Add and subtract polynomials using algebra tiles
key notes:
- Introduction to Polynomials:
- A polynomial is an algebraic expression consisting of variables and coefficients, combined through addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
- Examples of polynomials include 3�2+2�−53x2+2x−5 and 2�3−�+72y3−y+7.
- Algebra Tiles:
- Algebra tiles are physical or visual representations used to model algebraic expressions and equations.
- They are often square tiles, with different colors representing different variables or constants.
- Representation of Monomials with Tiles:
- A monomial is a single term in a polynomial.
- Use tiles to represent monomials by matching the number of tiles with the coefficient and using variables to represent the power.
- Addition of Polynomials with Tiles:
- To add polynomials, arrange the tiles for each polynomial separately and then combine like terms.
- Like terms are terms with the same variable and exponent.
- Subtraction of Polynomials with Tiles:
- To subtract polynomials, arrange the tiles for the minuend and the tiles for the subtrahend, then combine like terms.
- Zero Pairs:
- In the process of combining tiles, be aware of zero pairs, where positive and negative tiles cancel each other out.
- Degree of Polynomials:
- The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in any term.
- When adding or subtracting, make sure to arrange the terms in descending order of degree.
- Practice Examples:
- Work through practice problems to reinforce the concept of adding and subtracting polynomials using algebra tiles.
- Algebraic Notation:
- Translate the visual representation back into algebraic notation.
- Understand how tiles correspond to coefficients and variables in the expression.
- Check Solutions:
- After performing addition or subtraction using tiles, check the algebraic solution to ensure accuracy.
- Real-life Applications:
- Discuss real-life situations where polynomials are used, emphasizing the relevance of these algebraic skills.
- Problem-solving Strategies:
- Develop problem-solving strategies, such as breaking down complex expressions into simpler parts and tackling them step by step.
Learn with an example
➡️ Use algebra tiles to
find (x2+8x)+(5x2+9x+10).
Combine like terms. For example, write 3 instead of 1 + 1 + 1.
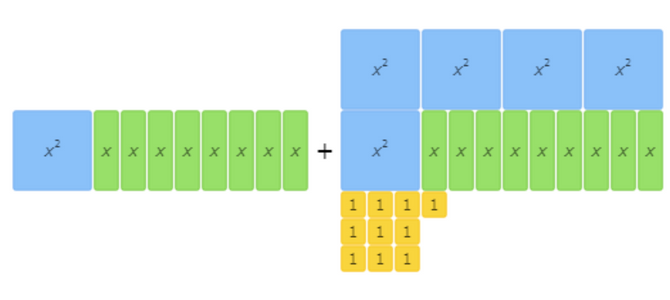
These algebra tiles represent the addition problem: (x2+8x)+(5x2+9x+10).
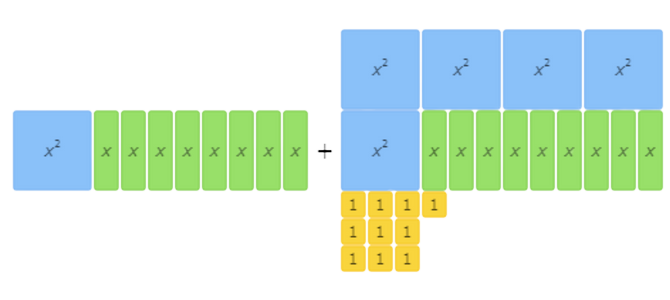
Use the algebra tiles to solve the addition problem.
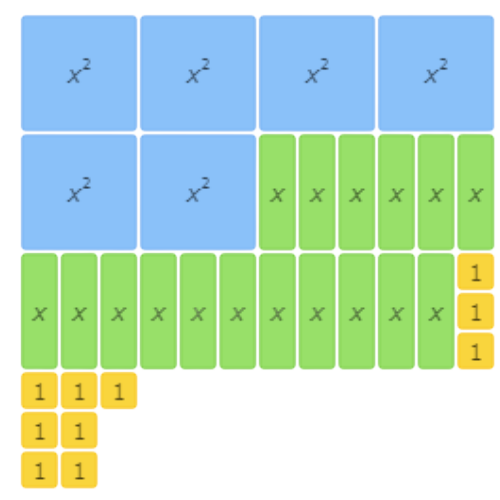
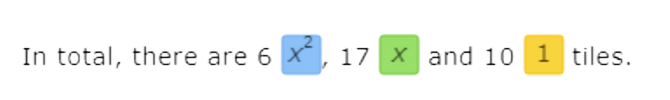
The result is 6x2 + 17x + 10.
➡️ Use algebra tiles to
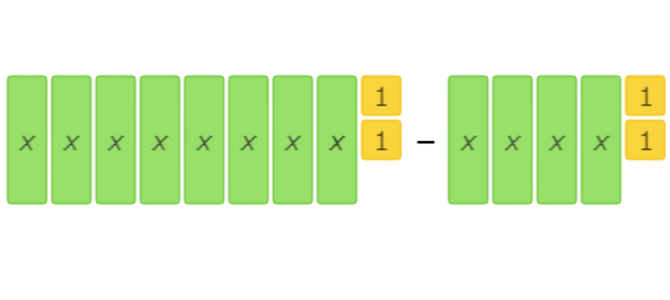
find (8x+2) – (4x+2).
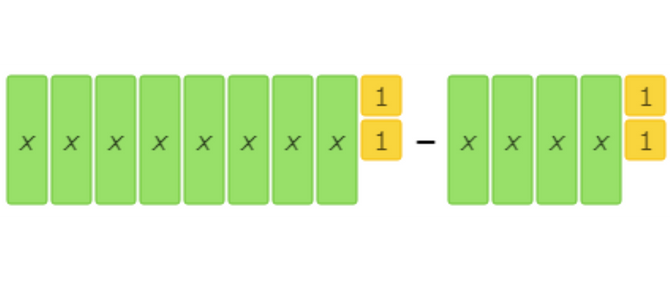
Combine like terms. For example, write 3 instead of 1 + 1 + 1.
These algebra tiles represent the subtraction problem: (8x+2) – (4x+2).
Use the algebra tiles to solve the subtraction problem. The tiles that are in the second set are the tiles that you should remove from each set.

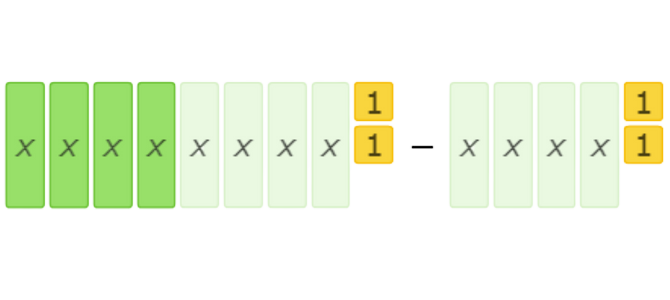

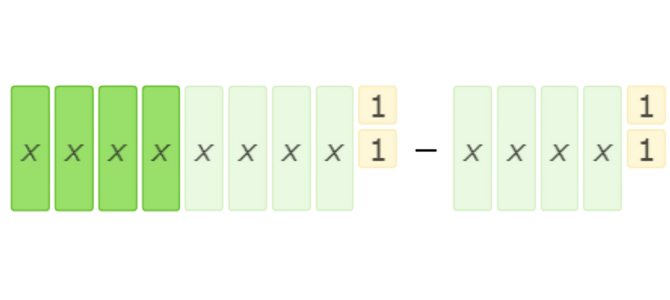
You are done subtracting because the second set is gone.
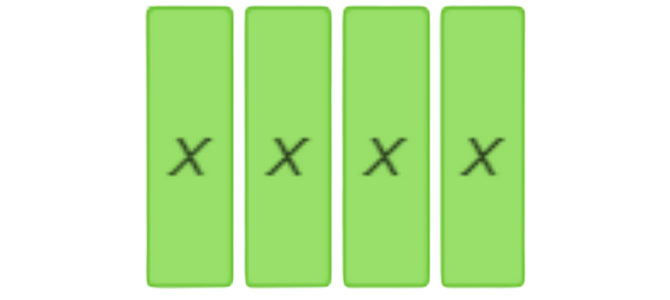

The result is 4x.
➡️ Use algebra tiles to
find (x2+1)+(7x2+5x+9).
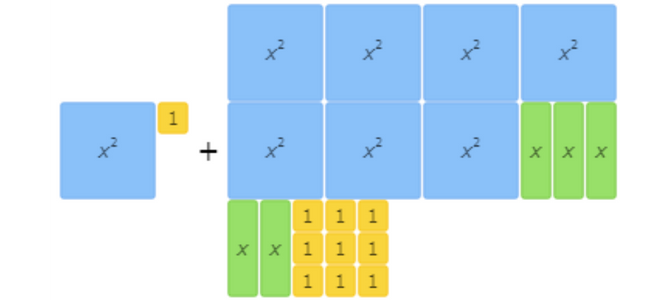
Combine like terms. For example, write 3 instead of 1 + 1 + 1.
These algebra tiles represent the addition problem: (x2+1)+(7x2+5x+9).
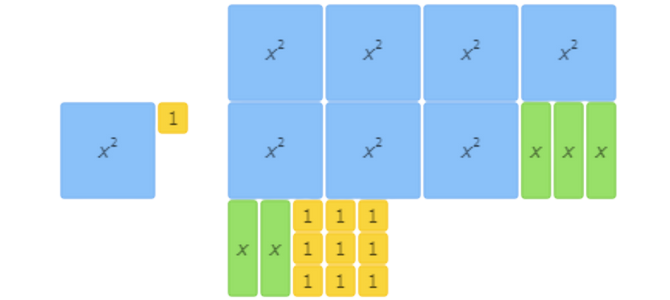
Use the algebra tiles to solve the addition problem.
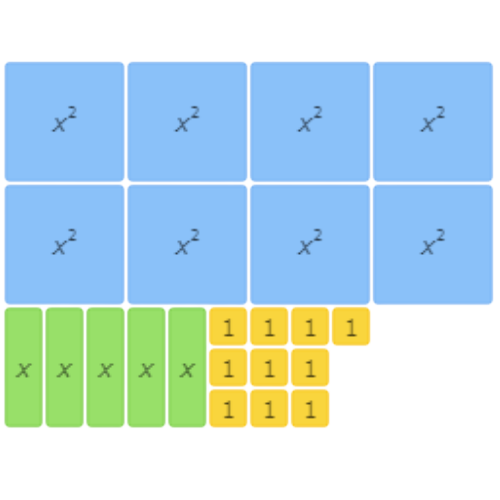
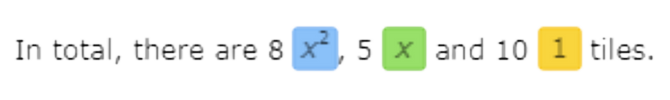
The result is 8x2+5x+10.
let’s practice!🖊️

