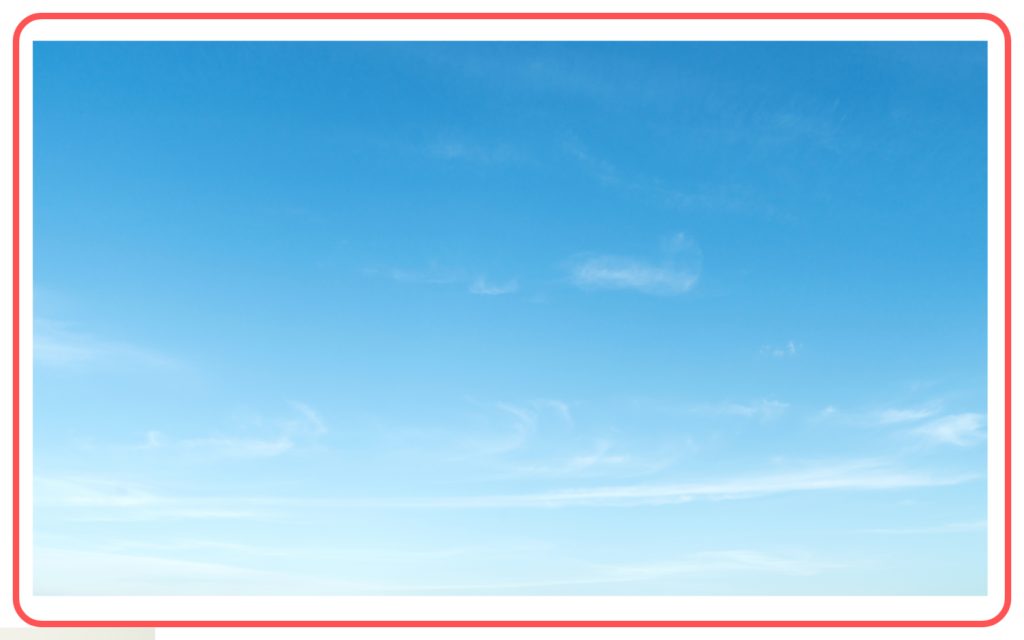
Blue Sky Phenomenon:
- The sky appears blue during the day due to Rayleigh scattering. Shorter wavelengths of light, like blue and violet, scatter more than longer wavelengths, making the sky appear predominantly blue.

Reddish Sunset and Sunrise:
- During sunrise and sunset, the sun appears reddish because the sunlight has to pass through more of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing shorter wavelengths (blue and green) to scatter and leaving the longer wavelengths (red and orange) to dominate.

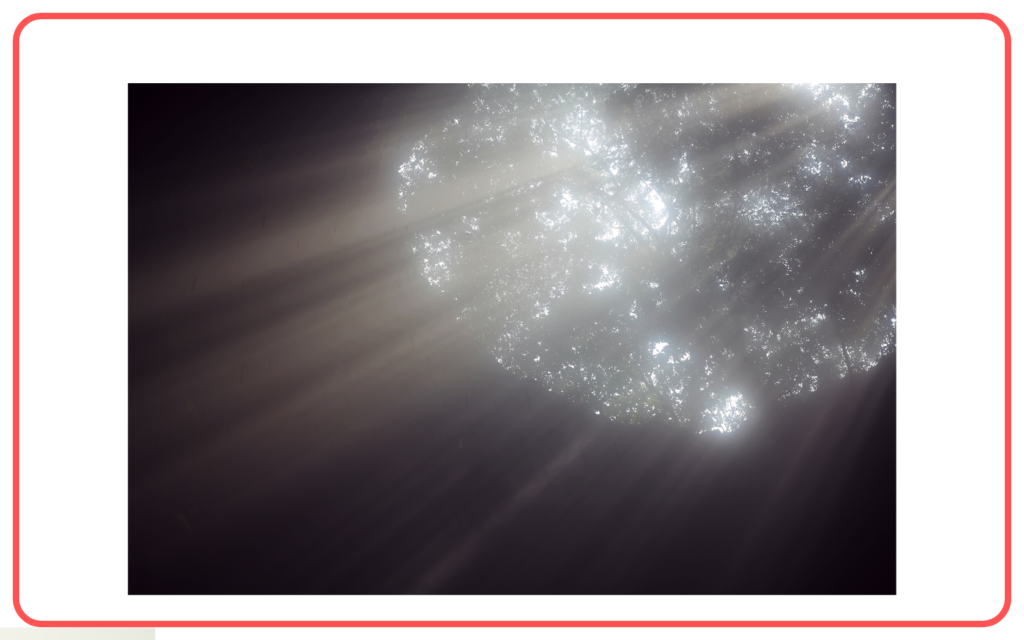
Tyndall Effect:
- The Tyndall effect is the scattering of light by colloidal particles or dust in a fluid. It’s responsible for the visibility of laser beams, dust particles in a beam of sunlight, and the blue color of some mountain lakes.

Applications of Scattering:
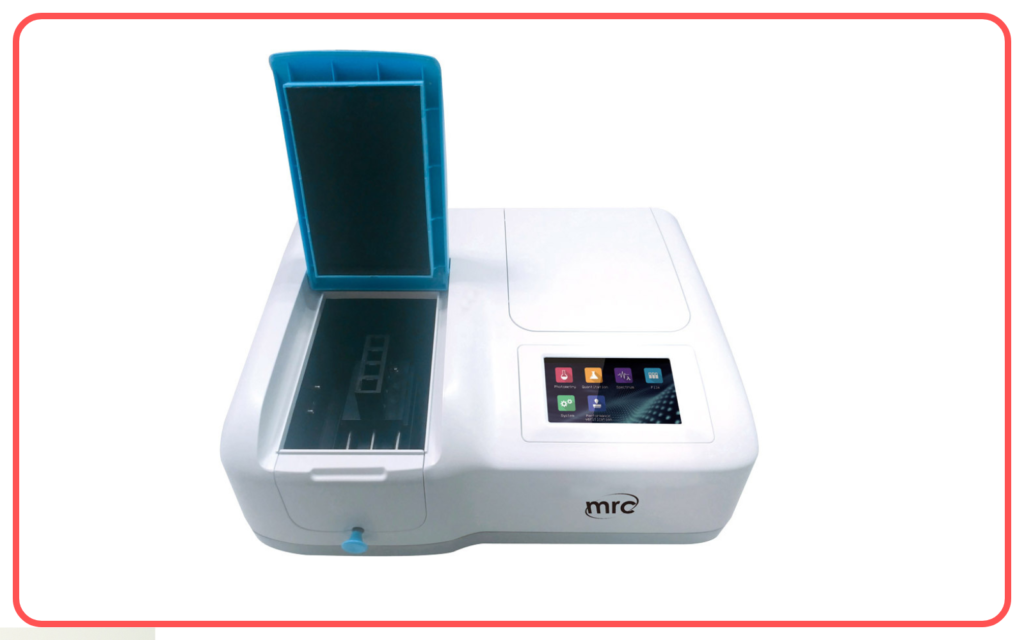
- Scattering is used in various scientific instruments, such as spectrophotometers and nephelometers, to study the properties of particles and molecules.
- It’s also important in the design of materials with specific optical properties, like anti-glare coatings on eyeglasses.
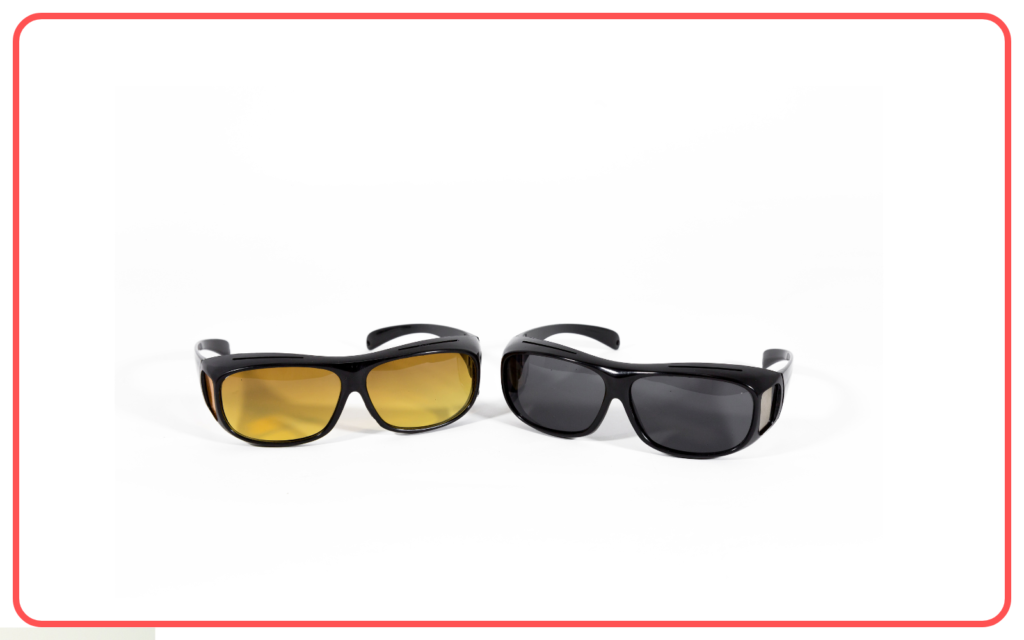

Safety Considerations:
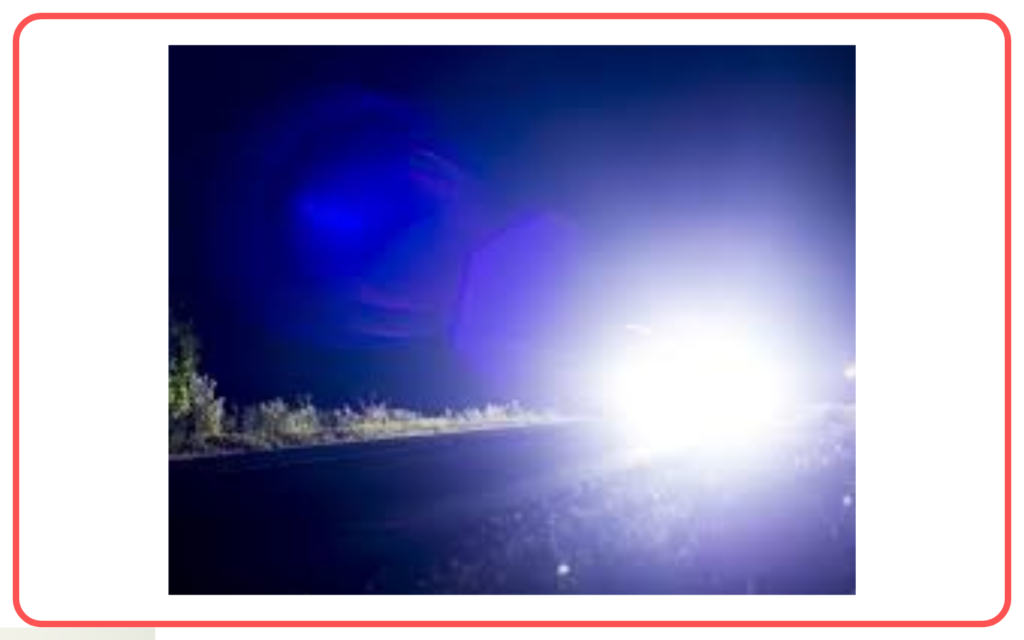
- Scattering of light can be a safety concern, such as the glare from headlights at night or the blinding effect of direct sunlight. Anti-glare measures are taken to reduce these effects.

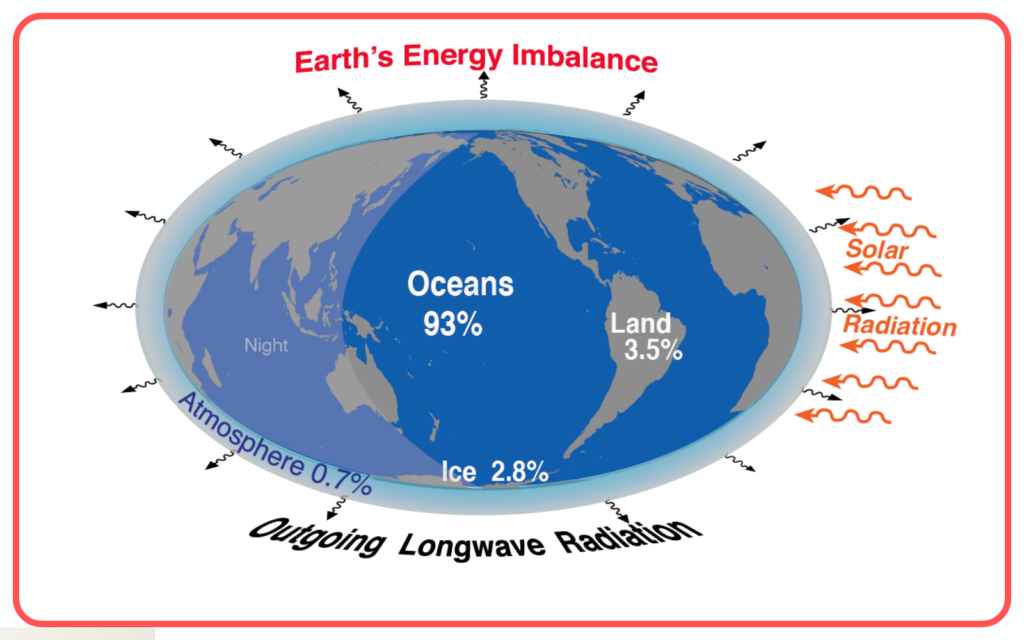
Environmental Impact:
- Scattering of sunlight in the Earth’s atmosphere affects the planet’s energy balance and plays a role in climate and weather patterns.
Conclusion:
- Understanding the scattering of light is essential in various fields, from physics and meteorology to optics and environmental science.
Let’s practice!

