Number lines
key notes :
| Introduction to Number Lines: |
- Definition: A number line is a visual representation of numbers on a straight line, where each point on the line corresponds to a number.
- Purpose: Helps visualize the relationships between numbers, perform arithmetic operations, and understand concepts of magnitude and direction.

| Basic Structure of a Number Line: |
- Zero Point: The center of the number line is typically zero.
- Positive and Negative Numbers: Numbers increase to the right of zero and decrease to the left.
- Equal Intervals: The distance between consecutive points (numbers) is equal.

| Types of Numbers on the Number Line |
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Integers | Whole numbers and their negatives | -3, 0, 4 |
| Fractions | Numbers between integers | ½, -¾ |
| Decimals | Fractions in decimal form | 0.2, -1.5 |
| Rational | Numbers that can be expressed as a fraction | ⅔, -0.75, 5 |
| Irrational | Non-repeating, non-terminating decimals | √2, π |
🧮 Note: Even irrational numbers can be approximately located on a number line.
Inequalities on a Number Line
| Symbol | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| > | Greater than | x > 2 |
| < | Less than | x < -1 |
| ≥ | Greater or equal | x ≥ 0 |
| ≤ | Less or equal | x ≤ 5 |
| Plotting Inequalities: |
- Use a filled circle for ≤ or ≥.
- Use an open circle for < or >.
- Shade the side that shows the possible values.
| Distance on a Number Line |
- Distance between two numbers is the absolute value of their difference.
Formula: Distance=∣a−b∣\text{Distance} = |a – b|Distance=∣a−b∣
Example:
Distance between -3 and 4: ∣−3−4∣=∣−7∣=7| -3 – 4 | = |-7| = 7∣−3−4∣=∣−7∣=7
Plotting Points:
| Distance on a Number Line |
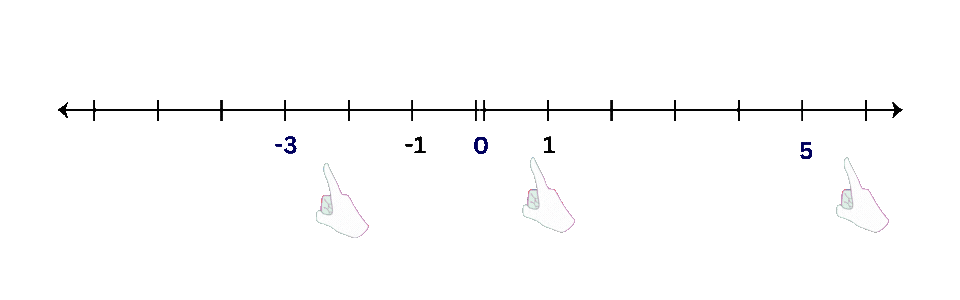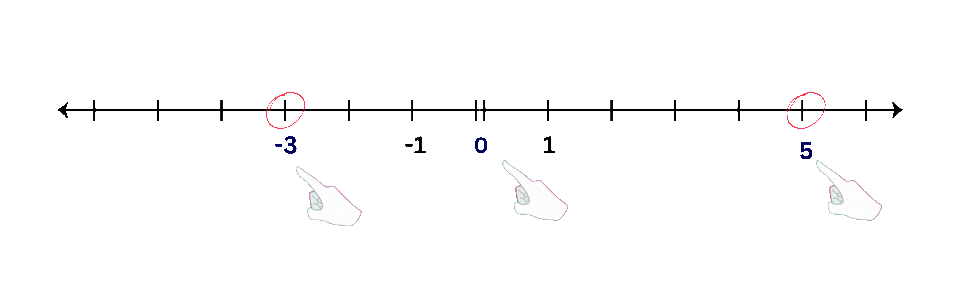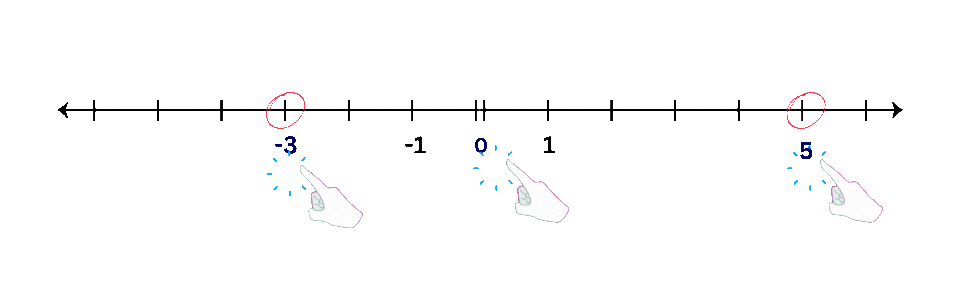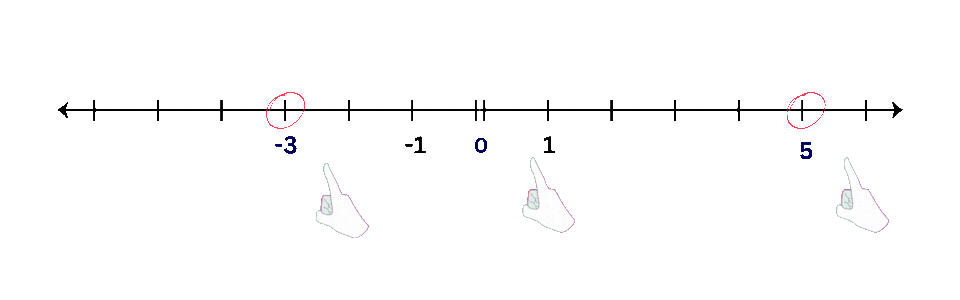
- Positive Numbers: Plot points to the right of zero.
- Negative Numbers: Plot points to the left of zero.
- Examples: Plot points like -3, 0, and 5 on a number line.
| Operations with Number Lines: |
- Addition: Move to the right to add. For example, to add 3 + 2, start at 3 and move 2 units to the right to reach 5.
- Subtraction: Move to the left to subtract. For example, to subtract 4 – 2, start at 4 and move 2 units to the left to reach 2.
- Adding and Subtracting Negative Numbers: Moving left or right depending on the operation’s sign.
| Understanding Fractions and Decimals: |
- Fractions: Plot fractions between whole numbers. For example, 1/2 is halfway between 0 and 1.

- Decimals: Plot decimals in the same manner. For example, 0.75 is between 0.7 and 0.8.

| Comparing and Ordering Numbers: |
- Comparison: Determine which numbers are greater or smaller by their position on the number line.
- Ordering: Arrange numbers from smallest to largest by their relative positions.
| Absolute Value: |
- Definition: The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line, regardless of direction.
- Notation: Denoted as ∣x∣.
- Example: ∣−7∣=7 because -7 is 7 units away from zero.
| Learn with an example |
🎯 Type the missing number.
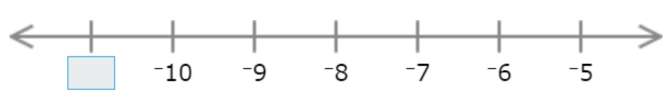
Each interval represents 1, so find the missing number by adding or subtracting 1.
The missing number is smaller than –10, so subtract 1. Since –10 − 1 = –11, the missing number is –11.

🎯 Type the missing number.
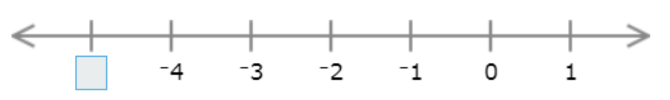
Each interval represents 1, so find the missing number by adding or subtracting 1.
The missing number is smaller than –4, so subtract 1. Since –4 − 1 = –5, the missing number is –5.
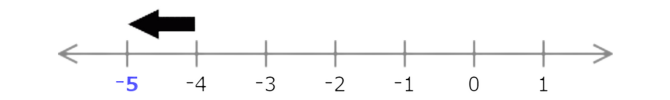
🎯 Type the missing number.

Each interval represents 1, so find the missing number by adding or subtracting 1.
The missing number is larger than –58, so add 1. Since –58 + 1 = –57, the missing number is –57.

Let’s Practice!

