Chemical Equation
Key Notes :
Definition:
- A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using chemical formulas and symbols
- It shows the reactants (substances that undergo change) and products (new substances formed) in a reaction.
Structure of a Chemical Equation:
- Reactants are written on the left-hand side (LHS).
- Products are written on the right-hand side (RHS).
- An arrow (→) separates the reactants and products, indicating the direction of the reaction.
Example:
H2 + O2 → H2O
Balancing a Chemical Equation:
- A chemical equation must obey the Law of Conservation of Mass (mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction).
- The number of atoms of each element on the LHS must equal the number of atoms on the RHS.
- Coefficients (numbers placed before formulas) are used to balance the equation.
Example:
Unbalanced:
H2 + O2 → H2O
Balanced:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Types of Chemical Equations:
- Skeletal Equation: Unbalanced equation showing only reactants and products.
H2+Cl2→HCl
- Balanced Equation: Follows the Law of Conservation of Mass.
H2 + O2 → 2H2O
- Ionic Equation: Represents only the ions involved in the reaction.
NaCl(aq) + AgNO₃(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO₃(aq)
Symbols and Notations in Chemical Equations:
- (s): Solid
- (l): Liquid
- (g): Gas
- (aq): Aqueous (dissolved in water)
- Heat/Δ: Heat is supplied
- ↑: Gas is evolved
- ↓: Precipitate is formed
Importance of a Chemical Equation:
- Provides a concise way to describe chemical reactions.
- Indicates the proportions of reactants and products.
- Helps in predicting the outcomes of reactions.
Steps to Balance a Chemical Equation:
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- List the number of atoms of each element on both sides.
- Add coefficients to balance the number of atoms for each element.
- Verify that all elements are balanced and the equation follows the Law of Conservation of Mass.
Limitations of a Chemical Equation:
- Does not indicate the reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, catalysts).
- Does not show the rate of the reaction.
- Does not provide information about the physical states of reactants and products unless mentioned.
Examples of Balanced Equations:
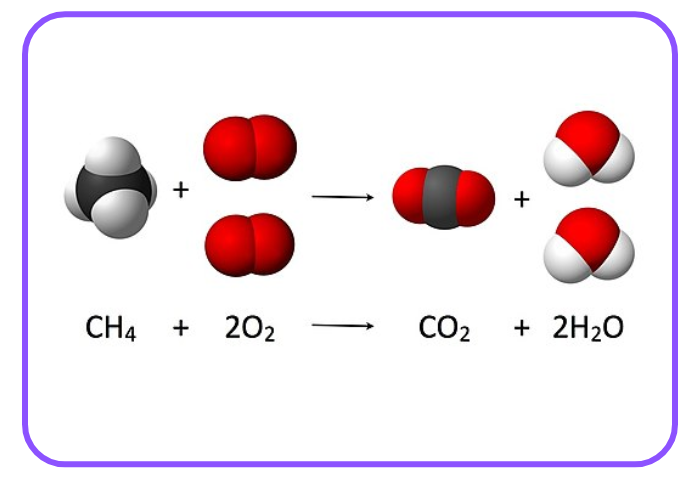
- Combustion of Methane:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
- Photosynthesis:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Applications:
- Used in laboratory experiments and industrial processes.

- Helps in stoichiometric calculations to determine the quantities of reactants and products.
Let’s Practice!

