Reflection Of Light
Key Notes:
Definition of Reflection
- Reflection of light occurs when light rays strike a surface and bounce back into the same medium.
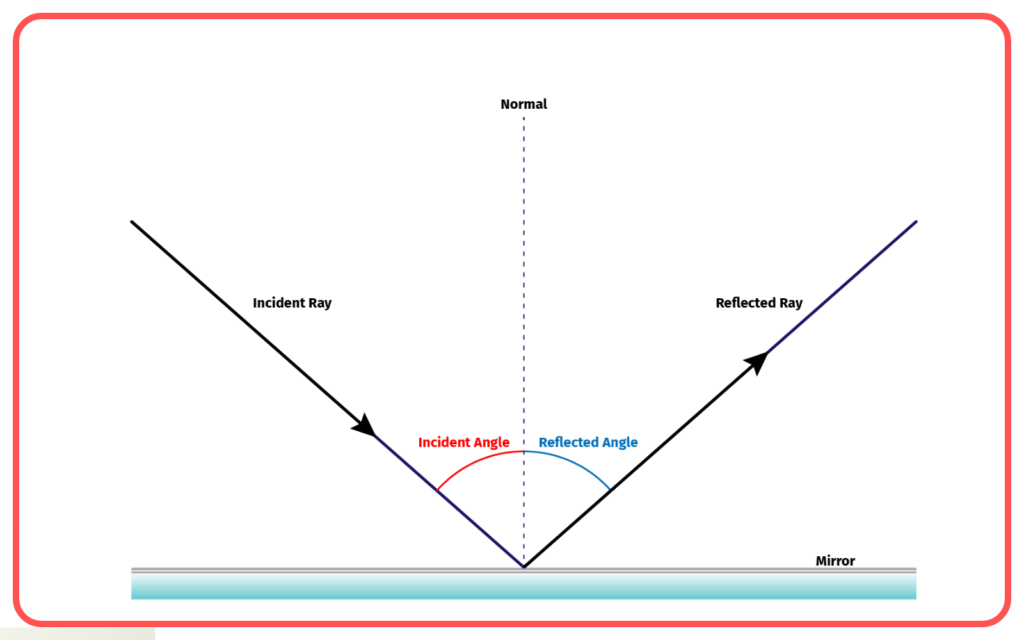
- The bouncing of light follows specific laws, known as the laws of reflection.
Laws of Reflection
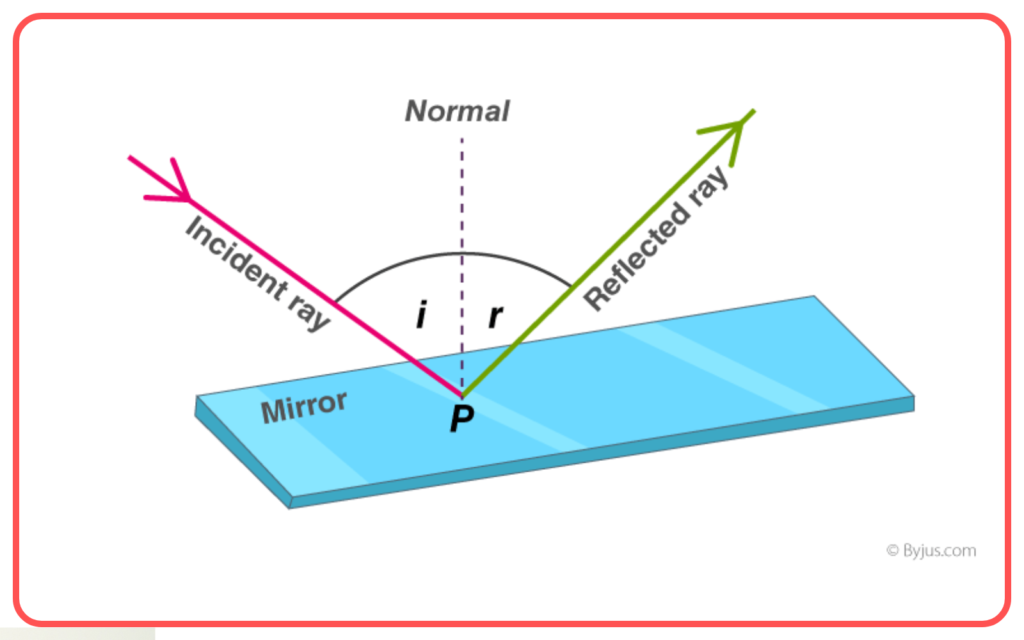
First Law: The angle of incidence (i) is equal to the angle of reflection (r).
- θi = θr
Second Law: The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Types of Reflection
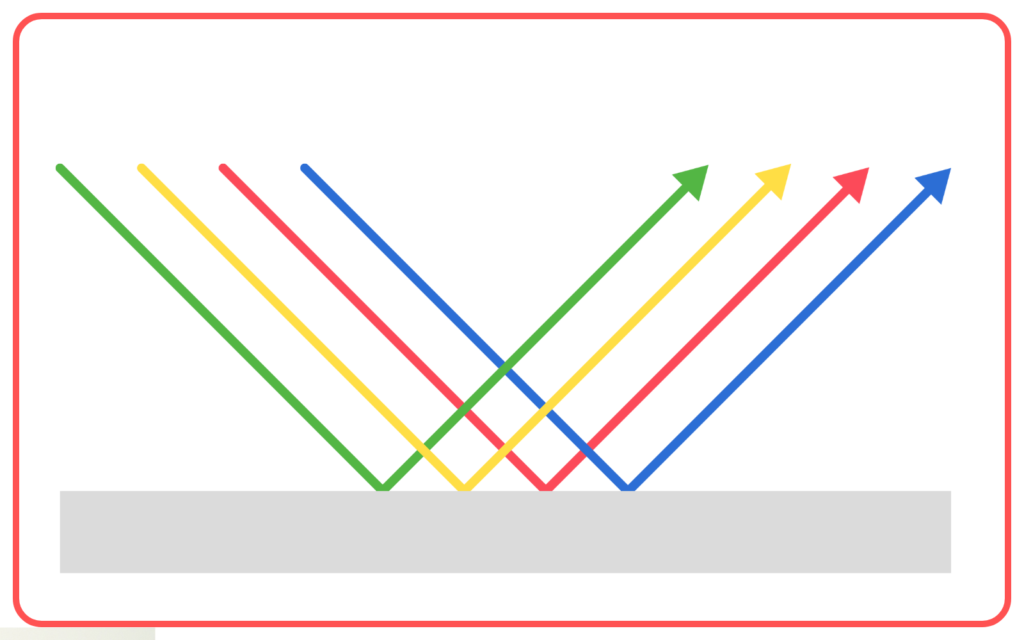
- Regular Reflection:
- Occurs on smooth surfaces like mirrors.
- Produces clear and sharp images.
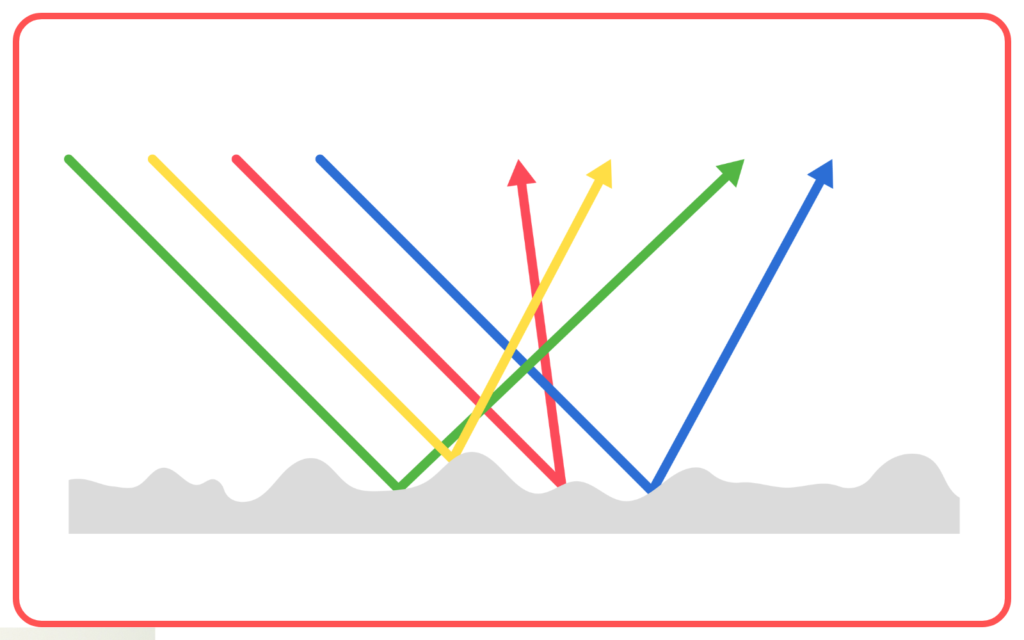
- Diffuse Reflection:
- Occurs on rough surfaces.
- Scattered light results in no clear image.
Terms Related to Reflection
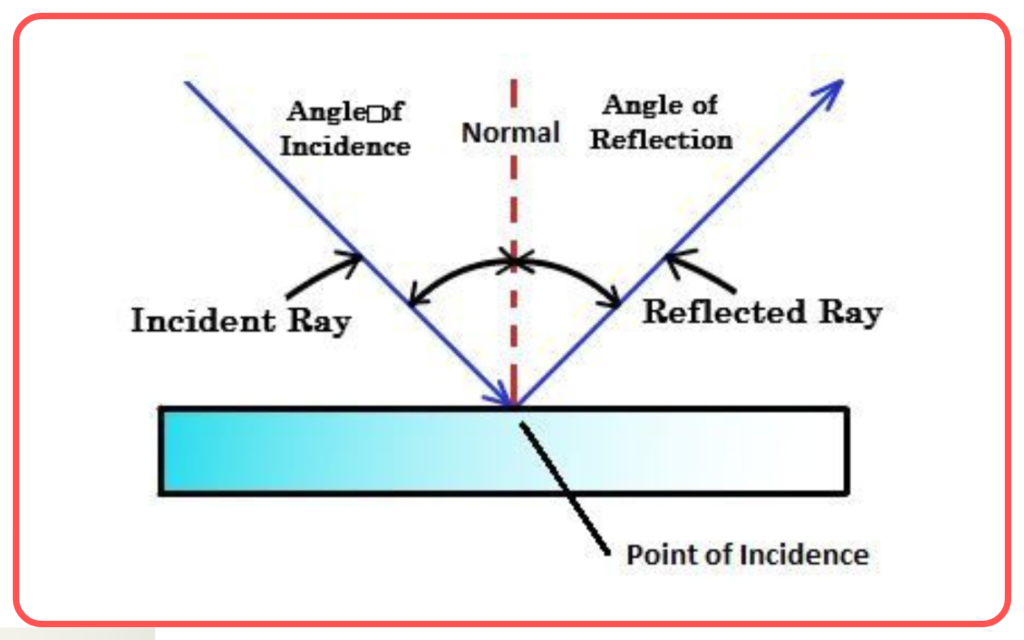
- Incident Ray: The light ray that strikes the surface.
- Reflected Ray: The light ray that bounces off the surface.
- Normal: A perpendicular line drawn to the surface at the point of incidence.
- Angle of Incidence: The angle between the incident ray and the normal.
- Angle of Reflection: The angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
Reflection in Plane Mirrors
- Image Characteristics:
- Virtual and upright.
- Same size as the object.
- Laterally inverted (left-right reversal).
- Appears to be at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front.
Applications of Reflection
- Used in periscopes, kaleidoscopes, and optical instruments.
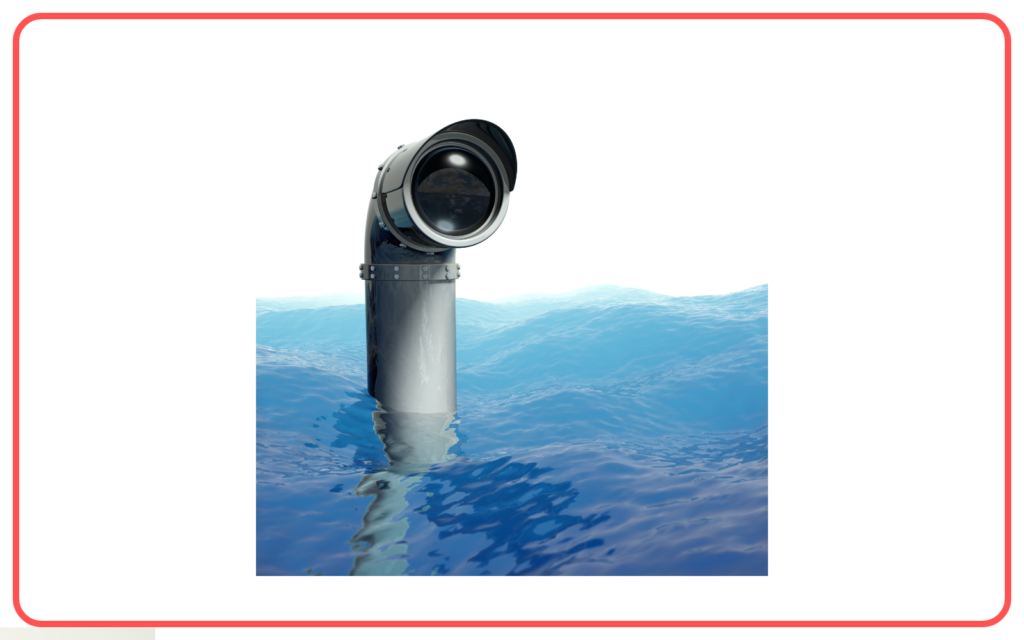

- Helps in the working of mirrors in vehicles and household applications.
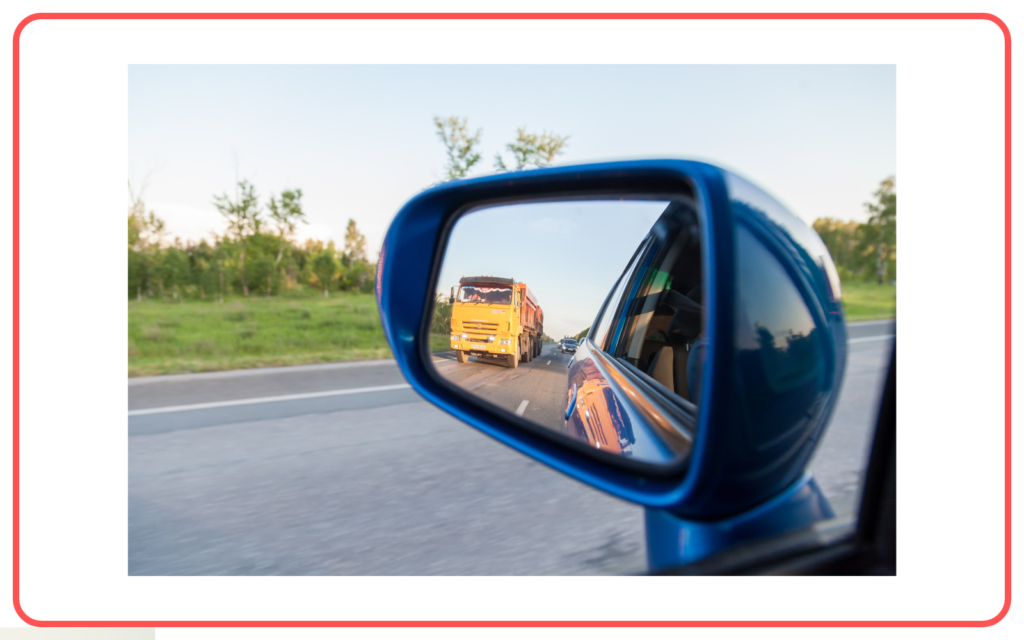

Multiple Reflections
- When light reflects multiple times between two mirrors, it forms multiple images.
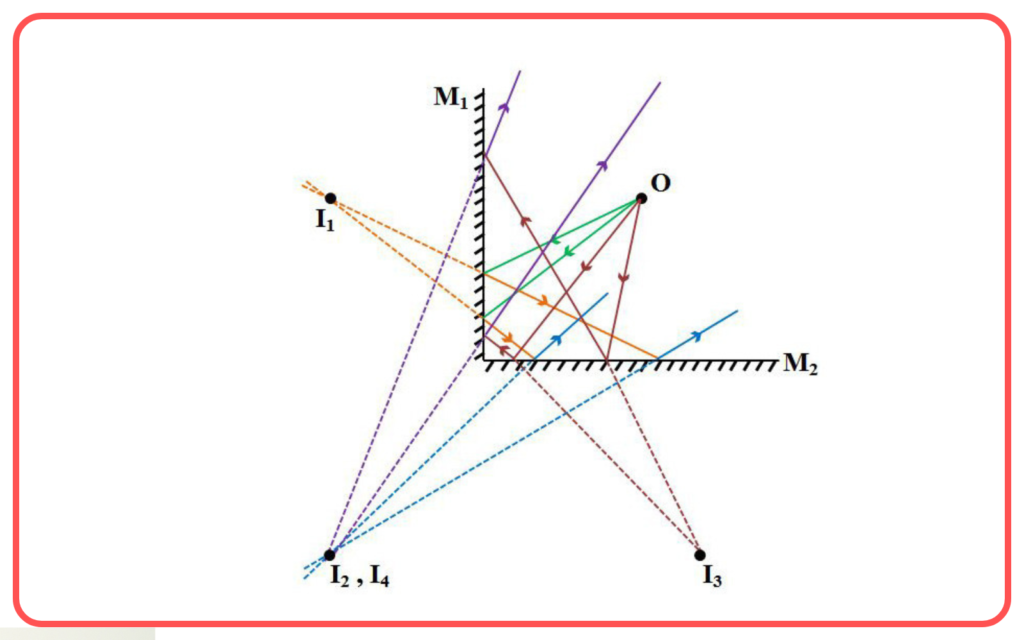
- The number of images formed depends on the angle between the mirrors.
Real-Life Examples
- Reflection on calm water surfaces.
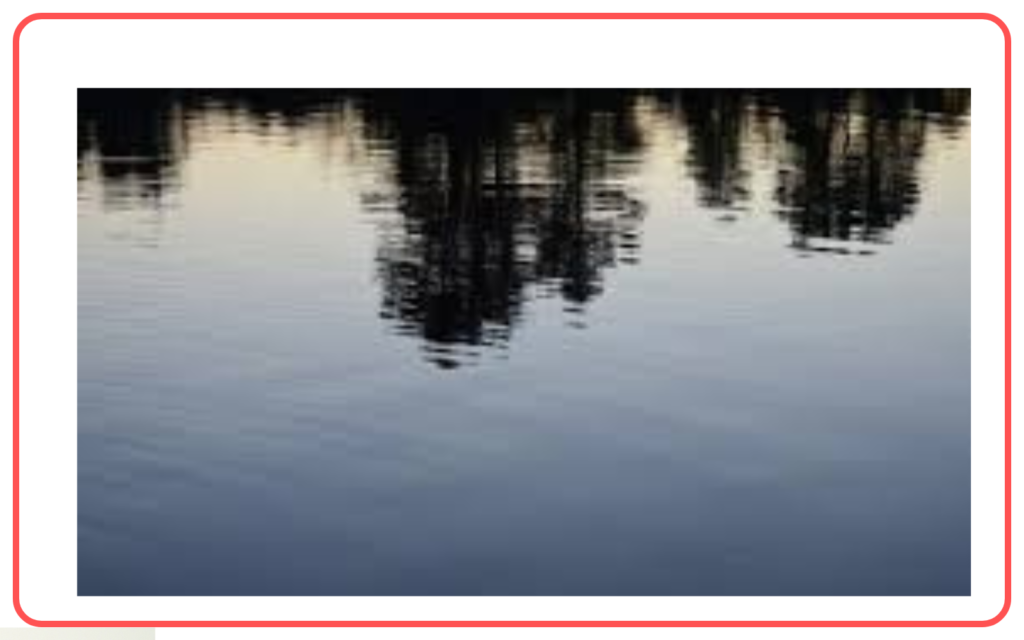

- Mirrors in dressing rooms and cars.

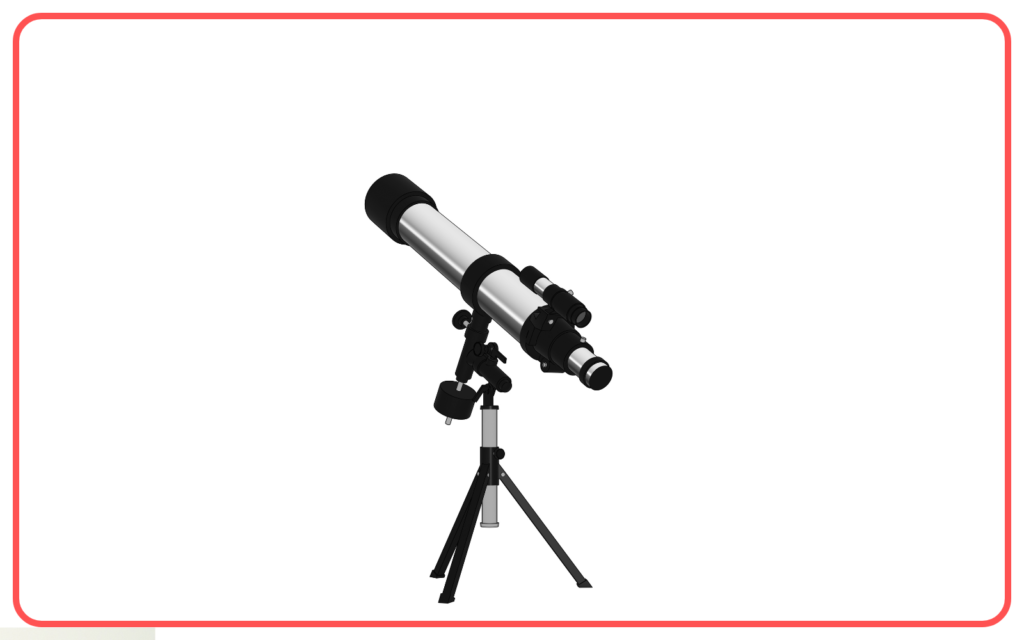
- Optical devices like telescopes and microscopes.

Let’s practice!

