Polygon vocabulary
Key Notes :
A polygon is a closed figure with straight sides. A closed figure starts and ends at the same point.
Title: Exploring Polygon Vocabulary
Introduction:
- Definition: A polygon is a two-dimensional geometric shape with straight sides.
- Polynomials come from Greek words “poly” (many) and “gonia” (angle).
- Examples: triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, etc.
Polygon Characteristics:
- Vertices: Points where the sides of the polygon meet.
- Sides/Edges: Line segments connecting consecutive vertices.
- Interior Angles: Angles formed inside the polygon at each vertex.
- Exterior Angles: Angles formed outside the polygon at each vertex.
Common Types of Polygons:
- Triangle:
- Three sides and three vertices.
- Types: Equilateral, Isosceles, Scalene.
- Quadrilateral:
- Four sides and four vertices.
- Types: Square, Rectangle, Rhombus, Parallelogram.
- Pentagon:
- Five sides and five vertices.
- Hexagon:
- Six sides and six vertices.
- Heptagon:
- Seven sides and seven vertices.
Polygon Properties:
- Sum of Interior Angles: The sum of interior angles in any polygon with n sides is given by the formula: (n-2) * 180 degrees.
- Exterior Angle Sum: The sum of exterior angles in any polygon is always 360 degrees.
- Regular vs. Irregular Polygons:
- Regular polygons have all sides and angles equal.
- Irregular polygons have sides and/or angles of different lengths and measures.
Real-world Applications:
- Architecture: Many buildings have polygonal shapes in their design.
- Computer Graphics: Polygons are used to create 2D and 3D shapes in digital environments.
- Urban Planning: City layouts often involve the use of polygons in zoning and land division.
Conclusion:
- Understanding polygon vocabulary is fundamental in geometry.
- The knowledge of polygons extends beyond mathematics to various fields.
- Exploring and recognizing polygons enriches our understanding of the world around us.
Note: The complexity of the content can be adjusted based on the specific curriculum and the familiarity of students with geometric concepts.
Learn with an example
1) Is this a polygon?
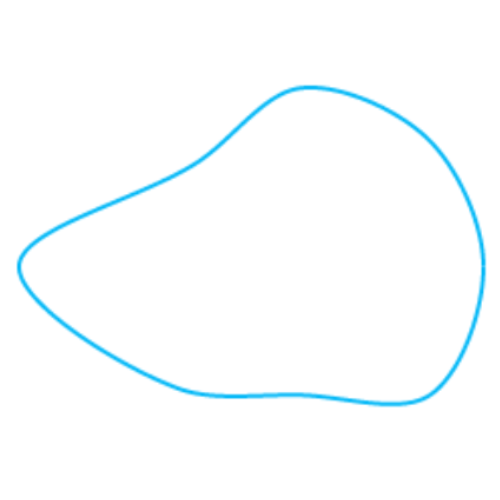
- yes
- no
This figure is not a polygon. Although it is closed, it does not have straight sides.
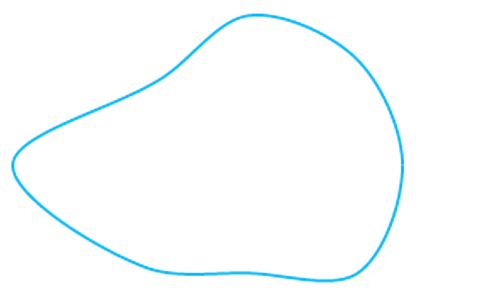
2) Is this a polygon?
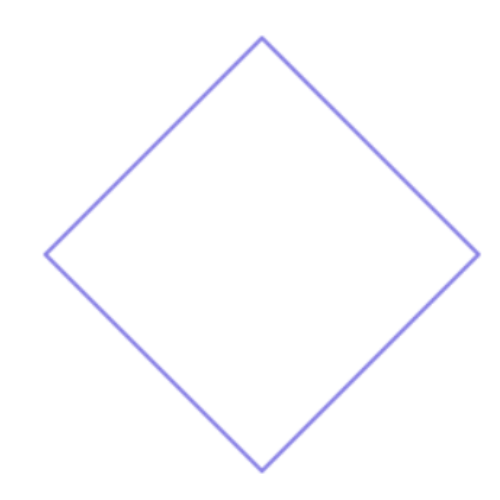
- yes
- no
This figure is a polygon.
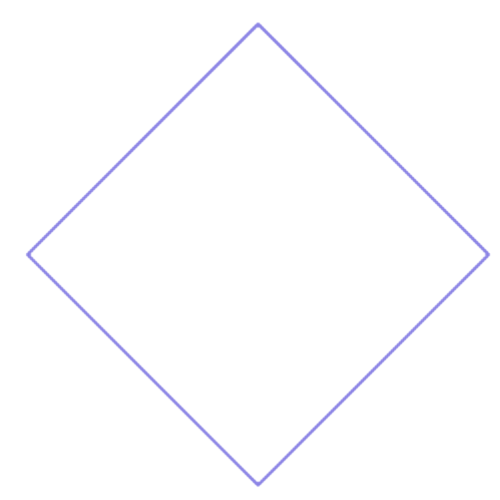
3) Is this a polygon?
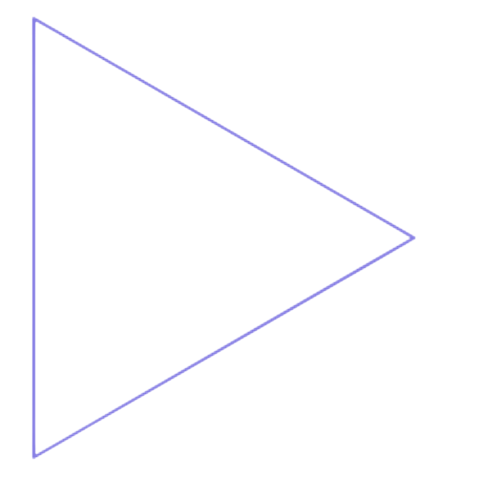
- yes
- no
This figure is a polygon.
let’s practice!

