Types of Chemical Reactions
Key Notes :
Combination (Synthesis) Reaction:
- Description: Two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
A + B → AB
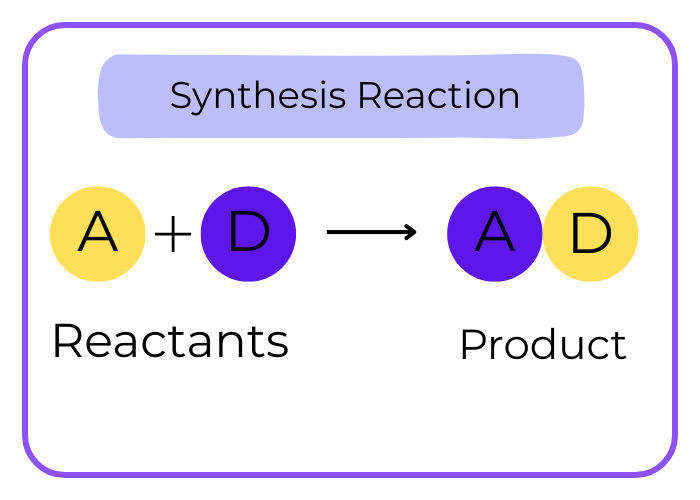
- Example:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O - Key Characteristics: Energy is often released as heat or light.
Decomposition Reaction:
- Description: A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
AB → A + B

- Example:
2HgO → 2Hg + O2 - Types:
- Thermal decomposition (heat-induced)
- Electrolytic decomposition (electricity-induced)
- Photochemical decomposition (light-induced)
Displacement Reaction:
- Description: One element displaces another in a compound.
A + BC → AC + B
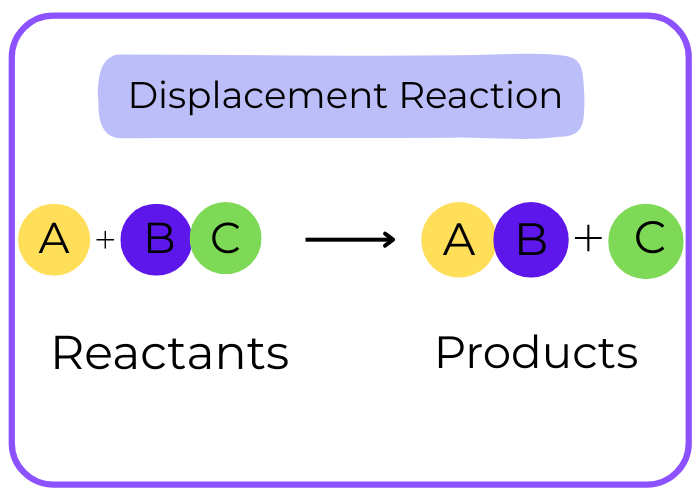
- Example:
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu - Key Characteristics: Often involves metals or halogens.
Double Displacement Reaction:
Description: Exchange of ions between two compounds.
AB + CD → AD + CB
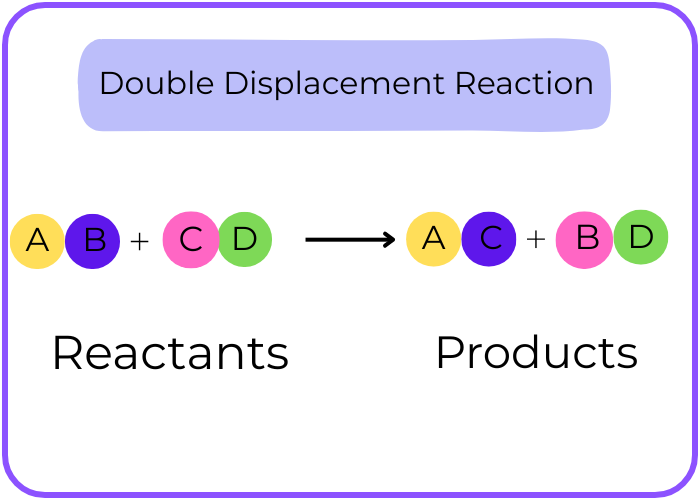
Example:
NaCl + AgNO3 → NaNO3 + AgCl
Types:
- Precipitation Reaction: Formation of an insoluble product (precipitate).
- Neutralization Reaction: Acid reacts with base to form salt and water.
Redox Reaction:
Description: Transfer of electrons where one substance is oxidized, and another is reduced.
- Oxidation: Loss of electrons.
- Reduction: Gain of electrons.
Example:
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Key Characteristic: Involves changes in oxidation states.
Combustion Reaction:
- Description: A substance reacts with oxygen, releasing heat and light.
Fuel + O2 → CO2 + H2O
- Example:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O - Key Characteristics: Exothermic process.
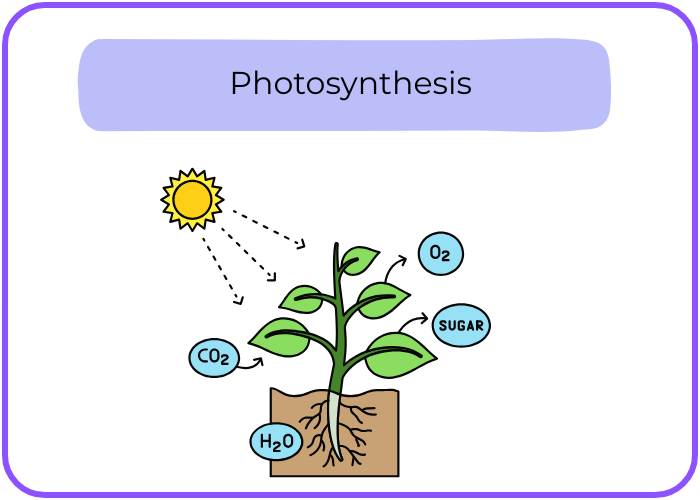
Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions:
- Endothermic Reaction: Absorbs energy from the surroundings.
Example: Photosynthesis.
- Exothermic Reaction: Releases energy to the surroundings.
Example: Combustion.
Let’s practice!

